
Fast, affordable Internet access for all.

UTOPIA trucks have started working in Centerville this week, putting in hub and connector points that will help bring the long-planned fiber optic network to public institutions in the city. Though this will also lay the groundwork for bringing the network to residents, the current phase of construction is covered by grant money that only involves government institutions. Construction on residential connections won’t begin until sometime this summer.Centerville has been stuck with considerably less reliable wireless connections that do not offer anywhere near the capacity of fiber-optic cables. The network will go beyond the typical anchor institutions (e.g. City Hall, muni buildings, and often schools) to connect traffic lights as well -- an increasingly common approach. After this phase, UTOPIA will begin expanding residential connections -- but they will prioritize areas that show the most interest in taking services.
Before the summer construction begins, residents should expect to see an information and advertising push explaining the different companies offering services on the UTOPIA network and seeking those wishing to sign up for the services (though UTOPIA and the UIA maintain the network, they offer no services. Outside companies, such as XMission, use the network for their services). Placing the advertising before the construction will determine whether or not there’s enough demand to justify the expense of laying in the network in a given area.UTOPIA continues to impress even past critics with its new management and approach.
Following 9/11, Washington DC built a muni fiber network for government use. We wrote about it Breaking the Broadband Monopoly -- noting its strong record of success. The Washington Examiner has noted that DC-Net is looking for expansion opportunites.
The city invested $87 million into D.C.-Net to get there. It now has 350 miles of fiber optic cable connecting city agencies at 355 locations in all eight wards. More than 33,000 District employees use it every day, and it handles calls to the emergency 911 call center and the city's 311 information line. The District also hasn't spent a dime on it since 2007. Instead, the network runs on a surplus, which is reinvested into its infrastructure, officials said. Now, the city stands to earn millions by leasing access to the network out to federal agencies.
While private companies constantly claim that local governments have no capacity to run fiber broadband neworks, DC-Net has proven not only can munis run these networks, they can offer faster speeds, lower prices, and better reliability. Now DC-Net has a $1.6 million contract with US Office of Personnel Management.
Martin County, Florida, is building a county-owned network (that we wrote about back in September) in response to gross overcharging by Comcast for the connections they need to connect their City Departments.
The County Commission voted unanimously Tuesday to allocate $100,000 to pay experts to advise county officials about ways the new broadband network the county government is constructing could be used to generate revenue as well as promote economic development and job creation.
...
Precision Contracting Services of Jupiter started construction on the $4.2 million network in January and is expected to finish the project by January 2012. The network is expected to serve 280 government, public safety, educational and health care organizations.
Having committed to building a network to meet their own needs, they are now searching for ways to leverage that investment to best meet community needs. They will evaluate laws, conduct a survey of residents and businesses to find what their needs/desires are, and possibly develop a business plan.
Last Monday, the day before the planned vote, a Comcast regional VP had the gall to ask the County Commissioners to delay their vote. No thanks Comcast, these folks have waited long enough for the broadband they need, that you have no interested in delivering in a timely nor affordable manner. On Tuesday, the Council voted unanimously to approve the contract.
Good for them.
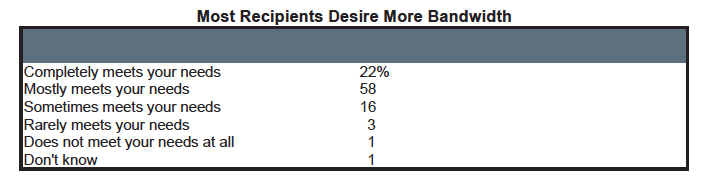 The question is why they want faster connections. Only 20% say their current connection completely meets their need to conduct online testing and assessment applications - with another 44% saying it "mostly" meets those needs.
The question is why they want faster connections. Only 20% say their current connection completely meets their need to conduct online testing and assessment applications - with another 44% saying it "mostly" meets those needs.
 These gaps represent a tremendous opportunity for growth - communities should be building their own fiber-optic connections to connect these key institutions and ensure they will have affordable, fast, and reliable connections well into the future. By owning the network, these institutions will have greater control over future costs and their capacity to take advantage of even newer applications.
The FCC should favor locally owned networks to encourage self-reliance instead of never-ending subsidies to private carriers who have little incentive to lower prices and increase investment.
These gaps represent a tremendous opportunity for growth - communities should be building their own fiber-optic connections to connect these key institutions and ensure they will have affordable, fast, and reliable connections well into the future. By owning the network, these institutions will have greater control over future costs and their capacity to take advantage of even newer applications.
The FCC should favor locally owned networks to encourage self-reliance instead of never-ending subsidies to private carriers who have little incentive to lower prices and increase investment.
Auditors observed as well that the city, a prime user of BT services, was charged “below market rates” and “below BT’s cost of service. The low rates charged by BT ... to the city could be viewed as a form of cross-subsidization,” which, the audit notes, is a violation of a provision of BT’s state license. The building of the system in general, auditors said, was marked by a “lack of timely and accurate accounting information.”While the quote does come from the Larkin report, it offers no foundation for the claim and later hedges against it (two paragraphs later -- all from page 26):
The fact that BT is providing services to various City departments at below- market rates that may be below BT’s cost of service, which could be viewed as a form of cross-subsidization, is a problem.After stating without referencing any evidence that BT is providing services to Departments below the cost of provisioning, the conclusion two paragraphs below states BT may be providing services to departments at prices below BT's cost of service ...
Washington, DC, has greatly increased the available free Wi-Fi hotspots available to those hanging out on the National Mall. DC-Net is a massive fiber-optic network used by public agencies, schools, community institutions, etc. and offers connections that are faster, less expensive, and more reliable than could be achieved by relying on leased connections from private providers. And now it is using this network to improve our experiences when we visit our capital (or Capitol for that matter). 
[T]he District of Columbia announced additions to its citywide wireless internet initiative. Over 220 Wi-Fi hotspots have been linked up to provide free Web access for city residents, visitors and businesses, District Chief Technology Officer (CTO) Bryan Sivak said in a statement. The municipal Wi-Fi network now extends coverage on the National Mall, from 3rd Street on the east to 14th Street on the west. The Office of the Chief Technology Officer (OCTO) partnered with several federal agencies including the Department of Agriculture, Department of Commerce and the General Services Administration. Hardware and Internet services were donated by Cisco and Level 3.
A more detailed explanation of both achievements and goals of the program notes:
In response to the growth of wireless hotspot users and in an effort to improve the overall wireless user experience, DC-Net increased the capacity of the wireless network from support for 1896 concurrent users in FY 09 to 6464 users in FY 10. It also tripled the number of wireless access devices deployed from 1,000 in FY 09 to 3,100 in FY 10, while modestly increasing hotspot locations from 218 in FY 09 to 230 in FY 10, thereby strengthening hotspot capacity. Wireless bandwidth also nearly tripled, from 50 Mbps in FY 09 to 130 Mbps in FY 10. Hotspots support 802.11 b/g Wi-Fi standards and user access speeds up to 20 Mbps.
The Wi-Fi network is both for visitors as well as City employees who have access to a secure wireless network to improve their efficiency.
The broadband funding will result in vastly improved Internet speeds for local government offices, schools, hospitals, and emergency communication networks across Maryland, officials said. More than 1,200 miles of new fiber-optic cable will be installed across Maryland — a 50 percent increase over the existing network capability, officials said. … The money will be used to link 458 schools, 44 libraries, 262 police and emergency centers, 15 community colleges, six universities and 221 other government and community centers in a statewide network designed to be available and secure in emergencies.As the networks are built with funds from the broadband stimulus, the networks will not be silo'ed, as is too often the case with public networks built primarily to connect community institutions. These networks will be available for the private sector to lease as well, creating more opportunities for broadband expansion and future competition. However, the track record of these middle mile networks creating last-mile connections is extremely poor. So let's not get too carried away, but it is a good step in the direction of local self-reliance and less of a dependency on massive absentee companies. Credit goes to Howard County's Ira Levy, who worked for more than a year to put the project together.
Much of the money — about $72 million dedicated to the 10 jurisdictions in Central Maryland — will be administered by Howard County.
But today, the market for bandwidth continues to grow along a nice smooth curve, with the demand doubling every two years, and we have fifteen years of data to back this up. While the incumbents are busy trying to convince us they can meet this demand with 1950s copper cable plant, smaller telecom firms are busy spreading bits of fiber through communities to cherry pick the more profitable business customers. These companies tend to have no interest in full fiber build outs, and instead just want to lock up a portion of the local business market.Some [not Cohill] have argued that when local governments stop overpaying for T1 lines and build their own networks to be fiscally responsible, incumbent telcos will be unable to continue investing there due to the reduced revenue. Of course, incumbent telcos have long ago ceased investing in these communities, so the proposition is off from the start. But even if it were true, it is an incredibly inefficient system (no matter how lucrative for the incumbent telcos). We need to actually start treating broadband as infrastructure (rather than simply talking about it as though it were infrastructure -- which most elected leaders seem to do). This means that when the community needs broadband, they are able to build it themselves and ensure the network will remain accountable to them in the future. The longer communities wait to build these networks, the more difficult a prospect it will be as private companies continue to pick off the high-revenue easy-to-serve subscribers.
The angst is over nearly $30 million that was awarded to build more than 600 miles of fiber optic cable that will bring high-capacity broadband connections to a range of key public entities and health care providers in the four communities, each of which has indicated a desire for more reliable broadband service and, not coincidentally, has a UW campus. This project’s budget is nearly $43 million when one adds in funds contributed from groups that will benefit from the infrastructure upgrade in each community. … [T]hose backing the undertaking argue it will bring faster and more reliable Internet service to public safety agencies, health care providers, schools and community organizations in Platteville, Superior, Wausau and the Chippewa Valley (Eau Claire) area.Private telecom companies (led by AT&T) are protesting the project with a rejoinder we commonly hear in these issues:
Bill Esbeck, the executive director of the Wisconsin State Telecommunications Association, argues the project will duplicate an existing network and take revenues out of the pockets of local Internet providers. The group is asking for a state review of the plan and is considering legal action, says Esbeck.Interestingly, both sides are mostly right. The public safety, health care, and educational institutions will see faster, more reliable, and less expensive broadband. Private existing providers (mostly AT&T), will lose some revenues. Of course, those lost revenues would have come from the tax base in the form of local governments having to greatly overpay for telecom services. The fiscally responsible path for local governments is to build and own (perhaps operate if they wish) their own broadband networks rather than leasing overpriced services from carriers like AT&T.
In 2007, DC-NET began with service to 135 sites, a number that has more than doubled to 280, including 140 school buildings alone. The network also provides connectivity for libraries, public hospitals, community centers, and some Wi-Fi networks. DC-NET staff designed, installed, and have maintained the overwhelming majority of the network. As is common with all these networks, some operations are contracted out (e.g. fiberoptic construction and some aspects of maintenance, such as fixing fiber cuts). DC-Net controls the locks and determines who has access to any part of its network, including key electronics on site in the buildings and elsewhere in the network, providing a high level of security. On the critical issue of reliability, DC-NET has proven impressive. The network has more layers of redundancy than one typically finds with a commercial carrier and the uptime shows it. In the first year of operation, it tallied an impressive record – with only four buildings briefly losing their network connection in three events – an average of 15 minutes of interruption per site for the year. This is far better than the industry standard – in DC-NET’s first year of operation. DC-Net is also more responsive to the needs of its subscribers. Though private companies like Verizon may require a month or even two to connect a new subscriber, DC-NET can do it in as quickly as a week to as long as twenty days. As for the services available, DC-NET will provide service from 2 Mbps -1000 Mbps, allowing subscribers far greater freedom to select the speeds they need than commercial providers offer. This publicly owned network saves DC some $5 million/year compared to the costs of duplicating functionality using leased circuits. Even then, it would not be nearly as reliable due to limits in redundancy from leased lines.