
Fast, affordable Internet access for all.


This week on the podcast, Christopher is joined by Joe Poire, Director of Petrichor Broadband in Whitman County, Washington. During the conversation, the two discuss the unique role of Ports in Washington State, which for years have been building robust broadband infrastructure that could be used for increasing competition or extending access into unserved areas. They talk about how the Port of Whitman has stepped up to fill the cracks of a deregulated telecom market, why Petrichor Broadband was established, and how they have used an open access dark fiber business model to bring broadband to communities across Washington State. Christopher and Joe also take time to respond to criticism of publicly owned open access networks, and discuss how Petrichor’s approach has encouraged competition in underserved communities.
This show is 30 minutes long and can be played on this page or via Apple Podcasts or the tool of your choice using this feed.
Transcript below.
We want your feedback and suggestions for the show-please e-mail us or leave a comment below.
Listen to other episodes here or view all episodes in our index. See other podcasts from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance here.
Thanks to Arne Huseby for the music. The song is Warm Duck Shuffle and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (3.0) license.
Once known as the center of bowling ball manufacturing, producing 60 percent of the world’s bowling balls, today Hopkinsville, KY (pop. 31,580) is on the verge of becoming a kingpin in a whole different lane: producing gig-speed broadband.
A municipal utility currently offering fiber Internet access to the residents of Hopkinsville, Hopkinsville Electric System (HES) is joining forces with Pennyrile Electric Cooperative to extend fiber-to-the-home Internet service to as many homes as possible in Pennyrile Electric’s service territory in southwestern Kentucky, starting with Christian, Trigg, and Todd Counties.
The three counties will contribute approximately $17 million of American Rescue Plan Act funds, while HES and Pennyrile will use a combination of state and federal grants and loans to contribute a 100 percent match for the $34 million project. When network construction is complete, it is expected to pass 28,000 households in the tri-county region.
Scoring Big in Public Partnership
While HES EnergyNet connected its first household in 2016, the utility has been utilizing the power of fiber-optic broadband for decades.
HES started as a municipal electric utility nearly 80 years ago, but in 1998, the board of directors decided to turn to fiber to connect its substations. By 1999, HES was offering fiber-fed broadband services to local businesses, industries, and city and county agencies through its ISP, EnergyNet.
In November 2018, HES EnergyNet announced it had plans to bring gigabit speeds to every address in Hopkinsville. Since then, the network has grown to serve more than 12,000 residents and businesses.
As HES was putting its fiber network to use, Pennyrile Electric reached out to its future partner and presented the idea to continue building fiber out into the surrounding rural areas. Pennyrile Electric has members across nine counties and had been getting numerous calls from co-op members asking whether or not the cooperative would get into the broadband business.
Is a major metropolitan Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) network on the horizon for one of the Sunshine State’s most populous cities?
Longtime Jacksonville, Florida (pop. 890,000) resident Eric Geller is spearheading a citizen-led effort to rally residents and officials around a vision that would catapult Jacksonville into the fiber-connected frontier of Internet access and reinvigorate the economy of a city that was once known as the "Bold New City of the South."
As an IT consultant and former public policy research analyst, from Geller’s tech-savvy perspective the key is for the city’s utility company, JEA, to move beyond providing electricity, water, and sewer services and expand into building the necessary Internet infrastructure that would give all Jacksonville residents access to reliable and truly high-speed connectivity.
“Nationally, it’s been well accepted that we are at a point where the Internet is absolutely mandatory. Every business and home has to be connected,” Geller said in a recent interview with WJCT Radio, noting how the pandemic has made it clear that universal access to broadband is nearly as important as running water and electricity.
JEA’s Dark Fiber Infrastructure
If it’s a pipe dream, it’s one with light at the end — if Jacksonville residents can first see and appreciate all the dark. That is to say, the city’s existing dark fiber network, or the unused capacity of the fiber optic cables JEA has already deployed and how it could be leveraged and lit up to serve as the backbone for a citywide FTTH network.
JEA already leases routes to businesses along its 500-mile fiber optic network spanning the Jacksonville metropolitan area, which includes all of Duval Country and parts of St. Johns and Nassau Counties. In fact, with all that underground (and overhead) fiber already in place, Jacksonville can boast of having “more fiber in the ground than any city in Northeast Florida,” much of it passing through vital commercial and industrial parts of the city.
St. Louis Park (pop. 49,000), a suburb west of Minneapolis, Minnesota, has demonstrated commitment and creativity in bringing broadband access to the region over the last two decades. They’ve done so by connecting community anchor institutions and school district buildings, in supporting ongoing infrastructure via a dig once policy, by working with developers to pre-wire buildings with gigabit-or-better-capable connections, and by using simple, easy-to-understand contracts to lease extra dark fiber to private Internet Service Providers (ISPs) to improve connectivity options for local residents.
Conversations about improving broadband in St. Louis Park began in the 1990s, when local government officials and the St. Louis Park School District began talking about replacing the aging copper infrastructure it was leasing from the cable and telephone companies with fiber to support educational use and municipal services. At the time the city was paying about $45,000/year to stay connected and online. A 2003 projection suggested it could invest $380,000 to build its own network instead, take ownership of its infrastructure, and see a full return on investment in less than a decade.
Fiber, both the city and the school district decided, offered the best path forward for the range of tools and bandwidth that would bring success. The school district led off in connecting its structures, but by 2004 both were done, with each contributing to joint maintenance and operational costs. The city thereafter decided to keep going and expand its infrastructure wherever it made the most sense. In 2006 it advanced this agenda by adopting a dig-once policy by adding conduit — and sometimes fiber — any time a street was slated for repairs.
Municipal Wi-Fi

This week on the podcast Christopher talks with Stacy Cantrell, Vice President of Engineering at Huntsville Utilities in Alabama. Huntsville’s (pop. 197,000) municipal utility serves well beyond the city boundaries, and its electric department built a major network that gets close to every house within the city limits.
Stacy shares how the 1,100-mile fiber project unfolded, what it took to overcome challenges, and how things are going now that they’re nearly done. The utility uses its network for internal services to bring value to those living in the city, but providers, of which Google will be the first, can lease that network and attach homes to it.
This show is 29 minutes long and can be played on this page or via Apple Podcasts or the tool of your choice using this feed.
Transcript below.
We want your feedback and suggestions for the show-please e-mail us or leave a comment below.
Listen to other episodes here or view all episodes in our index. See other podcasts from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance here.
Thanks to Arne Huseby for the music. The song is Warm Duck Shuffle and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (3.0) license.
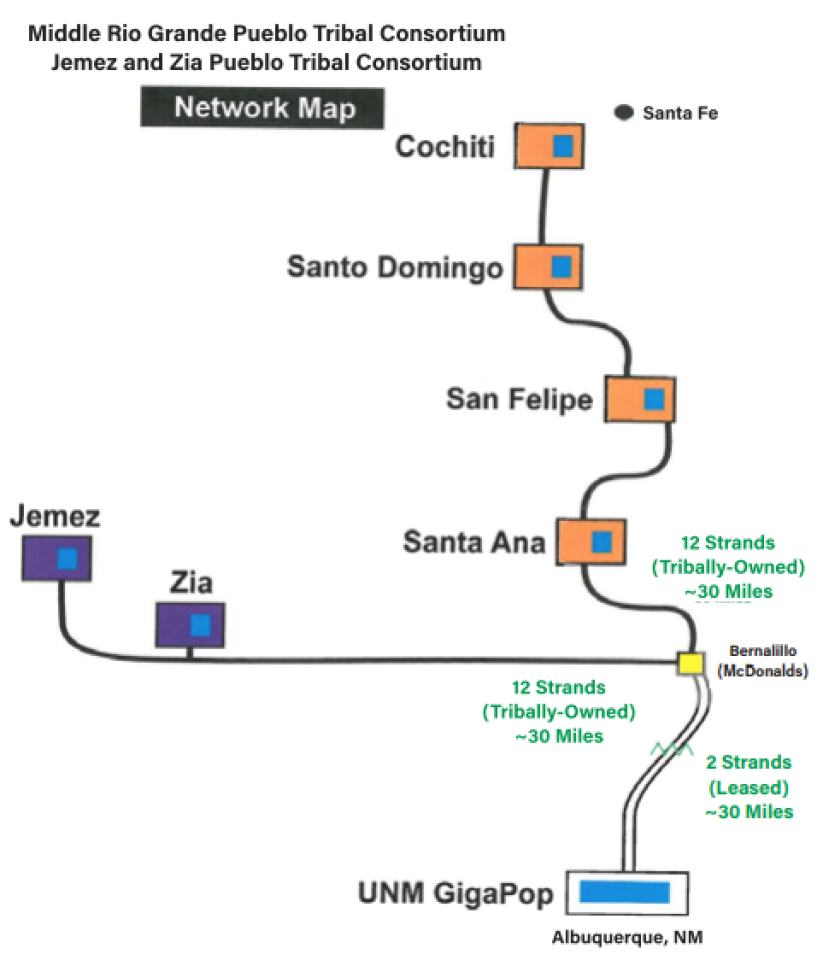
A new report out by the American Library Association shows how community anchor institutions — and libraries in particular — can serve as central players in expanding tribal connectivity efforts around the country. “Built by E-rate: A Case Study of Two Tribally-Owned Fiber Networks and the Role of Libraries in Making It Happen" [pdf] looks at the striking success of tribal efforts in New Mexico in putting together a coalition of actors to dramatically improve Internet access in the region.
The report examines networks built by two consortiums situated in the middle of the state in the summer of 2018: the Middle Rio Grande Pueblo Tribal Consortium and The Jemez and Zia Pueblo Tribal Consortium. An endeavor initially spearheaded by the Santa Fe Indian School (which long ago recognized the need for virtual learning, the value of fast, affordable Internet and the ongoing cost of slow, poor, high monthly costs), “Built by E-Rate” details how they came into being and the obstacles they faced along the way, and offers policy recommendations moving forward.
Faster Speeds, Lower Costs
Janesville, Wisconsin (pop. 64,000) Information Technology Director Gordon LaChance has been investing in fiber infrastructure for city needs for the last 12 years, but he’s been hoping it would lead to something more. That day may have come, with the recent award of a $114,000 grant from Wisconsin Public Utility Commission.
The grant allows the city to participate in a public-private partnership that will bring fiber to a handful of unserved or underserved commercial locations in town. The move is the first of its kind for the city, and involves an exchange of capacity that will allow WIN Technologies — a private Internet Service Provider (ISP) — to bring service to two SHINE Medical Technology locations (a small headquarters downtown as well as a large, new development being built south of town), the Janesville Centennial Business Park, the Beloit Avenue Corridor Business Park, and the Janesville Innovation Center.
The grant application was spearheaded by the city’s Economic Development Office, which gathered the players and helped iron out the details. LaChance described how the deal would work in a phone interview. The city will give WIN access to some of its dark fiber, which WIN will make use of along with the grant funds and additional private investment to build south and connect those areas of town. In return, WIN will lay extra fiber as it goes and hand it over the LaChance’s office, allowing the city plant to expand in that direction when it otherwise would not be able to justify the cost. It remains early, but the city estimates that around a dozen businesses will be connected with the expansion. Better connectivity will also spur the revitalization of the Janesville Assembly Plant, a General Motors factory decommissioned in 2008 that is being turned around by a commercial developer to bring manufcaturing production and jobs back to the area.
The Fruits of Forethought
After years of hearing from its citizens and business owners that Internet access was one of Fort Morgan’s most pressing problems, the Colorado city of 11,000 decided to do something about it. Like dozens of other communities around the state, in 2009 residents approved a ballot measure to opt out of SB 152, the 2005 state law preventing municipalities from offering broadband. (Today, more than 100 local goverments have opted out.)
Ten years later, a little forethought, hard work, and a public-private partnership with ALLO Communications has brought gigabit speeds and low prices to everyone in Fort Morgan over the city's dark fiber network.
Taking the First Steps
Between 2013 and 2015 Fort Morgan conducted a feasibility study while assessing its needs in the early stages of a plan to expand the city's existing fiber network connecting anchor institutions — itself the result of the state’s 2002 Beanpole Telecommunications Project [pdf] — to residents and businesses. The city reiterated the necessity of an affordable, reliable network in the 2016 Connect Fort Morgan [pdf] plan update. In May Fort Morgan awarded the initial design project to Manweiler Telecom Consulting, Inc., the firm that had built the city’s original fiber network a decade and a half before. The city paid $160,000 for the initial phase of the system’s design.
There’s a new Thor in town, but instead of lighting up the night sky like the Norse god of thunder, it’ll be lighting up communities in rural Colorado with fiber optic connectivity.
A group of local governments and private partners, led by Northwest Colorado Council of Governments (NWCCOG), recently completed the first phase of Project THOR, a middle mile fiber network that will enable better connectivity in the participating towns, cities, and counties. The network, owned by NWCCOG, provides backhaul to local governments looking to connect public facilities, schools, hospitals, and other community anchor institutions. It’s also available to Internet service providers (ISPs) to serve residents and businesses.
Project THOR brings much needed redundancy to the region’s broadband infrastructure, where previously a single fiber cut could take entire communities’ health and public safety services offline. It also promises great cost savings for localities and ISPs. Perhaps most importantly, the new network gives communities the necessary leverage to improve local connectivity beyond begging the incumbent providers for better broadband. Jon Stavney, executive director of NWCCOG explained on Community Broadband Bits episode 406:
This project allows these local governments to actually have a lever to pull to hopefully affect local service, however they can do that, with whatever partners come to the table . . . They’re able to actually act.
Building Toward a Network
NWCCOG, which is composed of member governments in and around Eagle, Grand, Jackson, Pitkin, and Summit Counties, coordinated broadband efforts in the region even before Project THOR began. A number of years ago, the council invested in a regional plan and hired a broadband coordinator, Nate Walowitz, to offer technical assistance to the member governments.

The breathtaking mountains of northwest Colorado have long attracted skiers and hikers, but broadband providers haven't found the region's rugged landscape and sparse population as appealing. Enter Project THOR, a middle mile fiber network developed out of a collaboration among local governments and private companies led by the Northwest Colorado Council of Goverments (NWCCOG). Over the last few years, the partners strung together more than 400 miles of fiber to provide reliable and affordable backhaul to municipal facilities, public schools, healthcare systems, and Internet access providers.
This week on the Community Broadband Bits podcast, Christopher talks with Jon Stavney, executive director of NWCCOG, and Evan Biagi, executive vice president of business development for network operator Mammoth Networks, to learn more about the recently completed project. Jon describes past broadband efforts in the region that led into Project THOR. The pair explain how the new middle mile network will allow localities to connect municipal facilities and anchor instutions and how broadband providers or the communities themselves can build off the network to serve residents and businesses. This will improve broadband reliability and affordability in the region, which had previously been plagued by network outages that cut access for hospitals and 911 calls.
Jon and Evan also discuss how the partners lowered project costs by leveraging existing infrastructure. They share some of the challenges involved in designing a network with so many partners. At the end, Jon explains how Project THOR will give communities more opportunities to take action on local connectivity instead of just impatiently waiting for better broadband.
This show is 33 minutes long and can be played on this page or via Apple Podcasts or the tool of your choice using this feed.
Transcript below.
We want your feedback and suggestions for the show-please e-mail us or leave a comment below.
Listen to other episodes here or view all episodes in our index. See other podcasts from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance here.
Thanks to Arne Huseby for the music. The song is Warm Duck Shuffle and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (3.0) license.