
Fast, affordable Internet access for all.

In June of 2020, Cullman Electric Cooperative launched Sprout Fiber Internet, a fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) network to bring broadband access to its members in rural Alabama. Sprout Fiber has taken significant strides since then, connecting its 1,300th subscriber in October of 2021.
By July of 2020, Sprout Fiber had started the first phase of network construction, with plans to connect 25 percent of Cullman’s membership – or 12,000 households – by spring of 2022. Sprout’s first customer was connected in January 2021. By the following September, Sprout was serving “over 1,000 broadband customers and handling about 12 activations per day,” with a little under half of its Phase I deployment finished. This puts its take rate around 20 percent in less than a year. By November, Sprout Fiber had completed a fiber ring backbone to connect its offices and substations.
Expanding Access and Choices
Local competition includes AT&T and Charter Spectrum, which offer service to the town of Cullman itself but not to its surrounding areas. Several wireless and satellite providers also offer service locally. There is significant demand for Sprout Fiber’s service, however, including from members in gap areas that don’t have other options for high-speed Internet access. According to Sprout Fiber, “twenty-five percent of [its] service territory still does not have any access to [the] Internet, and other areas do not have access to a quality Internet connection.”
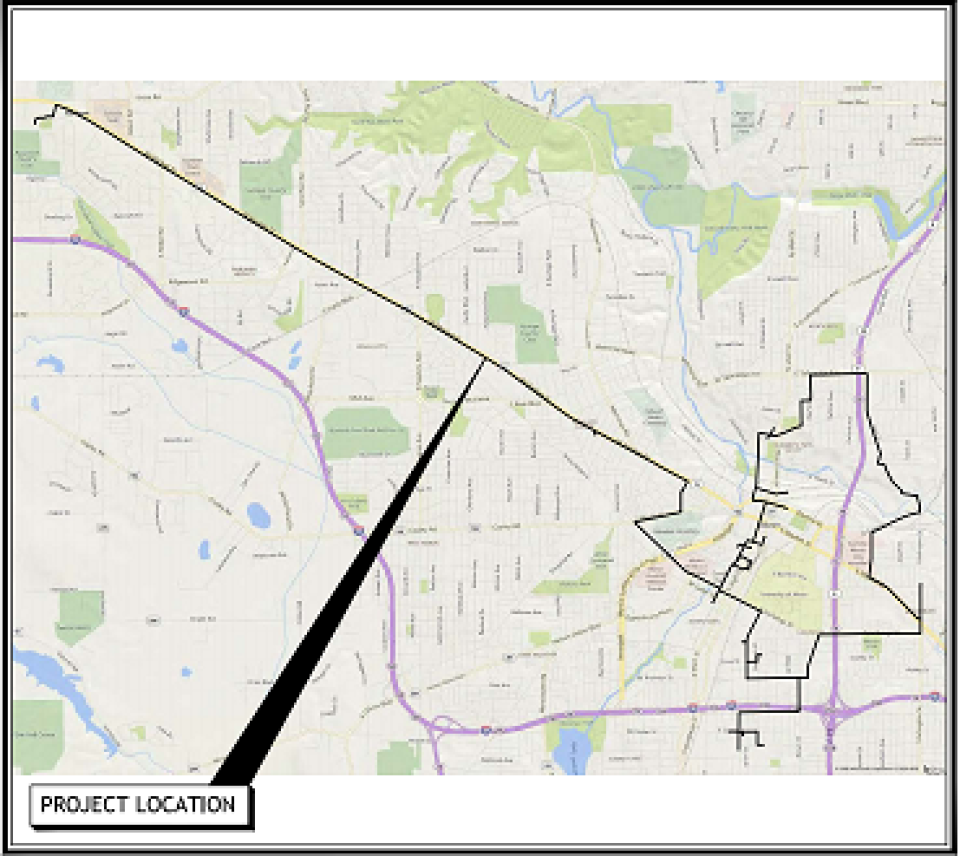
Guided by member demand and targeting areas without existing robust broadband infrastructure, Sprout Fiber plans to expand broadband service into ten new areas and to 9,000 additional members in 2022 (see map below, with green areas live right now, with pink scheduled to go live early in 2022 and purple to follow thereafter. For a high-resolution version of the map, click here). Cullman Electric CEO Tim Culpepper told members:
In Ohio’s Miami Valley, the final phase of construction for one of the country’s first multi-jurisdictional networks, the GATEWay Public Fiber Network, is underway.
The final network will connect the cities of Centerville, Kettering, Miamisburg, Moraine, Oakwood, Springboro and West Carrollton with more than 40 miles of fiber, with the resulting infrastructure bringing increased bandwidth, speed, and capacity at an affordable price to the local governments, schools, nonprofits and public safety facilities of seven communities under the Miami Valley Communications Council (MVCC).
Funding the Final Strands
Independents Fiber Network (IFN) has agreed to fund Phase II of the project with $1.8 million, bringing the total cost to just over $3 million. IFN currently owns some of the fiber connecting Springboro and Miamisburg, operating as a middle-mile provider over its 2,000 route-mile network throughout 31 Ohio counties.
“The unique public-private partnership with IFN made it possible for member communities to complete this project without any additional investment of taxpayer dollars,” Leanne Nash, MVCC Board Chair and West Carrollton City Council member told the Dayton Daily News. " At the end of the project, MVCC and IFN will equally split the available fiber and conduit assets which can then be sold or leased to interested technology providers.”
While new municipal networks often (and rightly!) catch headlines for dramatically improving the lives of residents by giving them access to high-speed, reliable, low-cost Internet access, institutional networks also remain a tried-and-true model for cities and regions looking to begin investing in their information future. And, by connecting government buildings, schools, public libraries, and other community anchor institutions, they save communities money and can serve as an alternative when monopoly ISPs like Comcast try to negotiate huge fee increases to basic city services without any explanation (like in the case of Martin County, FL).
The Miami Valley, Ohio, region accomplished the same goal a year ago, when GATEway Fiber lit up its intergovernmental, multi-jurisdictional fiber network connecting eight member cities and dozens of municipal buildings, schools, and other public anchor institutions. The result of six years of effort, the project provides the capacity and technical expertise for present and future undertakings to enhance educational initiatives, public safety programs, and utility work, and provides a model for other communities looking to work together to secure their information infrastructure moving forward.


A Joint Venture
Local governments have been creative in finding ways to conduct work remotely during the ongoing coronavirus pandemic, conducting city council meetings via Zoom or congregating in football stadiums to vote on referendums. Soon, Summit County, Ohio and the city of Akron will be better equipped to do similar work. Both have passed council measures approving an agreement with the neighboring city of Fairlawn to expand the latter’s municipal network southeast, and create a fiber ring connecting county- and city-level criminal justice and public safety buildings. The Summit County Criminal Justice Technology Project, which will be complete by the end of the year, is designed to facilitate court proceedings and public safety work remotely in response to the coronavirus pandemic.
A Burnin' Ring of Fiber
FairlawnGig, the municipal network run by the city of the same name, has issued a Request for Qualifications to design and build the network extension it will then manage. The ring will consist of 20 miles of mostly 864-strand fiber (with some places getting 24-strand additions or upgrades) and the $6.5 million cost will be paid for by Summit County (the money is coming from CARES Act funds).
Summit County Executive Ilene said of the investment:
COVID-19 has forced us to rethink how government operates and delivers services. As we begin to adjust to life with the virus, we have to consider how to safely and efficiently meet the needs of our community. This project prioritizes both safety and efficiency.

Back in June, Louisville had a close call with missing a key opportunity to build municipal fiber to local anchor institutions at a substantially reduced cost. An anti-muni broadband group pushed hard to disrupt the project but city staff educated metro council-members and moved forward with a unanimous vote.
Louisville Chief of Civic Innovation Grace Simrall and Civic Technology Manager Chris Seidt join us for episode 273 of the Community Broadband Bits podcast to discuss the project and the importance of educating local decision-makers well in advance of they decisions.
We talk about the network extensions Louisville is building to connect key anchor institutions and internal city offices. The network will not only save on connectivity costs by reducing leased lines but also provide increased security and opportunities for efficiency. We also discuss the key points Grace and Chris made to the Metro Council in arguing for this investment.
This show is 28 minutes long and can be played on this page or via Apple Podcasts or the tool of your choice using this feed.
Transcript below.
We want your feedback and suggestions for the show-please e-mail us or leave a comment below.
Listen to other episodes here or view all episodes in our index. See other podcasts from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance here.
Thanks to Arne Huseby for the music. The song is Warm Duck Shuffle and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (3.0) license.

The St Vrain Valley School District, north of Denver and including the Longmont area, is transitioning from a shared gigabit network to dedicated 10 Gbps links for schools. Just what does it do with all that bandwidth? School District Chief Technology Officer Joe McBreen tells us this week in Community Broadband Bits podcast episode 186. We talk about why the need for so much bandwidth and the incredible savings the school district has received from the municipal fiber network.
Additionally, we discuss how self-provisioning would have been the second more cost-effective solution, far better than leasing lines from an existing provider. Toward the end of our conversation, we touch on how students get access in their homes and what any business or manager needs to do to be successful, regardless of what industry he or she is in. See our other stories about Longmont here.
This show is 24 minutes long and can be played on this page or via Apple Podcasts or the tool of your choice using this feed.
Transcript below.
We want your feedback and suggestions for the show-please e-mail us or leave a comment below.
Listen to other episodes here or view all episodes in our index. See other podcasts from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance here.
Thanks to Arne Huseby for the music, licensed using Creative Commons. The song is "Warm Duck Shuffle."
The Gainesville City Council recently approved a plan to deploy a fiber ring throughout the Texas town of 16,000. The network will connect municipal facilities and offer gigabit connectivity to local businesses. Gainesville is located seven miles from the Oklahoma border in Cooke County.
According to City Manager Barry Sullivan, the planned route will provide access to 95% of local businesses. Sullivan told KXII:
"That is key to economic development now. People used to look at streets, water and sewer. Now the first thing a lot of companies look at is the communication infrastructure because that is more limited than streets, water and sewer in most communities," said Sullivan.
The project will cost $525,000; the City will pay $425,000 and the Economic Development Board will contribute the remaining $100,000.
Watch the news video or read the story for more information.Last summer we reported on Sebewaing, the community of 1,700 in the tip of the "thumb" in Michigan. At the time, Sebewaing Light and Water (SLW) was exploring the possibilities of deploying its own FTTH network. Like other small communities, Sebewaing could not get the service it needed from large corporate providers. We recently caught up with SLW's Superintendent, Melanie McCoy, to get an update.
The community released its RFP [PDF] and received responses from two bidders. McCoy tells us that in Michigan, such a low response rate allows the municipality to deploy its own network, so SLW decided to proceed.
The construction bid for the fiber backbone went to Earthcom, located in Lansing. Air Advantage successfully bid to supply bandwidth and the headend. Calix will provide the customer premise equipment that will offer data and voice services.
Sebewaing's network is 90% aerial and the final estimate is $1-2 million. The network will provide 1 gig capacity with the potential to expand to 10 gigs. Because the utility has its own poles and in-house expertise to handle labor, SLW is able to perform make-ready work themselves, lowering the final cost of the deployment. SLW will use an interdepartmental loan from its electric, water, and wireless utilities to fund the investment. According to McCoy, the RFP responses were both about $1 million higher than the final estimate.
In 2003, SLW began providing wireless Internet access to residents in Sebewaing so staff has experience as a broadband utility. They also installed a small fiber loop in the downtown area to serve businesses and municipal facilities. The old fiber loop will be retired because it has fewer strands and has been maxed out for some time.
The new fiber will replace connections between fifteen public facilities, including wells, public safety, and administration buildings. Each facility currently pays only $15-25 per month to be connected, saving thousands in yearly fees for leased lines from incumbents. Rates will not change, even though the new network will offer higher capacity.
Kevin Litten, of the Baltimore Business Journal has published a good discussion of why Baltimore is considering a public investment to expand the City's fiber network.
Councilman William H. Cole IV still bristles when he talks about the absence of FiOS in the city, a decision industry observers say has played out in other urban areas where the suburbs outrank the city in wealth. “When you look at a map of Maryland and what counties they chose to skip, Baltimore stands out, and it stands out for all the wrong reasons,” Cole said. “We need to explore every option we have to remain competitive. You can’t talk about being a great city for biotech and trying to attract startups and continue to expand the [University of Maryland] BioPark and not continue to invest.”
Litten also explored how Comcast is damaging area businesses by abusing its position as the sole citywide provider of fast Internet access (Verizon does poor DSL):
At No Inc., a 10-employee tech firm that develops software for commercial real estate, Chief Technology Officer Alex Markson said that Comcast wanted to charge $20,000 to build infrastructure to the company’s small office building on Water Street downtown.
The company had to settle for an affordable, but vastly inferior wireless connection from Clear using WiMAX. Keep this in mind the next time you hear that wireless is providing an alternative to the cable and telephone monopolies.
But that setup, which includes a barbecue grill-like satellite dish pointed out the window of the company’s offices, isn’t ideal. Productivity plummets when employees have to wait for long downloads. When using technology such as GoToMeeting to make sales pitches, “you’re not crushing it because you look like you’re slow,” Markson said.
And finally, Litten quotes some guy named Christopher Mitchell that seems to know what he is talking about: