
Fast, affordable Internet access for all.

The Atlantic Telephone Membership Corporation (ATMC) is expanding gigabit fiber Internet access with financial assistance from federal and state grants to provide high-speed broadband to residents living in some of North Carolina's most rural, poverty-stricken regions.
A $7.9 million federal allotment from the USDA’s ReConnect Program, to which the North Carolina-based telephone cooperative is contributing matching funds, has kickstarted a $15.87 million Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) broadband deployment project in one of the Coastal Plains’ southernmost counties.
ATMC recently completed construction of the first four phases of its 60-phase “Faster Columbus” project, connecting residents living in the New Life community east of Tabor City to its gigabit fiber service. Upon completion of all 60 phases, the project will provide ATMC’s FOCUS Fiber Internet service to 2,775 unserved households in rural Columbus County. The completed project will also serve over 50 businesses, ten educational facilities, three critical community facilities, and 23 agricultural operations in the communities of Hallsboro, Lake Waccamaw, Bolton, north Tabor City and Whiteville.
The fiber Internet service ATMC is providing is expected to have a substantial impact on the region’s agriculture industry, one of the main sectors of the local economy. The FTTH service will also benefit the Waccamaw Siouan Indian Tribe, whose reservation is located on the edge of the Green Swamp. Speaking of the anticipated service, Brenda J. Moore, Housing Coordinator of the Waccamaw Siouan Indian Tribe said, "Finally our Tribal students can look forward to no more boot-legging of Wi-Fi in order to do their homework."
Snapshot
Nebraska Senate rejects amendment supporting municipal broadband in spending plan
Michigan Governor vetoes bill granting private ISPs property tax exemptions
Montana, Iowa and Maine channel Rescue Plan funds towards new broadband grant initiatives
The State Scene
Nebraska
The Nebraska Senate approved a plan to spend $40 million over the next two years on expanding rural access to high-speed Internet by a unanimous vote on Tuesday, but only after an amendment to L.B. 388 that would have allowed municipalities to offer retail broadband services was rejected.
State Sen. Justin Wayne introduced the amendment, saying that “broadband should be considered a critical infrastructure need and that private telecommunications companies have not stepped up to serve the whole state,” the Lincoln Journal Star reports.
Wayne urged Nebraska Senators “to look to Nebraska's history of public power as a model, as well as to the example of other states that are allowing cities to offer broadband.” The amendment ultimately failed by a vote of 20-24. Wayne assured fellow Senators that he will reintroduce the amendment in the future.
The bill marked the first time the Nebraska Legislature has suggested using state tax dollars to fund broadband deployment. As it was submitted to Gov. Pete Ricketts for his signature, the bill would annually allocate, until funds run out, $20 million in grants to projects that increase access to high-speed broadband in unserved regions of Nebraska. It would prioritize projects in regions which lack access to Internet service with speeds of at least 25 Megabits per second (Mbps) download/3 Mbps upload. Grant recipients would be required to deploy networks capable of providing service of at least 100/100 Mbps within 18 months.
Michigan
Welcome to In Our View, a new series here at MuniNetworks. From time to time, we'll use this space to explore new ideas and share our thoughts on recent events playing out across the digital landscape, as well as take the opportunity to draw attention to important but neglected broadband-related issues.
Special thank you to ILSR Data and Visualization Researcher Michelle Andrews for noticing the Michigan discrepancy, and for her contributions to this piece.
Earlier this month, the Federal Communication Commission (FCC) released updated Form 477 data, the primary source of information used for the FCC’s broadband coverage maps and the basis upon which federal agencies and states make major funding decisions.
With new interim leadership from FCC Chair Jessica Rosenworcel – who has been well-aware of the FCC’s dubious track record of publishing imprecise, insufficient, and often inaccurate broadband coverage data – you will be disappointed if you were expecting any improvements in the newest data set.
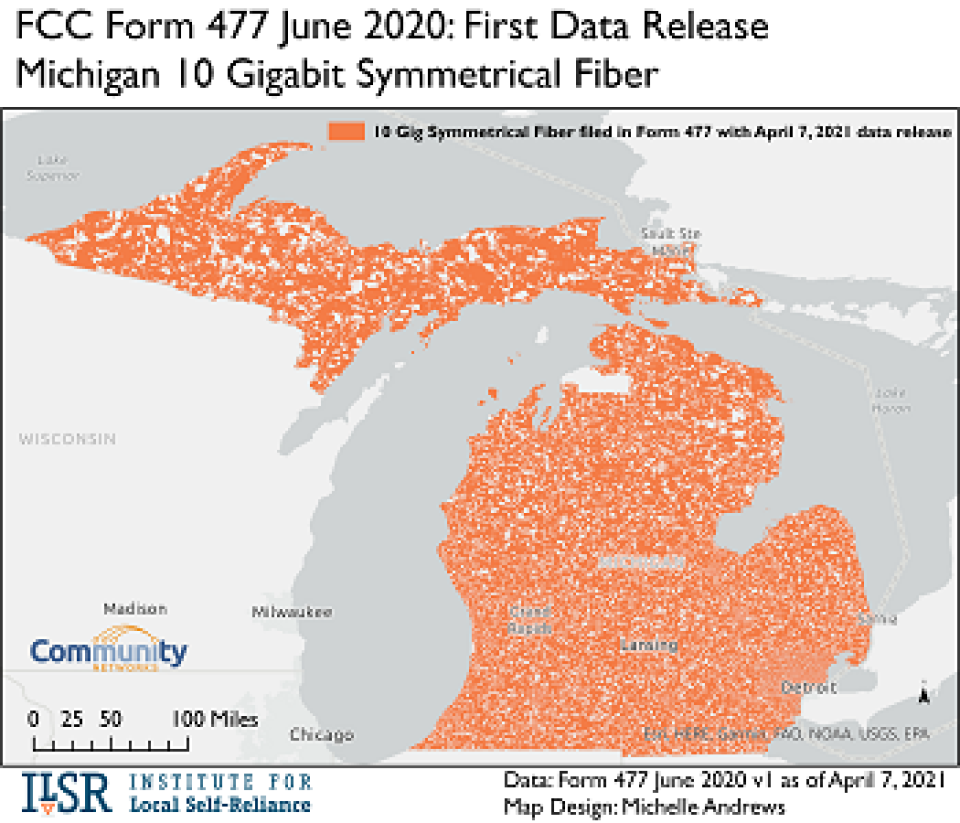
Filers had until March 26, 2021 to make revisions to data that was submitted by September 1, 2020 for service they provided as of June 30, 2020. When the updated data was first released on April 7, it indicated that nearly the entire state of Michigan had access to 10 Gbps (Gigabit per second) broadband, thanks to Form 477 data provided by Strategic Alliance CDC (see map below, or a high-resolution version here).
Historical Error Repeats Itself
Last fall we wrote about the launch of Project OVERCOME, a grant program "designed to connect the unconnected through novel broadband technology solutions" by soliciting applications from community-based organizations and ultimately award $2.7 million funded through the National Science Foundation and Schmidt Futures (the philanthropic initiative founded by Eric and Wendy Schmidt).
Project OVERCOME seeks to "[C]ollect data to measure the technical and social impacts of different connectivity strategies [in order to] discover patterns of success that can be repeated on a larger scale across the country, and to catalog the distinctions that emerge based on variations in the communities served."
Each of the winning projects will serve as an incubator of sorts, deploying proofs of concept with an array of wired and wireless technologies to connect households in
Winning applications were recently announced for projects in Blue River, Oregon; Detroit, Michigan; Buffalo, New York; Yonkers, New York; Cleveland, Ohio; Clinton County, Missouri; and Loiza, Puerto Rico.

On this episode of the Community Broadband Bits podcast, we're joined by Jonathan Chambers, a partner at Conexon. Conexon has helped rural electric cooperatives build fiber to the home networks since its founding five years ago.
Christopher and Jonathan talk about ideas for how to improve structuring rural broadband subsidies in a way that takes advantage of fiber infrastructure's long life. Jonathan and Chris dig into what this would mean for funding projects, and how it would change the way we think about and approach connecting rural communities in the future.
This show is 39 minutes long and can be played on this page or via Apple Podcasts or the tool of your choice using this feed.
Transcript below.
We want your feedback and suggestions for the show-please e-mail us or leave a comment below.
Listen to other episodes here or view all episodes in our index. See other podcasts from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance here.
Thanks to Arne Huseby for the music. The song is Warm Duck Shuffle and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (3.0) license.
Talladega, AL has long been known as the epicenter of NASCAR, a sport synonymous with speed. In 1987, Bill Elliot set the fastest recorded time of 212.089 mph on that very track.
Cars aren’t expected to start racing down the Talladega Superspeedway track until late April, but the Coosa Valley Electric Cooperative (CVEC) chose the location to announce the fittingly super fast speeds it expects to begin serving up with its new broadband subsidiary, Coosa Valley Technologies, last Wednesday.
Unfortunately, many residents in Talladega County and surrounding counties have long gone without fast connectivity, with average speeds as low as 5 Mbps (Megabits per second).
CVEC often holds events at the Superspeedway, but for this event they wanted to make sure that since people were gathering, social distancing was possible. Also they wanted to communicate a message.
“It also served as a good backdrop for what we were trying to communicate, which was, we’re going to be provided the fastest broadband service in our area,” Jon Cullimore, CVEC Manager of Marketing and Member Services, told us in an interview as the cooperative prepares to embark on a fiber build intended to bring fast, affordable Internet access to everyone in its electric footprint over the next four years.
Driven by Membership
It all started in 2019 with feasibility studies conducted by two different firms. Both found a profound lack of broadband service throughout CVEC’s service territory, which is situated east of Birmingham.
When the studies were completed, CVEC quickly put together a comprehensive information packet for members to get educated before their annual meeting last September. The members were asked to vote on whether or not CVEC should form a new broadband subsidiary and embark on a new phase of life.
A pair of bills making the rounds through Florida’s state legislature are an attack on the state’s urban municipal electric utility ratepayers to the financial benefit of big cable monopolies, under the guise of expanding rural broadband.
H.B. 1239 and S.B. 1592 read like regulatory wishlists for Florida’s big Internet service providers. Word around the capitol is that the bills are heavily influenced by Charter Spectrum, the major incumbent cable Internet provider in the region (insiders also noted in an interview that it was sponsored by the Florida Internet and Television Association, of which Charter and Comcast are members).
H.B. 1239/S.B. 1592 would require municipal electric utilities to provide private companies with access to their poles at a capped rate, though the cost of attaching new telecommunications infrastructure differs based on size, shape, and weight. Florida’s municipal electric utilities, and their ratepayers, would be burdened with any additional costs that surpass the capped rate.
The bills would further require electric utilities to reengineer utility poles to accommodate broadband providers’ attachment requests within 90 days of receiving them. In some instances, municipal electric utilities would be forced to cover the full costs of pole replacements, rather than the new attacher.
At ILSR, we are concerned that make-ready policies do discourage competition and we have encouraged streamlined access and consistent, fair rates to ensure Internet service providers can pursue efficient deployment. However, this bill would force electric ratepayers, including residents and local businesses, to shoulder more of the burden for private firms like Charter Spectrum and AT&T with the latter avoiding paying their fair share of attachment costs.
Snapshot
Colorado House passes bill that reduces broadband board membership and conceals mapping data
Michigan legislature approves bill granting ISPs property tax exemptions
New Mexico and Virginia bills await governors’ action
The State Scene
Tennessee
Tennessee is home to some of the most creative local solutions to bridging the digital divide. Municipal fiber networks across the state, including Chattanooga’s EPB Fiber network, Morristown’s FiberNet, and Bristol’s network, have been a boon to economic development, job creation, educational initiatives, and overall quality of life in the past decade.
The next city to potentially join the ranks of providing municipal broadband in Tennessee is Knoxville. On March 11, the Knoxville Utility Board approved a business plan to provide Internet services across its service area.
Despite the widespread success of municipal networks across Tennessee, the state restricts what populations they can serve. Although Tennessee law allows cities and towns to offer advanced telecommunications services if they have a municipal electric utility, the networks are not permitted to offer those services to residents who live outside of the utility’s service area. Removing these restrictions would permit substantial fiber expansion to connect more residents at no cost to the state or taxpayers.

This week on the podcast, Christopher speaks with Julie Bushell, President of Paige Wireless and Co-chair of Federal Communication Commission’s (FCC) Precision Ag Connectivity Task Force.
Christopher and Julie talk about the importance of reliable, symmetrical wireless data connections so farmers can deploy devices on farms which communicate across Long Range Wide Area Network (LoRaWAN) protocols to bring soil probes, combines, grain bins, wastewater management sensors, and other devices online to report conditions across far-flung fields. They also discuss how a robust rural network can support GPS for planting, irrigation, and harvest, as well as allow for data aggregation to increase efficiencies and allow mapping and maintenance via real-time drone operations.
Finally, Christopher and Julie dig into how more robust connectivity will help make sure high-quality jobs stay in the region, giving subsequent generations more incentive to stick around and help America's farms prosper.
This show is 31 minutes long and can be played on this page or via Apple Podcasts or the tool of your choice using this feed.
Transcript below.
We want your feedback and suggestions for the show-please e-mail us or leave a comment below.
Listen to other episodes here or view all episodes in our index. See other podcasts from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance here.
Thanks to Arne Huseby for the music. The song is Warm Duck Shuffle and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (3.0) license.

This week on the podcast we're joined by Berin Szoka, President of TechFreedom, to talk about the pressing broadband issues of today and tomorrow. Christopher and Berin share what they see as the biggest barriers to universal, high-quality Internet access today, including the jurisdictional issues facing communities large and small, as well as the regulatory solutions which would facilitate more rapid and efficient infrastructure deployment.
They debate whether we should spend public dollars not just on rural broadband where there are no options, but in town centers with slowly degrading copper networks where monopoly providers have signaled little intent to ever upgrade that infrastructure.
Christopher and Berin then dive into an issue Berin has been working on for the past few years: the Section 230 debate, and what it means for the future of the Internet if content platforms become liable for the third-party content they host.
This show is 51 minutes long and can be played on this page or via Apple Podcasts or the tool of your choice using this feed.
Transcript below.
We want your feedback and suggestions for the show-please e-mail us or leave a comment below.
Listen to other episodes here or view all episodes in our index. See other podcasts from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance here.
Thanks to Arne Huseby for the music. The song is Warm Duck Shuffle and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (3.0) license.