
Fast, affordable Internet access for all.

In June, Indiana’s Hendricks Power Cooperative and Endeavor Communications Cooperative announced that they will be partnering to expand fiber optic connectivity in west central Indiana. Endeavor will provide gigabit Internet and voice services over Hendricks's fiber optic network, bringing broadband to more than 5,000 households within the next four years.
Members Want It
According to the June press release, growth in Hendricks, Putnam, and Montgomery Counties have left businesses and residences in need of high-quality connectivity. The region is outside the Indianapolis metro and growing. Because it has been historically rural, large corporate Internet access companies have not made the same investments they’ve made in urban areas.
From the Hendricks Power press release:
“Our members and community leaders greatly expressed the need for access to high-speed Internet,” said Greg Ternet, CEO of Hendricks Power Cooperative. “Combining the resources of these two cooperative-based businesses will allow us to bring fiber-based technological services in a quicker and more efficient fashion. Joint investments by Hendricks Power and Endeavor Communications will help our community grow in terms of quality of life and economic development.”
Endeavor has been serving rural Indiana communities for around 65 years and began deploying fiber in 2006; they completed fiber deployment in 2016 in nine service exchange areas. With several awards under their belt at the state and national level, and ample experience at communications in rural environments, they seem a natural fit for another rural cooperative, such as Hendricks Power.
Hendricks began like many other electric cooperatives in the 1930s — with rural members working together to get power to their homes and farms. The co-op was formed in 1936 when the local utility, which was owned by private interests, would not expand out where population was sparse. Hendricks Power Cooperative now serves more than 30,000 members.
Getting A Gig
Across the country, state legislatures are ushering in better rural connectivity by passing new laws that enable electric cooperatives to expand high-quality Internet access. In recent years, much of this legislation has authorized co-ops to deploy broadband infrastructure along existing electric easements. Other bills have removed restrictions that previously prevented electric co-ops from providing Internet access. Together, the new legislation makes it easier for electric cooperatives to bring high-speed broadband access to their members, signaling a brighter future for unconnected rural communities
Indiana in the Lead
Indiana’s state legislature was ahead of the curve when it passed SB 478, the Facilitating Internet Broadband Rural Expansion (FIBRE) Act back in 2017. The FIBRE Act permits electric cooperatives to use easements for their electric poles to also deploy broadband networks. Before the General Assembly passed this legislation, cooperatives that wanted to install communications infrastructure, such as fiber optic lines, along their electric easements would have to gain permission from each individual landowner to attach fiber to the existing poles.
Since the passage of the FIBRE Act two years ago, a number of Indiana electric cooperatives have embarked on broadband projects, including Jackson County Rural Electric Membership Corporation (REMC), South Central Indiana REMC, Orange County REMC, and Tipmont REMC. At the announcement event for South Central Indiana REMC’s fiber project, State Senator Eric Koch, author of SB 478, noted that state legislation like the FIBRE Act was enabling electric cooperatives to expand modern connectivity to rural Indiana.
State Laws Advance Co-op Broadband
The lakes and forests of Aitkin County in northern Minnesota make it an ideal location for a vacation home, but poor connectivity has historically limited days spent at the cabin to weekends and holidays. However, a new partnership between Mille Lacs Energy Cooperative (MLEC) and Consolidated Telecommunications Company (CTC) is making it possible for families to extend their trips up north by connecting lakeside cabins with high-speed Internet access.
The two co-ops are working together to build a Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) network, XStream Fiber, that will bring fast, reliable broadband access to homes and businesses in MLEC's service territory. MLEC hopes that the improved connectivity will benefit the local economy by encouraging seasonal residents, who make up more than 40 percent of the cooperative's membership, to stay in the region for longer.
Partnership Lands State Grant
According to Stacy Cluff, Technology and Energy Services Manager at MLEC, the electric cooperative had been exploring its options for offering high-speed broadband access for a decade. But it wasn’t until 2016 when MLEC began working with CTC, which had previously partnered with Arrowhead Electric Cooperative on a broadband project, that the XStream Fiber network became a reality.
CTC’s role in the partnership is to provide network connectivity, Internet backhaul, and backend support while MLEC manages billing, marketing, and other subscriber services. The cooperatives coordinate technical support calls, with MLEC handling basic issues itself and pushing higher level problems to CTC. The electric co-op owns all of the fiber infrastructure within its service territory.
Since 2011, PCMag has collected speed data and written about the country’s Fastest ISPs based on download and upload results. This year’s results reflect, once again, that locations with publicly owned broadband infrastructure contribute to communities’ ability to offer faster connectivity.
How They Did It
PCMag asked readers to use a special speed test developed specifically for this reporting that measured download and upload speeds. PCMag's Speed Index assigned to each ISP represented 80 percent download speed and 20 percent upload speed. Filtering out non-U.S. tests, they ended up with 256,016 tests that applied to the comparisons. If, however, a location (for state and regional comparisons) or ISP had fewer than 100 tests, the folks at PCMag did not consider it a contender.
While editors further broke down results so as to stack major ISPs against each other in a head-to-head comparison, they also looked at all the results in a general comparison. PCMag broke down the results further by region and city. For more details on the results, check out the full article.
Munis New and Not-So-New
FairlawnGig in Ohio made the list this year, adding a third municipal Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) network to the list. The city’s retail service began serving residents with gigabit connectivity back in 2017, after firmly establishing their fiber services for local businesses.
When contemplating the investment, city leaders adopted the approach that their fiber optic network would be an essential piece of infrastructure on par with sewers or roads. Fairlawn used municipal bonds with no intention of turning a profit; they considered the network an investment that would keep the Akron suburb competitive. Residents, businesses, and institutions in Fairlawn, however, have enthusastically signed up for fast, reliable, connectivity where residents can get gigabit Internet access for $75 per month.
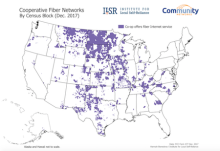
Decades after bringing electricity and telephone services to America’s rural households, cooperatives are tackling a new challenge: the rural digital divide. New updates to our report Cooperatives Fiberize Rural America: A Trusted Model for the Internet Era, originally published in 2017, illustrate the remarkable progress co-ops have made in deploying fiber optic Internet access across the country.
Download the updated report [PDF] here.
All versions of the report can be accessed from the Reports Archive for this report.
The report features new maps showing overall growth in areas served by co-ops, as well as expanded information about state legislation that supports co-op investment in broadband networks. A few important takeaways:
More than 140 co-ops across the country now offer residential gigabit Internet access to their members, reaching more than 300 communities.
Co-ops connect 70.8 percent of North Dakota and 47.7 percent of South Dakota landmass to fiber, and residents enjoy some of the fastest Internet access speeds in the nation.
Georgia and Mississippi have overturned state laws banning co-ops from offering Internet access, and other states, including Colorado, Maryland, North Carolina, and Texas, have implemented legislation that will further ease the way.
Co-ops have proven that this is a model that works. With increased support from federal and state governments, they will continue to connect rural Americans to economic and educational opportunities otherwise denied to them.
Read Cooperatives Fiberize Rural America: A Trusted Model For The Internet Era [PDF] here.
Decades after bringing electricity and telephone services to America’s rural households, cooperatives are tackling a new challenge: the rural digital divide. New updates to our report Cooperatives Fiberize Rural America: A Trusted Model for the Internet Era, originally published in 2017, illustrate the remarkable progress co-ops have made in deploying fiber optic Internet access across the country.
“Cooperatives should be the foundation for bringing high-quality Internet service to rural America... Small towns and farming communities need robust Internet service to support their local economies, educate themselves, and generally improve their quality of life. Cooperatives have quietly proved that they can build Fiber-to-the-Home networks that are capable of speeds of greater than 1 Gigabit per second (1,000 Mbps). More than 140 cooperatives offer gigabit service to residents or businesses.”
The report features new maps showing overall growth in areas served by co-ops, as well as expanded information about state legislation that supports co-op investment in broadband networks. A few important takeaways:
Co-ops have proven that this is a model that works. With increased support from federal and state governments, they will continue to connect rural Americans to economic and educational opportunities otherwise denied to them.
As data changes, we stay current so you can get the most recent information. It's important to be up-to-date, but seeing how broadband and related issues have changed over time also has value. As we release new versions of our report, Cooperatives Fiberize Rural America: A Trusted Model for the Internet Era [pdf], with updated information we’ll connect you with prior publications here.
Decades after bringing electricity and telephone services to America’s rural households, cooperatives are tackling a new challenge: the rural digital divide. This report explains why co-ops are a model that works for rural areas, and features:
Links on this page will take you to original and current publications of the report.

The Central Virginia Electric Cooperative (CVEC) announced in January 2018 that they had solidified plans to deploy fiber across 14 counties for smart grid operations and to bring Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) to the region. The project, dubbed Firefly Fiber Broadband, is underway, and we’ve got President and CEO Gary Wood along with Communications and Member Services Manager Melissa Gay on the podcast this week to discuss the multi-year project.
During this interview, we learn about the CVEC service territory, which is a mix of a few denser populated areas and very rural communities where poor Internet access, when it’s available, is a real problem. CVEC members have been dealing with unreliable connections, oversubscription, and outdated technologies for years. Those problems will be eliminated, however, with FTTH from the co-op that many have come to trust. By obtaining grants, working with local communities, and approaching the process in a strategic manner, CVEC plans on bringing gigabit connections to about 37,000 potential subscribers within five years.
Gary and Melissa describe the cooperative’s process, the discoveries they made about attitudes toward the co-op from members in the community (including some interesting stories), and lessons learned. We hear about some of their marketing approaches that focus on the uniqueness of the region and what it was like to establish a subsidiary in accordance with state law. Through all the hard work, Melissa and Gary have nothing but accolades for employees of the cooperative and compliments for local officials who helped get the project off to a strong start.
Learn more about the status of project from CVEC.
This show is 40 minutes long and can be played on this page or via Apple Podcasts or the tool of your choice using this feed.
Transcript below.
We want your feedback and suggestions for the show-please e-mail us or leave a comment below.
Listen to other episodes here or view all episodes in our index. See other podcasts from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance here.
Thanks to Arne Huseby for the music. The song is Warm Duck Shuffle and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (3.0) license.
Legislative changes are helping electric cooperatives continue to expand high-quality Internet access in rural parts of America. At least three state governments have bills in the works that empower cooperatives to provide high-speed Internet service in their service territories.
Georgia, Maryland, Alabama
Georgia Governor Brian Kemp recently signed into law SB 2 and SB 17, which clarify that both electric and telephone cooperatives are able to provide broadband service. This change allows the electric cooperatives to use their easements which have been used for electric service to extend those easements so they also apply to equipment and lines needed in order to supply broadband service. Electric cooperatives have already been at work on providing Internet service in Georgia: Habersham Electric Cooperative operates Trailwave Network, and the Pineland Telephone and Jefferson Energy Cooperatives have partnered to bring Internet service to their communities.
In Maryland, Governor Larry Hogan has just approved SB 634 which similarly underscores how electric cooperatives can use their easements to provide broadband. Meanwhile in Alabama, HB 400 will codify in existing law that electric cooperatives have the ability to offer broadband service and that their easements are valid for that use. Alabama HB 400 has passed in the House and is now working its way through the Senate. Alabama cooperatives North Alabama Electric and Tom Bigbee Electric already provides high-speed Internet service in their service territories.
Cooperatives Bring New Tech to Rural Areas
Cooperatives are building the next-generation networks that will support rural areas long into the future. We’ve covered this extensively at ILSR as we have gathered materials on community networks from across the country into one place. We want to share this fact sheet from National Rural Electric Cooperatives Association (NRECA) on how electric cooperatives are well-situated to bring high-speed Internet service to another 6.3 million households.
6.3 Million Households Have a Co-op, But No Broadband
The fact sheet features an insightful map of the areas within electric cooperative service territories that do and do not have broadband. (Note: The FCC defines broadband as a speed of at least 25 Mbps download and 3 Mbps upload.) Many telephone and electric cooperatives can take the credit for bringing needed connectivity to their communities. For example, more than 90 electric cooperatives across the U.S. have built Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) networks, which offer some of the fastest Internet service in the country.
The NRECA fact sheet, however, reveals the 6.3 million households in rural electric cooperative service areas that still need high-speed Internet access. These areas are primarily in the Midwest and the South. Creating pathways for electric cooperatives to extend Internet service is increasingly a priority in a number of these states, and state legislatures are now passing laws to empower both electric and telephone cooperatives. NRECA offers more policy recommendations to continue the momentum.
You can learn more about the ways rural cooperatives are bringing better connectivity to rural areas by reading our 2017 report, Cooperatives Fiberize Rural America: A Trusted Model For The Internet Era.
Check out the NRECA fact sheet, and drop us a line if you know of more resources to add to the ILSR’s Community Networks Initiative archives.