Image


Danville City Manager Joe King received the Chairman's Award for his leadership in advancing the development of a modern telecommunications infrastructure in the region, a key factor in Danville's economic development renaissance.King had been the director of the city-owned utility when it drew up plans for a fiber-optic network to be built incrementally until it could connect every home, business, and community anchor institution in Danville Utility's territory. At the time, Danville was suffering tremendously from the loss of tobacco and textile industries.
Today, the nDanville net-work connects hundreds of businesses, has sharply re-duced costs for local gov-ernment, health care provid-ers, and local schools, and has introduced more competition into the telecommunications marketplace.Danville Utilities has 44,000 electric meters, half of which are located in Danville (44 sq miles). The others are scattered across over 450 sq miles surrounding the city. The Southern Piedmont Technology Council serves the technology industry in Danville as well as nearby counties and another city. Even in 2004, many in Danville did not have broadband access to the Internet, as outlined in an early document explaining the network. Verizon barely offered DSL and Adelphia offered limited cable modem service. Andrew Cohill, a consultant assisting the project, has offered more background in a recent article of Broadband Communities.
Once upon a time, the old, old AT&T was the sole supplier of telephones and other equipment to consumers and businesses. The FCC, in a series of market-opening orders, culminating in the 1968 Carterfone ruling, finally freed the non-AT&T world to provide telephone equipment. Through the years, consumers and businesses had many more choices as new companies sprang up to provide home phones, business phones, and business switching equipment for voice and data. Anyone could buy a phone and plug it in. At one telephone equipment show in the mid-1980s, a small California computer company said it was going to enter the telephone business, but only put up an empty booth promising products later. (Whatever happened to those Apple guys and their phones, anyway?) ... One reason is that the FCC over the years succumbed to the Big Telecom campaign to put all the little guys out of business through subterranean means that the public would never see (like charges big phone companies levy to connect to their network). Another is that the FCC gave up the authority over Internet access (broadband), which leads to its current troubles in trying to justify legally how to get an open Internet and will likely lead to future controversies over how to support broadband deployment (universal service).Right now, it doesn't matter whether Democrats or Republicans appoint FCC Commissioners so long as 3 of the 5 commissioners are more concerned with what benefits a few massive companies rather than the vast majority of businesses and citizens.
 This is exactly why communities are smart to build their own networks -- they have more control and are less damaged by the poor decisions and waffling of the federal bodies charged with making telecom policy.
This is exactly why communities are smart to build their own networks -- they have more control and are less damaged by the poor decisions and waffling of the federal bodies charged with making telecom policy. #6 is a great explanation of why communities should directly invest in broadband. Local economic growth and secondary investment enabled by broadband expansion is 10 times the initial investment.
Think about that. While private companies have long built, owned, and operated most of the broadband networks, they have seriously underinvested. They underinvest because they cannot monetize many of the benefits from broadband. Faster, more reliable connections simply do not translate into more revenue for cable and telephone companies. So the big incumbents have largely ceased investing in next-generation networks.
These massive corporations do not care about the growth of secondary investments or other spillover effects from better broadband in communities because it does not change their bottom line -- the one thing they are supposed to prioritize over all other matters.
This is why communities should be investing in themselves. Communities do care about secondary investments and spillover benefits from broadband. In fact, they are specifically tasked with investing to benefit the community!
So when it comes to maximizing the benefits of broadband, community investments tend to make a lot of sense... and other secondary benefits.
#6 is a great explanation of why communities should directly invest in broadband. Local economic growth and secondary investment enabled by broadband expansion is 10 times the initial investment.
Think about that. While private companies have long built, owned, and operated most of the broadband networks, they have seriously underinvested. They underinvest because they cannot monetize many of the benefits from broadband. Faster, more reliable connections simply do not translate into more revenue for cable and telephone companies. So the big incumbents have largely ceased investing in next-generation networks.
These massive corporations do not care about the growth of secondary investments or other spillover effects from better broadband in communities because it does not change their bottom line -- the one thing they are supposed to prioritize over all other matters.
This is why communities should be investing in themselves. Communities do care about secondary investments and spillover benefits from broadband. In fact, they are specifically tasked with investing to benefit the community!
So when it comes to maximizing the benefits of broadband, community investments tend to make a lot of sense... and other secondary benefits. The 4G offered by major wireless carriers (with the notable exception of Sprint) is a waste of money because it comes with strict data caps. These data caps actively discourage the types of activities that 4G enables. Activities that are made possible by 4G, such as watching movies or uploading video to the internet, are made impossible by the data caps. As a result most users will avoid taking advantage of these new services out of fear of incurring large overage fees. That makes capped 4G little more than a bait and switch, like being sold a handful of magic beans.I have been disturbed by statements from a number of policymakers and elected officials suggesting they believe the future of connectivity in rural America is wireless, specifically 4G because it is better than the horrible DSL that is mostly the only "broadband" connection available in much of rural America. President Obama has suggested that investing in 4G wireless will spur economic development in northern Michigan. Not hardly. What are small businesses going to use the last 29 days of the month after they exceed their data caps? People in Wired West have told me that those in charge of broadband in Massachusetts have at times been dismissive of their project to bring affordable, fast, and reliable broadband to everyone in their towns because the state would prefer to pretend that cheaper wireless solutions will accomplish the same goal. 4G wireless is not the solution to connecting rural America. It could be an interim solution while we build real broadband out to those areas, but it is insufficient as a solution in and of itself due to the many very real limitations of the technology and the business model of those controlling the spectrum necessary to access to it.
Redwood County’s Economic Development Authority (EDA) opted to move forward with a broadband feasibility study that would determine just what the county would need to do in order to get fiber to every premises. … The study, which is being conducted by the Blandin Foundation through what is known as the Robust Broad-band Networks Feasibility Grant Program. The grant, which includes up to $40,000 for the county as it addresses the needs of every community and farm site from one end of the county to the other, requires matching funds, which are available through the county EDA.
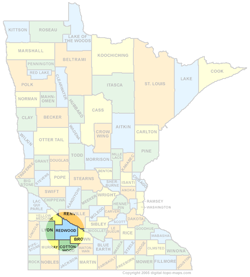 Redwood County is in an interesting area, just north of the Windom area muni FTTH networks and west of the proposed project in Sibley and Renville counties. This study comes not long after Todd County started a feasibility study as well (the the latest on that). And though we haven't discussed it much on MuniNetworks.org, Lac qui Parle County to the northwest is working with a rural telephone cooperative to bring FTTH to many in their border as well.
And then beyond them, we have Cook County going FTTH with their electric coop and Lake County going its own way, both with the assistance of the broadband stimulus awards.
Minnesota could very well become the state with the most impressive rural connections. Unfortunately, thus far we have seen no assistance from the state in this matter, but perhaps the Dayton Administration will chart a new course.
Redwood County is in an interesting area, just north of the Windom area muni FTTH networks and west of the proposed project in Sibley and Renville counties. This study comes not long after Todd County started a feasibility study as well (the the latest on that). And though we haven't discussed it much on MuniNetworks.org, Lac qui Parle County to the northwest is working with a rural telephone cooperative to bring FTTH to many in their border as well.
And then beyond them, we have Cook County going FTTH with their electric coop and Lake County going its own way, both with the assistance of the broadband stimulus awards.
Minnesota could very well become the state with the most impressive rural connections. Unfortunately, thus far we have seen no assistance from the state in this matter, but perhaps the Dayton Administration will chart a new course.Arizona Avenue, the Mid-City area and the city's office district will all be getting makeovers if the City Council approves two contracts that will connect 40 signalized intersections to City Hall's centralized traffic control system. The work represents the fourth phase in a five-phase effort to connect all of Santa Monica's intersections using fiber optic cables.
Wright said J2, which specializes in providing high-tech software to law enforcement agencies to handle dispatching, records management and other related functions, needed to have the highest speed, most dependable Internet service available. He said TUB, through its LightTUBe broadband communications service, provides exactly what his company needs to thrive and expand. "What LightTUBe has is top of the line," Wright said, adding that normal cable TV service and higher speed digital subscriber line, commonly referred to as DSL, were not adequate to meet the company’s volume and demand.Sounds like confirmation of the story we we just wrote about AT&T's CEO admitting DSL is obsolete. Congratulations to Tullahoma for making smart investments in its own future.
In 1999, Greenville, Texas' economic development leaders were unable to attract certain businesses and on the verge of losing existing companies due to a lack of high speed Internet. In response, Mayor Sue Ann Harting asked SBC for a commitment to deploy DSL. That request was denied. The city's cable franchise, Time Warner, also declined to commit to cable modem Internet deployment. Greenville found itself in a situation similar to one that many towns had faced years ago when railroads changed transportation. If the railroad was not routed through a town, that town just might die. What would happen to Greenville if the information superhighway did not come through the city?Incumbent cable and telephone companies, their lobbyists, and associated "think tanks" like to claim that communities are somehow "duped" into building publicly owned networks. The truth is that just about every community wants to avoid the hassle of building a network but incumbents refuse to invest sufficiently to keep the community competitive for economic development and a high quality of life. They build networks when backed into a corner, not because they want to. Fortunately, all that hassle almost always pays off with far more benefits than problems over the long term as communities transition from depending on some distant corporation to solving their own problems locally. In fact, the results are often like that of Greenville:
Greenville citizens were not willing to take that chance. They took destiny into their own hands by amending the city charter to allow their revenue-only supported, municipally-owned electric system to build a hybrid fiber coaxial system to make high speed Internet available to everyone.
The medical network connects Danville Regional Medical Center and about half of the area’s medical facilities to nDanville, a fiber optic network established by the city. The high performance fiber allows real-time access to patient medical records and allows for the exchange of CT and MRI scans instantly.Another article notes praise for the city's efforts:
"It enables us to better serve our patients by having their information available across multiple sites," Deaton [CEO of Danville Regional Medical Center] said. "We will continue to support the city's efforts in linking our medical community together, and I want to commend the city for the success of this network and making healthcare a top priority."The Intelligent Community Forum brought the above success to my attention in awarding Danville a recipient of its 2011 Founders Awards. (Chattanooga is in the running for Intelligent Community of year and really, how could it possibly lose?) But ICF details more impressive details from nDanville:
On average, fiber connections for these facilities provide twice the bandwidth of the previous connection but at a 30% savings. More than 90% of the medical facilities (approximately 125 locations) are to be connected by December 2011, said Jason Grey, the Broadband Network Manager of Danville Utilities, who led Danville’s charge to become a recognized intelligent community by ICF. … ICF further noted that the nDanville Network provides a crucial link between the Danville Diagnostic and Imaging Center and the Danville Regional Hospital.