Image


"The private sector is handling this exceptionally well," Rogers said. "What they don't need is for a governmental entity to come in and compete with them where these types of services already exist.

Broadband infrastructure is this century’s interstate highway system: a public investment in an infrastructure that will rapidly connect Washington’s citizens statewide, nationally, and internationally; fuelling growth, competition, and innovation. Like highway access, the path to universal broadband access varies with the needs of the local community. Our primary goal is to expand broadband access. We believe allowing municipalities and PUDs to provide broadband services addresses the most significant hurdles to broadband expansion: the high cost of infrastructure. In conjunction with a state USF, PUDs and municipalities are well placed to address the needs of their consumers. A secondary goal is to promote a competitive marketplace.
 Reforming this system is a deep, seemingly intractable problem. But for those looking for answers, a good place to start is with the work of Lawrence Lessig. I just finished his Republic, Lost, which offers a grand tour of the problems resulting from the present system of campaign finance.
You can also see a number of his presentations here.
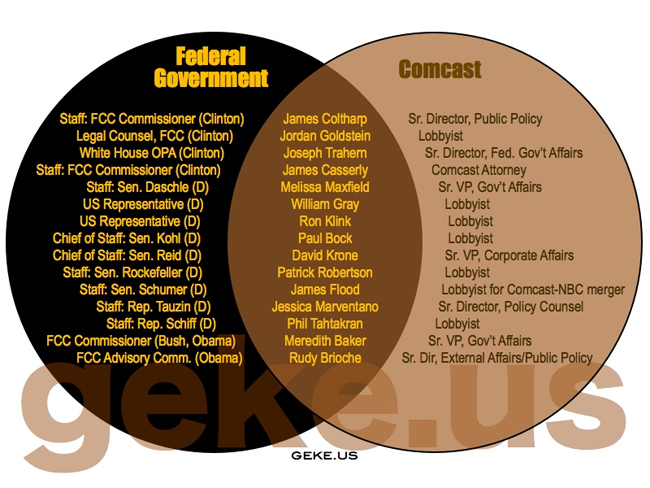
His organization, the Rootstrikers aim to get to the root of problems rather than being distracted by trying to fix symptoms of deeper problems. This is precisely what we do with our focus on community networks.
Many focus solely on resolving digital divide issues, improving rural access to the Internet, lowering the cost of broadband, or the various other problems that result from narrowly-focused private corporations owning and controlling essential communications infrastructure with inadequate regulations.
Reforming this system is a deep, seemingly intractable problem. But for those looking for answers, a good place to start is with the work of Lawrence Lessig. I just finished his Republic, Lost, which offers a grand tour of the problems resulting from the present system of campaign finance.
You can also see a number of his presentations here.
His organization, the Rootstrikers aim to get to the root of problems rather than being distracted by trying to fix symptoms of deeper problems. This is precisely what we do with our focus on community networks.
Many focus solely on resolving digital divide issues, improving rural access to the Internet, lowering the cost of broadband, or the various other problems that result from narrowly-focused private corporations owning and controlling essential communications infrastructure with inadequate regulations. As you read this, remember that the FCC's National Broadband Plan largely places the future of Internet access in the hands of these corporations.
As you read this, remember that the FCC's National Broadband Plan largely places the future of Internet access in the hands of these corporations.In 1889, Statesville, N.C., opted for self-reliance by building its own municipal power system after failing to attract an investor-owned utility. Half a century later, said Bowen, most American farms still lacked electricity, so Congress passed the Rural Electrification Act of 1936 to help finance nonprofit rural electric cooperatives. In the 1980s, Morganton, N.C. opted for self-reliance by expanding its municipal power system to offer cable TV, after years of complaints – including the 1982 blackout of the UNC-Georgetown national championship game – about its commercial cable provider. Bowen cautioned that corporate interests often oppose local communities which “self provision” critical infrastructure. Morganton’s commercial cable-TV provider sued the city to block its cable venture. Only in 1993, after a decade-long legal battle, did Morganton win the right to self-provision cable TV. Today, Morganton’s municipal cable system offers broadband Internet access at competitive rates and with no contract.Unfortunately, the North Carolina Legislature has made it much harder for local governments to build the necessary networks (as a favor to Time Warner Cable, which just happened to have given massively to many of the candidates). But Wally has an answer -- nonprofit approaches that have been inspired by rural electric cooperatives. MAIN is making important investments in western North Carolina and should be recognized as making a difference in a region the private sector has largely abandoned.
