
Fast, affordable Internet access for all.

The Federal Communication Commission (FCC) recently published rules for its broadband nutrition label provides a partial victory for Internet subscribers and a potential marketing advantage for fiber providers – but may pose a challenge for wireless Internet service providers.
Though the new rules were finalized in October, Internet Service Providers (ISPs) have until April 10, 2024 to publish their broadband labels, though providers with 100,000 or fewer subscriber lines have until October 10, 2024.
Just like the label on the back of packaged food in grocery stores helps shoppers understand the nutritional value of the food they are buying, the broadband label requires ISPs to disclose their broadband pricing and service information (at the point of sale) to help potential subscribers make informed decisions about the service they are signing up to get.
Transparency on Display
Though the label is just another red-tape requirement for some providers, others see it as an opportunity to show off the quality of their services.
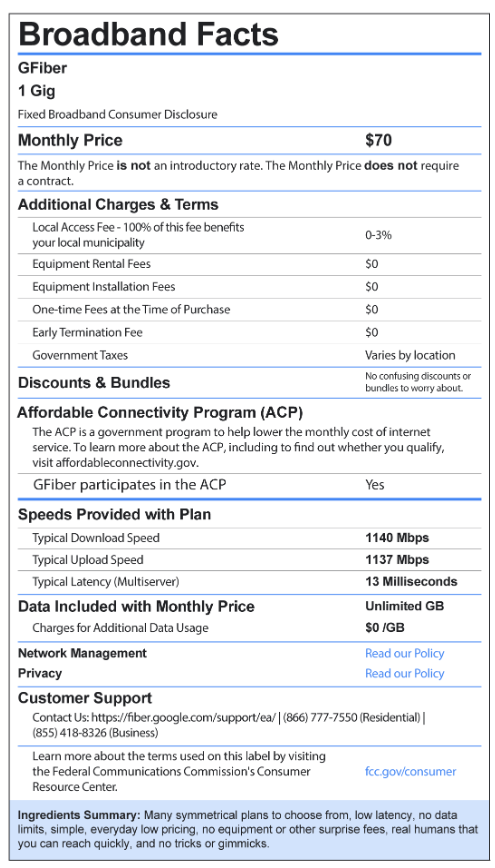
Google Fiber, for example, published via social media and its blog a preliminary version of its own broadband consumer label, just days after the final rule was published, and six months before its deadline.
In November 2021, Congress passed the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) which, in addition to funding the single largest federal investment in broadband infrastructure expansion, also mandated the implementation of a broadband nutrition label.
Similar to the nutrition label on the back of packaged food in grocery stores, the broadband label requires the transparent disclosure of broadband pricing and service information to help customers make informed decisions about service.
In November of 2022, the FCC issued a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking detailing how the label will be implemented. Industry and consumer advocates alike submitted nearly 250 filings during the public comment period, which ended in March 2023.
Most recently, the FCC released an Order of Reconsideration in response to three petitions it received from coalitions pushing back on or clarifying the rules outlined in the proposed rulemaking.
FCC Says 'Up To' Amounts Not Transparent Enough
The first petition was submitted by a broad swath of trade groups – including ACA Connects, America’s Communications Association; NTCA, The Rural Broadband Association; NCTA, The Internet & Television Association; The Cellular Telephone Industries Association; and USTelecom, The Broadband Association – and specifically pushed back on the FCC’s proposed requirement that ISPs disclose every one of their fees on the label, as well as requesting permission to list “up to” amounts for fees, citing the amount of administrative work it would take to comply with the requirement.

This week on the podcast, Christopher is joined by Dustin Loup, Project Manager of the National Broadband Mapping Coalition, housed at the Marconi Society. Dustin joins us to talk about the new national Federal Communications Commission broadband maps, currently under construction and intended to replace the current and hopelessly broken one to prepare for tens of billion in federal broadband funding.
There will hopefully be many improvements in the new maps, the first version of which is due out this month (we're not holding our breath): more granular data, more precision, and a better picture to drive future infrastructure investment in smart, efficient ways. Christopher and Dustin talk through what they hope to see, before turning to some of the problems the see emerging. This includes the frustrating walls already placed around the (tax dollar-funded) data, almost entirely restricting access to researchers and policy makers for accountability purposes, the probability of abuse by large providers, and the troublingly large $50-million contract to ConstQuest proposed in a recent announcement by NTIA to get access to something the federal government has already paid for, to administer the $42.5 billion BEAD program.
This show is 18 minutes long and can be played on this page or via Apple Podcasts or the tool of your choice using this feed.
Transcript below.
We want your feedback and suggestions for the show-please e-mail us or leave a comment below.
Listen to other episodes here or view all episodes in our index. See other podcasts from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance here.
Thanks to Arne Huseby for the music. The song is Warm Duck Shuffle and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (3.0) license.
Nearly one year ago on November 15, 2021, Congress passed the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA), which contained significant legislation around broadband. One piece, which the Institute for Local Self-Reliance (ILSR) has studied closely over the past year and a half, is the implementation of a broadband nutrition label which would require the transparent disclosure of broadband pricing and service information.
While this issue gets very little news coverage, it is an important undertaking as the big providers have a long-established habit of hiding pricing and speed information from subscribers, which prevents them from making informed choices and can leave them vulnerable to exploitation. Our advocacy for the label, and the original research behind our position, can be found here. The FCC is now under deadline to release an order to “promulgate regulations to require the display of” the label by November 15 of this year. We’ve taken a moment here to re-access the issue, offer a few updates, and highlight the ingredients of a strong broadband nutrition label.
Pushing for Clarity, Easy Accessibility, and Enforcement
ILSR, along with 30 other digital equity organizations, recently filed a letter to the FCC supporting the creation of the broadband consumer label and advocating that it be published in a way that makes it clear and easily accessible for customers. While ILSR believes the label is a key decision-making tool and should be published at the point of sale, we reject proposals to limit the label’s display to the point-of-sale only. We emphasize in this letter that the label should also be published on the monthly bill to provide an additional provider accountability mechanism that allows customers to understand what they're paying for.

This week on the podcast, Christopher is joined by Jessica Engle, Director of Community Outreach at Althea to talk about the Affordable Connectivity Program, the $14-billion fund that provides a $30 monthly service benefit ($75 on Tribal lands) to help defray the cost of Internet access to qualifying families around the country. It's a large and complicated program, and Jessica and Christopher talk about some of the bottlenecks that are causing friction both for households and for Internet Service Providers (ISPs). This includes verifying eligibility in a timely fashion, modifying administrative and accounting systems, a lack of information transparency from USAC and the FCC, and the seeming lack of mechanisms for an audit should it become necessary down the road.
Jessica has started a Discord to help navigate the ACP.
How much money is going out the door each month to pay for the Affordable Connectivity Program? Where have funds been spent at the state and zip code level? When will the money run out? Check out our dashboard at ACPdashboard.com.
This show is 17 minutes long and can be played on this page or via Apple Podcasts or the tool of your choice using this feed.
Transcript below.
We want your feedback and suggestions for the show-please e-mail us or leave a comment below.
Listen to other episodes here or view all episodes in our index. See other podcasts from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance here.
Thanks to Arne Huseby for the music. The song is Warm Duck Shuffle and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (3.0) license.
With a little less than a year left in its projected build schedule, Fort Collins (pop. 168,000) continues to make progress on its municipal fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) network, while also releasing new resources to help keep citizens informed and help households with affordability challenges stay online.
When we last checked in on Fort Collins' Connexion a little more than a year ago, the network was nearing a milestone, having spent roughly 49 percent of its construction budget. Today, the network is well over the halfway point of its $142 million-dollar build. In fact, it expects to be done placing vaults and with boring work in July.
Along the way, local officials have taken steps to increase transparency and improve communication with local residents. Last summer, it released a construction map of the networks' anticipated 357 fiberhoods, delineating which areas were in design, under construction, or fully lit.
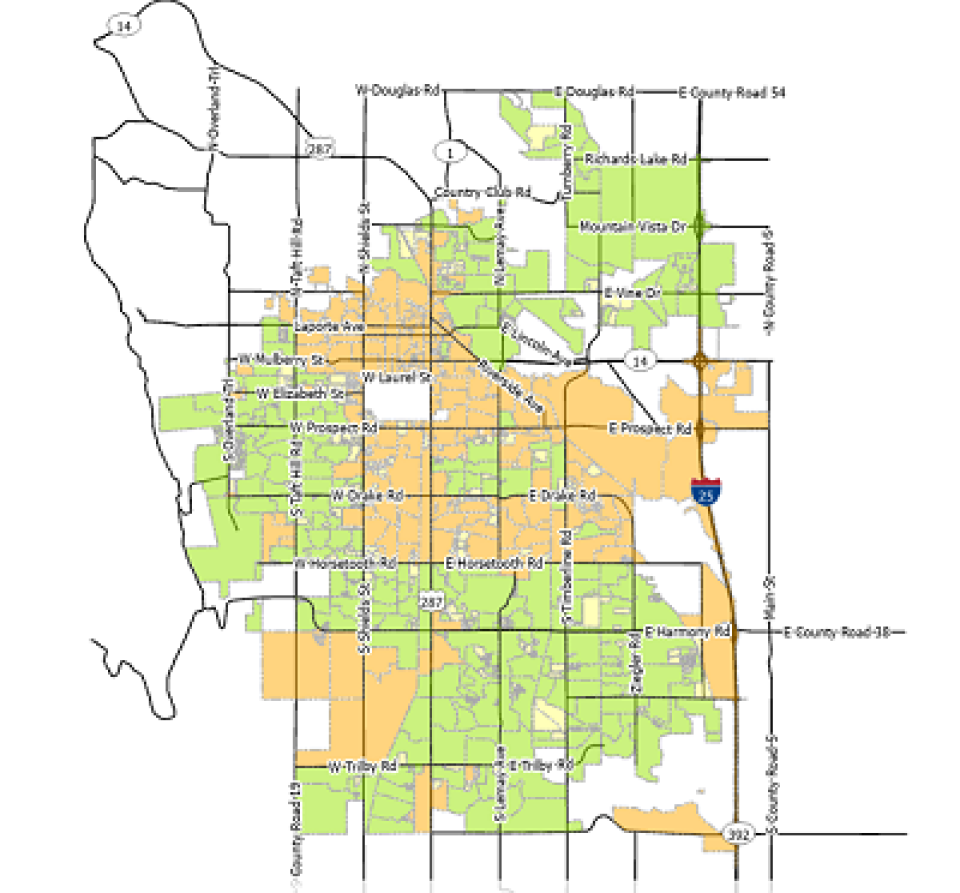
In addition, at the end of November of 2020 the network released a Network Status tracker so that users could see in each of the four quadrants of the city if connections were down.
In November, the Institute for Local Self-Reliance published a report examining the transparency practices of Internet Service Providers (ISPs). Shopping for Broadband: Failed Federal Policy Creates Murky Marketplace [pdf] identified locally-controlled broadband networks as the most transparent around key service details.
Large ISPs, however, were found to be more likely to make information like upload speed and pricing difficult or impossible for potential customers to find.
After the report’s original publication, a WISP advocate suggested that our fixed wireless sample may not appropriately represent the industry and requested that we review and re-issue our analysis with an alternative list of ISPs that have been more aggressive in pursuing federal funding and spectrum opportunities. These WISPs greatly outperformed our original sample, which was selected based on those claiming the largest population coverage.
New Set of WISPs Shows Better Transparency
While many of the original WISPs failed to disclose basic pricing and service information, only two of the second set offered less than excellent information in all categories. The second set had less poor quality information and slightly more missing information than our set of cooperatively-run networks. Municipal networks remained the most transparent.
Though many of the fixed wireless providers originally studied do seem to claim the greatest number of potential customers, we agree with some reviewers that they are not actually among the largest fixed wireless ISPs with the most subscribers. The new list of WISPs, which is included alongside the original one on the Broadband Transparency Rule Compliance Scorecard, may be a more accurate representation of providers’ transparency practices in this industry.
A new report by the Electronic Frontier Foundation argues that the general lack of fiber network coverage across the United States - with barely a third of homes able to choose a fiber option - comes in large part from the domination of the broadband marketplace by incumbent providers who both own and operate the infrastructure that provides Internet access to the vast majority of Americans. It’s a classic market failure, authors Benoît Felten and Thomas Langer argue, where there’s a clear profitable business case for the existence of more fiber access that continues to go unaddressed. At its core, the failure is driven by the attitudes of monopoly Internet Service Providers (ISP) which prefer to reap the profits from existing legacy copper and cable infrastructure rather than invest in new build outs. As a result, a larger proportion of Americans than many other nations remain stuck on slower, more expensive connections.
The solution, the report shows, is relatively straightforward and economically viable for as many as 78 percent of all households across the country: the construction of a series of local or regional fiber networks operated on a wholesale basis, whereby any ISP that wants to can join an open, transparent marketplace, creating much more competition than exists in the current arena.
“Wholesale Fiber is the Key to Broad US FTTP Coverage” offers an economic case for open access fiber in improving access, affordability, and driving competition. Comparing the potential of what it calls a Vertically Integrated Operators deployment (i.e. traditional incumbent broadband providers that build, own, and operate networks for end users) and Wholesale Network Operators deployment (an open access arrangement where the physical infrastructure is owned by one entity that invites providers to operate on the network and connect end users for a fee), the report finds that the Wholesale Network Operator model reduces the risk of capital investment, drives infrastructure expansion, and would lead to future-proof connectivity for hundreds of millions of Americans.

Report updated in January, 2022.
A new report from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance (ILSR) examines Internet Service Providers’ (ISPs) transparency — or lack thereof — around the Internet service packages they offer. Shopping for Broadband: Failed Federal Policy Creates Murky Marketplace [pdf] finds that locally-controlled broadband networks are the most transparent around key service details. Large ISPs, on the other hand, are more likely to make information like upload speed and pricing difficult or impossible to find.
Missing or unclear information is frustrating for anyone shopping for a new Internet service. It can make it especially difficult for low-income customers, who need to know pricing details (such as the difference between a service’s promotional price and standard monthly cost) in order to navigate the market and budget for service. Federal standards for transparency exist, but are not currently enforced in any real way by either federal regulation or market pressure.
Recently, Congress passed the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, which includes new information disclosure requirements for ISPs. To underscore the value of these requirements and the need for their proper enforcement, this report offers detailed analysis of 50 of the nation’s largest private wireless, private fiber, cable, municipal, and cooperative ISPs based on how clearly they disclose basic service and pricing information. Key findings include:
Frustrated while shopping for Internet service? Blame federal policy (and monopoly power).
A new report from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance (ILSR) examines Internet Service Providers’ (ISPs) transparency — or lack thereof — around the Internet service packages they offer. Shopping for Broadband: Failed Federal Policy Creates Murky Marketplace [pdf] finds that locally-controlled broadband networks are the most transparent around key service details. Large ISPs, on the other hand, are more likely to make information like upload speed and pricing difficult or impossible to find.
Missing or unclear information is frustrating for anyone shopping for a new Internet service. It can make it especially difficult for low-income customers, who need to know pricing details (such as the difference between a service’s promotional price and standard monthly cost) in order to navigate the market and budget for service. Federal standards for transparency exist, but are not currently enforced in any real way by either federal regulation or market pressure.
Recently, Congress passed the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, which includes new information disclosure requirements for ISPs. To underscore the value of these requirements and the need for their proper enforcement, this report offers detailed analysis of 50 of the nation’s largest private wireless, private fiber, cable, municipal, and cooperative ISPs based on how clearly they disclose basic service and pricing information. Key findings include: