
Fast, affordable Internet access for all.

Two decades into the twenty-first century, it still feels a little strange to justify all of the obvious ways that Internet access serves as a key pillar among the social determinants of health (SDOH) that govern our individual and collective wellbeing. The concept itself is at least two hundred years old: a German pathologist named Rudolph Virchow is often quoted as saying in the late 1840s, in response to the privation he saw in the run-up to the 1848 revolutions, that “medicine is a social science and politics is nothing else but medicine on a large scale.”
Our modern framing of the problem comes in large part from the World Health Organization, which in the preamble to its 1946 constitution wrote that “health is a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity.” In 2020, the FCC has called broadband access a “super social determinant of health” in 2020, precisely because it serves as a gateway to all of the other elements of life that foster healthiness and wellbeing, from access to education, information, better food, economic opportunity, and socialization.
But a recent study published to the JAMA Open Network makes the connection even more explicit. In it, a team of researchers at The Center for Spatial Data Science at the University of Chicago show that a lack of Internet access has been strongly correlated with higher Covid-19 mortality rates across every type of household and in rural, suburban, and urban areas alike.
Internet Access Most Strongly Correlated with Covid-19 Mortality Rates
That community networks act as a positive force in the broadband market is something we’ve covered for the better part of a decade, but a new study out in the journal Telecommunications Policy adds additional weight (along with lots of graphs and tables) which shows that states which enact barriers to entry for municipalities and cooperatives do their residents a serious disservice.
“State Broadband Policy: Impacts on Availability” by Brian Whitacre (Oklahoma State University) and Robert Gallardo (Purdue University), out in the most recent issue of the journal, demonstrates that enacting effective state policies have a significant and undeniable impact on the pace of basic broadband expansion in both rural and urban areas, as well as speed investment in fiber across the United States.
Digging into the Data
The research relies on the State Broadband Policy Explorer, released in July of 2019 by Pew Charitable Trusts, and focuses on broadband availability across the country from 2012-2018. Whitacre and Gallardo control for the other common factors which can affect whether an area has broadband or not (like household income, education, and the age of the development), and combine the FCC’s Form 477 census block-level data along with county-level data to explore expansion activities over the seven-year period. By making use of an analytical model called the Generalized Method of Moments, Whitacre and Gallardo are able to track all of these variables over a period of time to show that there is a statistically robust connection between specific state policies and their influence on the expansion of broadband Internet access all over the United States.
While new municipal networks often (and rightly!) catch headlines for dramatically improving the lives of residents by giving them access to high-speed, reliable, low-cost Internet access, institutional networks also remain a tried-and-true model for cities and regions looking to begin investing in their information future. And, by connecting government buildings, schools, public libraries, and other community anchor institutions, they save communities money and can serve as an alternative when monopoly ISPs like Comcast try to negotiate huge fee increases to basic city services without any explanation (like in the case of Martin County, FL).
The Miami Valley, Ohio, region accomplished the same goal a year ago, when GATEway Fiber lit up its intergovernmental, multi-jurisdictional fiber network connecting eight member cities and dozens of municipal buildings, schools, and other public anchor institutions. The result of six years of effort, the project provides the capacity and technical expertise for present and future undertakings to enhance educational initiatives, public safety programs, and utility work, and provides a model for other communities looking to work together to secure their information infrastructure moving forward.


A Joint Venture
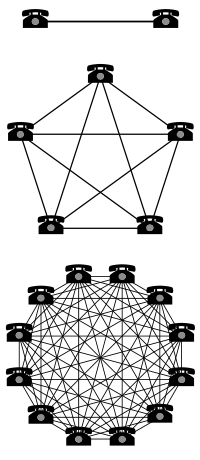 Recognizing this principle flips common arguments about connecting rural areas on their head. Ensuring that people in rural areas are connected benefits everyone -- it is not charity. Connecting people in rural areas increases the value of the connections in urban areas, creating more value for everyone.
But the flip side may be too rarely considered. As these networks have grown in size (and therefore value), the cost of those who are excluded from them also increases significantly. This means that while the costs of not connecting rural areas are high today, those costs will be even greater in coming years. The argument is rather intuitive, but for those who want to learn more, Rahul Tongia and Ernest J Wilson III published an academic paper this year in the International Journal of Communications.
The abstract for "The Flip Side of Metcalfe's Law: Multiple and Growing Costs of Network Exclusion" is here:
Recognizing this principle flips common arguments about connecting rural areas on their head. Ensuring that people in rural areas are connected benefits everyone -- it is not charity. Connecting people in rural areas increases the value of the connections in urban areas, creating more value for everyone.
But the flip side may be too rarely considered. As these networks have grown in size (and therefore value), the cost of those who are excluded from them also increases significantly. This means that while the costs of not connecting rural areas are high today, those costs will be even greater in coming years. The argument is rather intuitive, but for those who want to learn more, Rahul Tongia and Ernest J Wilson III published an academic paper this year in the International Journal of Communications.
The abstract for "The Flip Side of Metcalfe's Law: Multiple and Growing Costs of Network Exclusion" is here:
The study of networks has grown recently, but most existing models fail to capture the costs or loss of value of exclusion from the network. Intuitively, as a network grows in size and value, those outside the network face growing disparities. We present a new framework for modeling network exclusion, showing that costs of exclusion can be absolute, and might, at the extreme, eventually grow exponentially, regardless of underlying network structure. We find that costs of exclusion can also be spread to the “included” through several mechanisms such as parallel networks, and we also highlight how future research needs to capture the interaction of alternate or parallel networks to the network at hand. Backed by empirical evidence, this will have wide-reaching policy and design implications, particularly for the role of subsidies or direct intervention for network access and inclusion.