
Fast, affordable Internet access for all.


As Ammon, Idaho, celebrated the official launch of its publicly owned open access network on October 5th, 2017, the folks from Harvard University’s Digital Access to Scholarship at Harvard (DASH), shared Ammon’s story in their new report. Enabling Competition and Innovation on a City Fiber Network, by Paddy Leerssen and David Talbot provides the details of the community’s pioneering network that uses technology to increase competition for the benefit of citizens.
The report explains Ammon’s “Network Virtualization” strategy and how they accomplish it with software-defined networking (SDN) and networking function virtualization (NFV). The results reduce costs and allow users to take advantage of more specialized services, including allowing them to easily switch between Internet service providers. The environment encourages ISPs to take extra steps to please their subscribers.
Leerssen and Talbot also take the time to explain the network’s evolution from classic I-Net to groundbreaking Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH). Information in the report includes detail about pricing, and how the city determines the cost for connectivity to property owners. Readers can also learn about the ways users are taking virtualization to the next level by creating their own private networks.
Readers can learn how the Ammon Model has changed prior conceptions of municipal networks because the community needed and wanted a new approach. While Idaho is not one of the states where legal barriers discourage municipal Internet networks, the authors address how some state laws have effectively crippled local attempts to improve connectivity.
Key Findings from the report:
Ammon’s network initially served government and business users. Construction of a residential network—paid for by a property assessment equal to $17 monthly for 20 years—began in September of 2016. As of August 2017 it had 145 residential customers, with more than 270 homes expected to be connected by November 2017 in the first connected neighborhood.
If you can’t make it to Ammon to attend the launch of the city’s ground breaking open access fiber network, you can still enjoy the festivities. The event will be livestreamed starting at 10:30 eastern at this link:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCmATax9osBK4K2ZUiAtjXmQ/live
Ammon’s Mayor Deb Kirkham, State Senator Brent Hill, and even former FCC Chairman Tom Wheeler, in a video address, will share thoughts about the city’s pioneering infrastructure and what it means for this Idaho city of about 14,000 people. Christopher is in Ammon to celebrate with the community and speak on the significance of this local project.
If you need to brush up on Ammon’s software defined network (SDN) and the ways it has already improved life in the community, read our coverage before the event on October 5th. You can also take a few minutes to listen to episodes 259, episode 207, episode 173, and episode 86 of the Community Broadband Bits podcast to listen to conversations that describe the evolution of Ammon’s network.
Lastly, check out our video about the network and hear from the people in Ammon who are early adopters:
The City of Ammon, Idaho, in partnership with Next Century Cities will host an event titled “The Launch of the Ammon Fiber Utility” to bring together representatives from Ammon and the region, policy and broadband experts, and key stakeholders to show off Ammon’s open access fiber network.
The City’s open access fiber network, named 2016 Community Broadband Project of the Year by the National Association of Telecommunications Officers and Advisors (NATOA), is delivering gigabit connectivity to a community of 14,500 people.
The Launch of the Ammon Fiber Utility
The event will offer attendees the opportunity to hear more about the Ammon Model, learn how a conservative, rural town secured a high take rate, its software defined networking technologies (SDN), as well as a tour of its cutting edge facilities.
The full day event will take place Thursday, October 5, 2017, at the Ammon Operations Center and will include presenters from local government, nonprofit, and the private sector. In addition to Christopher, you can expect to see:
A Learning Experience
If you attend the conference, the morning program will start with keynote speakers and a series of panels:
Smart Cities Panel; researchers, developers, legal and policy experts will discuss current and future challenges.
Policy Discussion with Christopher Mitchell; on the role of government to solve the broadband challenges faced by communities utilizing historical experience inform future policy.

Sonic is one of the best ISPs in the nation - well beloved by its California subscribers and policy geeks like us in part because of its CEO and Co-Founder, Dane Jasper. Dane combines a tremendous amount of technical and business knowledge in a thoughtful and friendly personality. And while we don't always agree, we are always interested in what he is thinking about.
Dane joins us for Community Broadband Bits episode 261, where we focus on how cities can invest in infrastructure that will both allow firms like Sonic to thrive and permanently break any concerns about a monopoly over Internet access. Dane encourages cities to focus on dark infrastructure -- conduits or dark fiber that allow ISPs more freedom to pick and perhaps change the technologies they want to deploy services.
We also talk about network neutrality and a very brief history of Sonic.
Additionally worth noting, Sonic gets five stars from the "Who Has Your Back" evaluation from the Electronic Frontier Foundation.
This show is 35 minutes long and can be played on this page or via Apple Podcasts or the tool of your choice using this feed.
Transcript below.
We want your feedback and suggestions for the show-please e-mail us or leave a comment below.
Listen to other episodes here or view all episodes in our index. See other podcasts from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance here.
Thanks to Arne Huseby for the music. The song is Warm Duck Shuffle and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (3.0) license.
This is the transcript for episode 259 of the Community Broadband Bits Podcast. Christopher Mitchell discusses Ammon, Idaho, with Ammon Technology Director Bruce Patterson and Strategic Networks Group's Michael Curri. Listen to this episode here.
Christopher Mitchell: As they understand the model, and that's the key. As they understand the model, they start to understand how to leverage the infrastructure in a way that works for them and their business model.
Lisa Gonzalez: This is episode 259 of the Community Broadband Bits Podcast from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance, I'm Lisa Gonzales. We've been following Ammon, Idaho for some time now, having written numerous stories and producing a video about the Ammon Model. The community is continuing to grow their open access network and also reap the benefits of the public investment. This week, Christopher talks with Bruce Patterson from Ammon and Michael Curri from Strategic Networks Group to offer more details about Ammon's network. In addition to sharing details about community savings and benefits to both residents and businesses, we learn more about the Ammon Model and how it works for subscribers. Before we get started, we want to remind you that this commercial free podcast isn't free to produce. Take a minute to contribute at ilsr.org. If you're already a contributor, thanks. Now, here's Christopher, Bruce, and Michael with more information on the Ammon Model.
Christopher Mitchell: Welcome to another addition of the Community Broadband Bits Podcast. I'm Chris Mitchell, and I'm back with two well known guests to long time listeners of our show. We're going to start with Bruce Patterson, the technology director for the city of Ammon in Idaho. Welcome back.
Bruce Patterson: Thank you, Chris. Happy to be here.
Christopher Mitchell: And we also have Michael Curri, the president of the Strategic Networks Group with just a lot of analysis of various broadband networks. Welcome back.
Michael Curri: Hi, Chris. Thanks. Great to be here.

For episode 259 of the Community Broadband Bits podcast, we are going back to the well in Ammon, Idaho - one of the most creative and forward-thinking fiber network deployments in the country. Strategic Networks Group has completed a study examining the impact of Ammon's open muni fiber network on local businesses and residents.
To discuss the results, we welcome back Ammon Technology Director Bruce Patterson and SNG President Michael Curri. After a quick reminder of how Ammon's network works and what SNG does, we dive into how Ammon's network has materially benefited the community.
The city is expected to realize savings approaching $2 million over 25 years. Subscribers will be saving tens of millions of dollars and businesses seeing benefits over $75 million over that time frame. Listen to our conversation to get the full picture.
Bruce has visited us for the podcasts, including episode 207 on Software-Defined-Networks, episode 173 in which he described public safety uses for Ammon's network, and episode 86 from back in 2014 when local momentum was starting to grow for better connectivity.
Michael has also joined been on the show in the past. He participated in episode 93, talking about the benefits of broadband utilization.
This show is 31 minutes long and can be played on this page or via Apple Podcasts or the tool of your choice using this feed.
Transcript below.
We want your feedback and suggestions for the show-please e-mail us or leave a comment below.
Listen to other episodes here or view all episodes in our index. See other podcasts from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance here.
Thanks to Arne Huseby for the music. The song is Warm Duck Shuffle and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (3.0) license.
Ammon’s fiber optic utility is opening up competition for residents and businesses in the Idaho community of about 15,000 people. Their software defined network (SDN) allows users on the network to increase efficiencies and explore all sorts of creative visions that require high-quality connectivity.
Innovation Just Keeps On Keepin' On
Now, Ammon is partnering with one of the providers on its infrastructure to launch the Ammon Tech Hub & Research Infrastructure Virtual Ecosystem (THRIVE). The project is available at no cost to researchers and developers and supports:
1. Research requiring cloud functionality, high bandwidth, low latency network connectivity and a ‘living lab.’
2. Developers working on next generation networking services, products or Internet of Things (IoT) hardware in need of cloud functionality, high bandwidth, low latency network connectivity and a community of willing Beta testers.
THRIVE is designed to allow Ammon premises that are connected to the Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) network participate in projects so locals can contribute to research and development. In its press release, the city described research on aging and “smart” smoke detectors in its press release. The project will allow researchers and developer from all over the world to access Ammon’s network for collaborative projects.
For more on Ammon’s ground-breaking approach, check out the video we produced with Next Century Cities:
“Monopoly” may be a fun family night activity, but if you live in a place where you have little or no choice for Internet access, it’s not fun and it’s not a game.
According to FCC data, most families don’t have a choice in Internet access providers, especially providers they like. Nevertheless, the biggest companies keep reporting increasing revenues every year. People aren’t happy with the service they’re receiving, but companies like AT&T and Comcast continue to thrive. What’s going on?
In a recent State Scoop piece, Christopher wrote:
[T]he market is not providing a check to AT&T or Comcast power. They are effectively monopolies — and as we just saw — can translate their market power into political power to wipe out regulations they find annoying.
At the Institute for Local Self-Reliance, where we work to support local economies, this broken market is a major problem. Cable monopolies are bad for local businesses, which become less competitive from paying too much for unreliable Internet access. Communities cannot thrive without high quality Internet access today.
We created this infographic to present the evidence showing that the market is broken. This resource also discusses why creating more competition in the current market is such a challenge. An effective way to overcome this broken market, however, is to consider what hundreds of local communities are already doing - investing in publicly owned Internet infrastructure. Our infographic offers a few examples of different models, each chosen to suit the communities they serve.
Get a larger version of the infographic here.
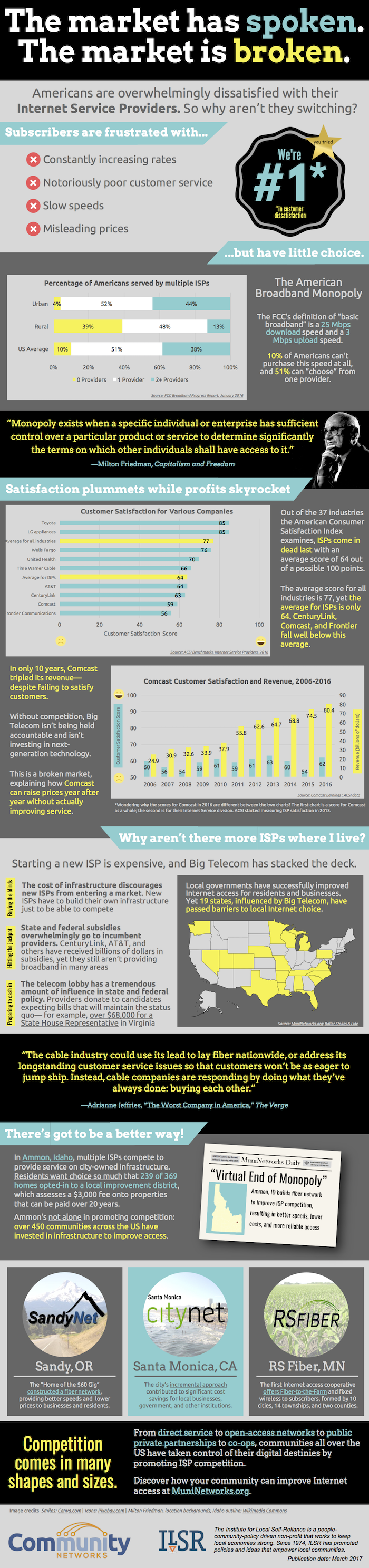
Get a larger version of the infographic here.
Kudos to intern Kate Svitavsky who created the infographic.
Stay up to date on community networks with our newsletter.
On March 24th, Christopher was on episode 232 of the web show "This Week in Enterprise Tech." Christopher discussed the future of community broadband networks in the Trump era as well as shared information about the models of successful networks across the country.
Christopher begins his discussion of these issues at 29:45 with host Friar Robert Ballecer and guest co-hosts Lou Maresca and Brian Chee. Throughout the show, the group covers the beginning of the FCC Chairmanship of Ajit Pai, how the Senate is legislating against Internet privacy regulations, and how community networks are pushing ahead to achieve better connectivity for local businesses and residents.
The folks at TWiT.tv share excerpts from our video on Ammon, Idaho, and the guys get into a deeper discussion about the possibilities of local empowerment from community networks.
You can stream the episode at TWiT.tv, or watch here:
Folks in Ammon, Idaho, are now getting choice, speed, and affordability from their new municipal Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) network. Home owners are making the switch and waving "bye-bye" to the burdens of a broken market for the benefits of publicly owned infrastructure.
High Demand
Out of 369 homes in the first district, 239 have signed up to be connected to the open access network; 22 installations are complete. Installations are on hold until winter is over, but the city’s Technology Director Bruce Patterson expects to add more as people experience their neighbors’ fiber service.
In order to connect to the network, homeowners pay for the cost of the installation themselves either with a $3,000 direct payment when the project is completed or through a special property assessment over a 20-year period. Property owners who don’t want to be connected aren’t obligated to pay. Residents or businesses connected to the network then choose an Internet Service Provider (ISP) from those offering services over the network infrastructure. The network’s technology makes switching providers a simple task that can be done online.
ISP Like It, Too
Ammon makes it easy and inexpensive for new providers to offer services on their fiber as a way to encourage competition. Ammon told the Post Register:
“We tried to make sure the barriers to entry were as low as possible to encourage competition,” Patterson said. “There’s the potential for market disruption. If somebody else can get to you cheaper and present a better economic number, they have the potential to disrupt the marketplace, which is better for all of us.”