
Fast, affordable Internet access for all.

With a little less than a year left in its projected build schedule, Fort Collins (pop. 168,000) continues to make progress on its municipal fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) network, while also releasing new resources to help keep citizens informed and help households with affordability challenges stay online.
When we last checked in on Fort Collins' Connexion a little more than a year ago, the network was nearing a milestone, having spent roughly 49 percent of its construction budget. Today, the network is well over the halfway point of its $142 million-dollar build. In fact, it expects to be done placing vaults and with boring work in July.
Along the way, local officials have taken steps to increase transparency and improve communication with local residents. Last summer, it released a construction map of the networks' anticipated 357 fiberhoods, delineating which areas were in design, under construction, or fully lit.
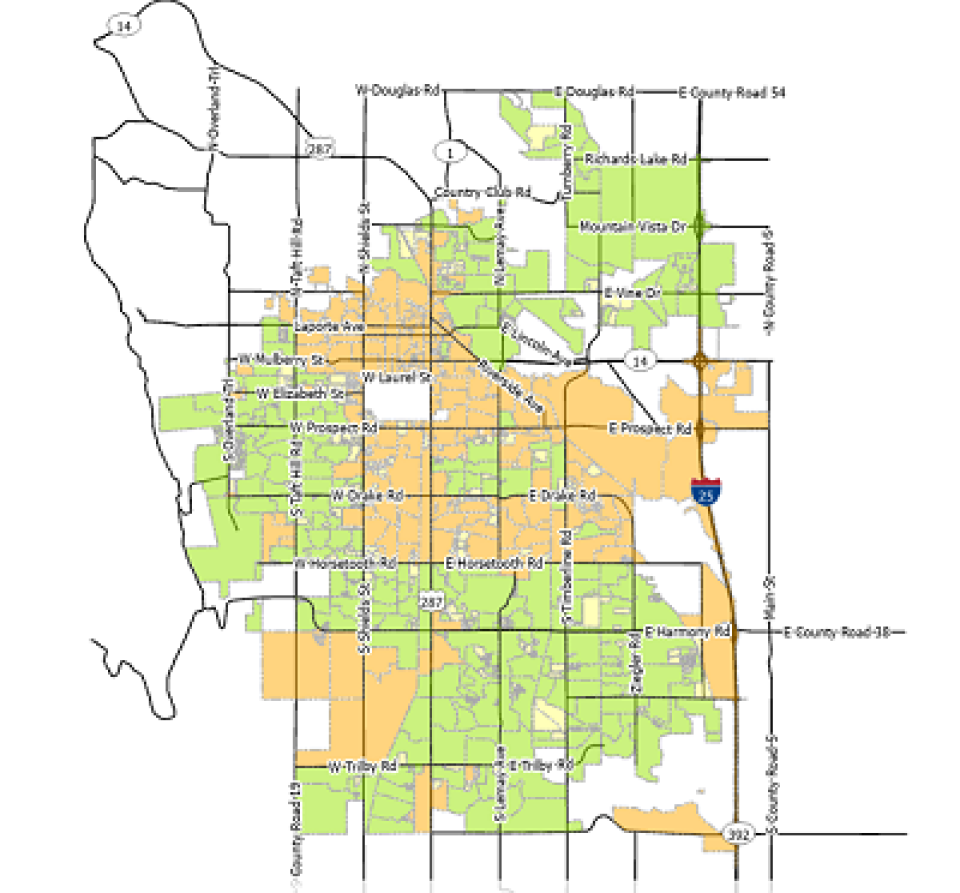
In addition, at the end of November of 2020 the network released a Network Status tracker so that users could see in each of the four quadrants of the city if connections were down.
Broadband was on the ballot as voters went to the polls for Election Day in many areas. Here’s a quick run-down of what happened.
Colorado
The Colorado state law (SB-152) that bans local governments in the Centennial State from establishing municipal broadband service suffered another defeat at the ballot box. Since the law was passed nearly two decades ago, more than 150 Colorado communities have opted out. That number continues to grow and we can now add the town of Windsor to the list of municipalities in the state who have voted to restore local Internet choice.
At the polls yesterday, 77 percent of Windsor voters said yes to Ballot Question 3A, which asked “shall the Town of Windsor, without increasing taxes by this measure, be authorized to provide high-speed Internet services (advanced services), telecommunications services, and/or cable television services … either directly or indirectly with public or private sector partners?”
A month ago, President Biden visited the city of Golden, Colorado to tout his Build Back Better Agenda, which includes a bipartisan infrastructure package that invests $65 billion to expand access to high-speed Internet connectivity. But years before that, city officials had already been preparing for the possibility of building a municipal fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) network.
Although the President didn’t say it during his remarks after a tour of Golden’s National Renewable Energy Lab (NREL), the city’s desire to offer municipal Internet service is a prime example of what the Biden Administration’s American Jobs Plan envisioned: investing in local, publicly-owned community broadband networks.
Though this city of approximately 20,000 is served by CenturyLink and Comcast Xfinity, along with a handful of other smaller Internet Service Providers (ISPs), city councilors agree that a municipal FTTH network would be a boon for business and offer more affordable and reliable options to residents.
It’s an idea that has garnered the support of voters when five years ago a referendum was passed authorizing the city to opt out of the Colorado state law (SB 152) that bars local governments in the Centennial State from establishing municipal Internet service. Golden is one of over 150 communities in the state to have opted out of SB 152 since the law was passed 15 years ago; most notably Loveland, Fort Collins, and Estes Park, all of whom are building out municipal fiber networks in the Front Range region.
With American Rescue Plan funds flowing into state government coffers, about a third of the nation’s 50 states have announced what portion of their Rescue Plan dollars are being devoted to expanding access to high-speed Internet connectivity.
The federal legislation included $350 billion for states to spend on water, sewer, and broadband infrastructure, though everything we have seen suggests that the vast majority of that will not go to broadband. There is also another $10 billion pot of rescue plan funds, called the Capital Projects Fund, that mostly must be used to expand access to broadband.
Laboratories of Broadband-ification
As expected, each state is taking their own approach. California is making a gigantic investment in middle-mile infrastructure and support for local Internet solutions while Maryland is making one of the biggest investments in municipal broadband of any other state in the nation. And although Colorado does not prioritize community-driven initiatives, state lawmakers there have earmarked $20 million for Colorado’s two federally-recognized Indian tribes to deploy broadband infrastructure with another $15 million devoted to boosting telehealth services in the state.
Undoubtedly, individual states’ funding priorities vary. Some states may be relying on previously allocated federal investments to boost broadband initiatives and/or have been persuaded the private sector alone will suffice in solving its connectivity challenges. And in some states, such as Illinois, Minnesota, and Maine, lawmakers have prioritized using state funds to support broadband expansion efforts while other states may be waiting on the infrastructure bill now making its way through Congress before making major broadband funding decisions.
As of this writing, 17 states have earmarked a portion of their Rescue Plan money (totaling about $7.6 billion) to address the digital divide within their borders. Those states are Arizona, Arkansas, California, Colorado, Delaware, Hawaii, Indiana, Kentucky, Maine, Maryland, Montana, Missouri, Virginia, Tennessee, Vermont, Washington, and Wisconsin.
Join us live this Thursday, October 14th at 5pm ET for Episode 22 of the Connect This! Show, where co-hosts Christopher and Travis Carter (USI Fiber) will be joined by Dennis Pappas (Longmont, Colorado) and Christy Batts (Clarksville, Tennessee) to talk about large municipalities successfully deploying broadband infrastructure for an array of community benefits.
Longmont, Colorado's Nextlight has been wildly successful during its first five years of life in uncommon ways. Clarksville, Tennessee's CDE Lightband has overcome early challenges to bring significant savings to the public, especially to members of the municipal electric utility. Christopher, Travis, Dennis, and Christy come together to unpack how they got there and what it means for the future.
Subscribe to the show using this feed, or visit ConnectThisShow.com
Email us broadband@muninetworks.org with feedback, ideas for the show, or your pictures of weird wireless infrastructure to stump Travis.
Watch here or below on YouTube Live, or via Facebook Live here.
The Centennial State has been a leader over the last fifteen years in showcasing how communities can take back local authority from restrictive state laws which place barriers in front of municipal broadband efforts. More than 150 communities in the state have done so since the 2005 law went into effect, and cities like Longmont, Loveland, and Fort Collins continue to show the value of investing in local broadband infrastructure and bringing the service residents, businesses, and community anchor institutions need.
Cortez, Colorado (pop. 8,700) is the latest municipality to join the club. In a referendum last month, residents raised their hands to opt out of SB 152, with 78 percent in favor.
Afterwards, former Mayor Karen Sheek remarked that “To move forward on finding solutions to improve Internet service for our community, we need the exemption. It is the next natural step." Cortez General Services Director Rick Smith said that broadband service remains weak outside the "downtown corridor, in schools, libraries and government offices."
The city already operates an I-Net for public facilities, businesses, and anchor institutions (listen to Christopher talk with General Services Director Rick Smith on the podcast about it).
What's next for the city remains to be seen, but others in the state are forging ahead. Four other communities - Berthoud (pop. 7,200), Mead (4,600), Johnstown (15,000), and Milliken (7,200) - have banded together together to perform a survey of residents as a prelude to taking next steps. Berthoud opted out of the preemption law last November (along with Denver and Englewood) while Johnstown did so in April 2020 and Mead opted out in the fall of 2019.
After three years in a row with similar results, PCMag’s “Fastest ISPs in America” for 2021 analysis shows a clear trend: community owned and/or operated broadband infrastructure supports networks which, today, handily beat the huge monopoly Internet Service Providers (ISPs) - cable and telephone alike – for sheer speed.
The latest list proves it. Of the ten-fastest ISPs in the country, all of them feature operators that either are cities themselves or use city-owned fiber or conduit to deliver service across whole or parts of their footprint.
City-run networks making the list again this year include Longmont, Colorado (third); Chattanooga, Tennessee (sixth); and Cedar Falls, Iowa (seventh). Cedar Falls topped the list last year, but all three networks are regulars over the last three analyses done by the outlet. Broken down regionally, they are also joined by other municipal networks around the country, including FairlawnGig in Ohio and LUS Fiber in Louisiana.
After pausing for a year, the 2021 Mountain Connect conference is scheduled to return this year, taking place the second week of August in picturesque Keystone, Colorado.
Panel topics are arranged, as usual, on key topics, including: "Intelligent/Smart Infrastructure, Funding, Economic Development, Healthcare, Education, Emerging Technologies, Policy Impacting Broadband, and Broadband 101 Education for Elected Officials."
The agenda is still being finalized, but the conference will feature a list of industry veterans, policy advocates, nonprofit leaders, and local officials, including ILSR's Christopher Mitchell. Other scheduled speakers include Deb Socia (The Enterprise Center), Brian Worthen (Mammoth Networks), Monica Webb (Ting), Matt Rantanen (Arcadian Infracom and Tribal Digital Village), and many others.
Panels at this time range across a variety of timely topics, including municipal partnerships, middle mile challenges, resilient communities, and digital inclusion. It will also present the opportunity to hear about network project efforts and municipal success stories from Wyoming, Colorado's Front Range, Iowa. See the current agenda here.
Learn more about Mountain Connect below.
Municipal networks in the United States have proven that when dollars are invested in publicly owned information infrastructure, they often return value back to the community several times over. This new fact sheet [pdf] highlights municipal broadband success stories from across the country and some of the many benefits the networks have brought to the communities they serve.
These networks are directly accountable to the community and have proved themselves for more than 20 years in some cases, bringing lower prices to households than the large private providers. Municipal networks and partnerships account for 9 of the top 10 fastest broadband networks in the nation.
Download Snapshots of Municipal Broadband: A Much-Needed Part of America's Digital Ecosystem [pdf] here.
For timely updates, follow Christopher Mitchell or MuniNetworks on Twitter and sign up to get the Community Broadband weekly update.
Closing the homework gap has been a top priority for Federal Communications Commission (FCC) acting Chair Jessica Rosenworcel. She has a long track record advocating for Wi-Fi-enabled school buses, lamenting viral images of school children completing homework in fast food parking lots, and making the case that no child should be left offline. At the onset of the pandemic, she pledged to use her influence at the agency to fight to increase the flexibility of the E-Rate program, saying “every option needs to be on the table.”
When the American Rescue Plan Act established the Emergency Connectivity Fund (ECF) in March, a $7 billion program to connect students and library patrons to the Internet at off-campus locations, Rosenworcel had an opportunity to follow through on those promises. She could have seized the moment to steer the program in the direction of allowing schools and libraries to build, own, and operate their own school and community networks (what the federal government refers to as self-provisioned networks). Many schools serving areas with poorly connected students already do this, but without much help from the E-rate program.
But when the rules on how to spend the money were finalized on May 10th, the FCC’s Report and Order declared that schools and libraries could not use Connectivity Funds to build self-provisioned networks, but instead could only use the funds to purchase Wi-Fi hotspots, modems, routers, and connected devices, such as laptop computers and tablets. The one exception in which schools and libraries can use Connectivity Funds to build self-provisioned networks is in “areas where no service is available for purchase,” based on data self-reported by private ISPs.