
Fast, affordable Internet access for all.

National ISPs with millions of customers are some of the most hated companies in the U.S. Poor customer service, contract tricks, and a refusal to upgrade services are only a few of the common complaints from subscribers who are often trapped due to lack of competition. Frontier Communications is proudly carrying on that tradition of deficiency in Minnesota. In fact, the company’s excellence at skullduggery has drawn the attention of the state’s Public Utilities Commission (PUC), which launched an investigation into the service quality of Frontier this spring.
So Much Going On Here
While many of us are used to some level of poor service when it comes to the big ISPs, Frontier in Minnesota accumulated so many complaints, the PUC felt they had no choice but to take action. According to Phil Dampier from Stop the Cap!, the Commission received 439 complaints and negative comments in a five-week period in early 2018. Some but not all, of the types of issues that subscribers described included:
Over the past year, towns in rural areas of Maine have mobilized and are taking steps to improve local connectivity. The latest is the community of Penobscot, where the local Broadband Committee recently released a Request for Information (RFI) to seek out firms interested in helping them bring broadband to the coastal community. Responses are due by July 11, 2018.
Design and (Perhaps) Implementation
Primarily, the Committee seeks to find a firm interested in providing engineering design. Penobscot clearly states that their goal is to bring symmetrical service to every premise, that speeds are consistent and reliable, and that they expect to see proposals suggesting speeds higher than the FCC’s 25/3 broadband standard.
Like many of the smaller towns in rural Maine and elsewhere, Penobscot isn’t jumping at the chance to operate their own fiber optic network. They're hoping that respondents will be ISPs interested in also operating the network and offering services via the infrastructure.
Goals for Penobscot
According to the RFI, many of the 1,200 year-round residents support themselves with home-based businesses, one of the many sectors that require faster upload speeds for day-to-day operations. In addition to craft and artisans, seasonal businesses cater to tourists that visit each year. People in Penobscot feel that it’s time to take steps to attract younger families to keep the community alive and thriving and Penobscot understands that broadband is a priority for their target demographic. They also want to convince seasonal visitors to stay longer or relocate and free public Wi-Fi is a priority.
If you have fast, affordable, reliable Internet access, there’s a good chance you don’t live in rural America. With the exception of areas served by local municipal networks, cooperatives, and a few small independent ISPs, businesses and residents in rural areas suffer along with aging, slow, and often expensive connections. In a docu-series by Maria L. Smith, titled “Dividing Lines,” viewers get the opportunity to hear firsthand what it’s like for people who live in places where there is no high-quality connectivity.
The docu-series uses the situation in Tennessee to focus on how big corporate ISPs like AT&T, Comcast, and Charter, heavily influenced the state legislature to revoke local telecom authority. The state is still subsidizing the big incumbents, but their not keeping their promises for better connectivity in rural Tennessee.
Smith describes her project and its purpose:
The online world is no longer a distinct world. It is an extension of our social, economic, and political lives. Internet access, however, is still a luxury good. Millions of Americans have been priced out of, or entirely excluded from, the reach of modern internet networks. Maria Smith, an affiliate of the Berkman Klein Center for Internet & Society and Harvard Law School, created Dividing Lines to highlight these stark divides, uncover the complex web of political and economic forces behind them, and challenge audiences to imagine a future in which quality internet access is as ubiquitous as electricity.
This four-part series is being deployed by organizations and community leaders across the country, from San Francisco to Nashville to Washington, DC, in an effort to educate stakeholders and catalyze policymaking that elevates the interests of the people over the interests of a handful of corporations.
Watch the trailer:
If you are interested in hosting a screening of the capstone video, email Smith@DividingLines.org
Visit the website for a second trailer and to learn more.
Approximately 20 U.S. states have some form of legal restriction that creates barriers when local communities want to develop publicly owned Internet infrastructure. In North Carolina, where the state experiences a severe rural/urban digital divide, people are fed up with poor service from influential telephone and cable companies. Folks like Ned Barnett, Opinion Editor from the News & Observer, are calling on elected officials to remove the state’s restriction so local governments can do all they can for better connectivity.
Things Must Change
Barnett’s recent editorial begins out of frustration as he describes how unreliable Internet access forced him to take pen to paper. His own connection prevented him from tending to emails, doing online research, and his phone service also suffered due to momentary loss of connectivity at his office. He goes on to consider how the annoying but temporary inconvenience to him is a way of life for many in rural areas of his state.
While North Carolina has many of the same challenges as other states in getting rural folks online — lack of interest from national ISPs, challenging geography that complicates deployment — Barnett correctly zeroes in on the state’s restrictive HB 129. The law prevents communities with existing broadband infrastructure from expanding to neighboring communities and puts requirements in place that are so onerous, they make it all but impossible for communities considering similar investments to move forward.
Barnett rightly points out that the true purpose of the law was to protect national ISPs from competition, securing their position as monopolies and duopolies. He describes the problems with the state's approach and what North Carolinians have faced in the aftermath:
For one, Internet access isn't a consumer product. It's as basic as access to a phone, electricity or indoor plumbing. Secondly, there isn't any real competition involved. Rural areas often are limited to one provider offering slow access.
The Problem is Real
The Rocky Mountains are beautiful, but they make Internet access difficult -- that’s the long and short of our research on Colorado. While community networks are making some headway in providing much needed connectivity, much of the state still may only have access to fixed wireless or Satellite service.
Internet Service by Technology
We investigated Internet access in Colorado using the Federal Communication Commission's (FCC) Form 477 data. Many of the most rural areas of the state do not have any form of Internet access other than satellite or fixed wireless services. For our analysis, we exclusively looked into wireline Internet service because it is less weather-dependent than satellite or fixed wireless. We added county subdivisions onto our map to help readers differentiate between more urban and predominantly rural areas.
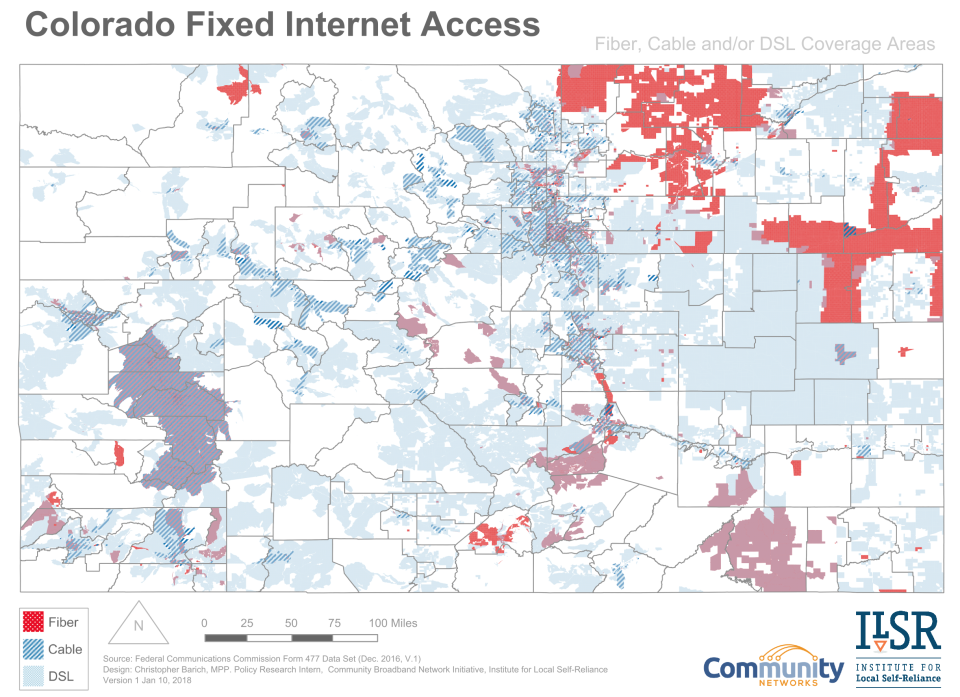
Broadband Service
That map, however, shows only Internet service availability across the state; it does not show broadband service. The FCC redefined broadband as 25 Mbps download and 3 Mbps upload in 2015. Earlier definitions of broadband included speeds as low as 4 Mbps download and 1 Mbps upload.
DSL service, while widely available, often cannot support this latest definition of broadband. It relies on copper telephone lines, and the actual speeds customers experience are often not as fast as advertised, "up to" speeds. Cable can provide broadband speed, but its actual speed can vary in times of peak traffic, such as the early evening. Fiber is the most reliable form of Internet service. In some communities, fiber networks are providing speeds of 10 Gbps (400 times the speed of broadband).
Looking at the Community Network Map, anyone can see that Iowa is filled with towns that have chosen to invest in publicly owned Internet infrastructure. On May 1st, the community of Pella took a step at the polls that will bring them a little closer to having a "pin" on our map. Ninety-two percent of those voting in the special election chose to authorize the City Council to establish a telecommunications utility.
Approval to Move Ahead
The election results don't establish a timeline for construction or operation of a fiber network or authorize any funding, simply allow city leaders to take the initial steps at forming the utility in the future. The city already operates its own municipal electric utility, so they have the same advantage of many other rural Iowa communities that go on to deploy fiber networks. At a March 12 City Council meeting, elected official unanimously approved the resolution to hold the election. From the minutes of the meeting:
The need for a municipal telecommunications utility is being driven by concerns expressed by citizens and businesses regarding access to highspeed Internet. Furthermore, a municipal telecommunications utility could help meet the long-term high-speed internet access needs of our citizens and businesses.
It is also important to note that many rural communities across Iowa have either formed municipal telecommunications utilities, or are in the process of forming the utility. The reasons these communities have authorized the formation of a municipal telecommunications utility are similar to the reasons the City of Pella is considering this issue.
At the Institute for Local Self-Reliance, we analyze data and explore public policies to empower local communities. Our initiative staff work on varied issues from composting to broadband, but all these issues affect our daily lives and our communities. In the Community Broadband Networks Initiative, we often analyze high-speed Internet service availability using the best data that is publicly available. Some of this data, however, is inaccurate, outdated, and misconstrued.
FCC Form 477 Fails in at Least Four Ways
The most common source of this data is the Form 477. It is designed to be standard, uniform, and provide the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) with detailed information to make sound decisions. The FCC distributes form 477 to Internet Service Providers (ISPs) in order to collect data on their service availability. This form is only accessible online through a government web portal, and it has an accompanying 39-page instruction document. Some of the information is confidential and stripped away before the FCC releases the data to the general public.
The FCC Form 477 may not accurately reflect broadband availability in four main ways:
1). ISPs may fill out the form improperly. Some ISPs may misplace key information into the form, creating havoc for those analyzing the data. They may input numbers in Kbps instead of Mbps, causing further confusion. For example, a fixed wireless ISP outside of Rochester, Minnesota, offers a maximum speed of 10 Mbps on their website, but the FCC Form 477 states that this ISP advertises a speed of 244 Mbps. Perhaps the ISP meant customers can usually expect a maximum speed of 244 Kbps? Even then, that doesn’t make sense.
2). The data is out of date. ISPs submit the form twice a year, but the FCC takes time to process this data. By the time we produce maps and research, the underlying data may already be too old to be useful. Mergers may not yet be adequately reflected. For example, at this writing in May 2018 the most recent data currently available is from December 2016. That means the data, the maps, and the research are about a year and a half out of date.
There are often common characteristics among communities that have invested in fiber optic infrastructure. While many of them can't get the connectivity they need from the incumbents or lack reliable Internet access, many begin their ventures into better broadband by connecting utility facilities. A new nonprofit, the Post Road Foundation, sees a valuable link between intelligent infrastructure, high-quality connectivity, and sustainability. By bringing together members of the public and private sectors, the Post Road Foundation is implementing an innovative approach to funding. With support from the Rockefeller Foundation, they've selected five partners to begin implementing their new approach to funding, connectivity, and sustainability.
Bringing It All Together
Co-founders of the Post Road Foundation, Waide Warner and Seth Hoedl, have decades of experience between them in law, policy, and leadership. Their areas of expertise span cyberlaw, government and finance, environmental law and policy, electricity, telecommunications and energy law and policy, nuclear physics, and the list goes on. Through their years of research and in consulting with both public and private entities, Warner and Hoedl both saw that many rural communities needed better connectivity for economic development, better quality of life, and to keep populations strong. They've also found that if local communities or cooperatives are able to use fiber optics to synergize multiple utilities, the community is resilient and more self-reliant.
Nestled along the south eastern border of Maine are Baileyville and Calais. As rural communities situated next to Canada in the state's "Downeast" region, neither town is on a list of infrastructure upgrades from incumbents. With an aging population, a need to consider their economic future, and no hope of help from big national ISPs, Baileyville and Calais are joining forces and developing their own publicly owned broadband utility.
Baileyville and Calais
There are about 3,000 residents in Calais (pronounced "Kal-iss") and 1,500 in Baileyville, but according to Julie Jordan, Director of Downeast Economic Development Corporation (DEDC), many of those residents are aging and younger people find little reason to stay or relocate in Washington County. The community recognizes that they need to draw in new industries and jobs that will attract young families to keep the towns from fading off the map.
Most of the residents in the region must rely on slow DSL from Consolidated Communications (formerly FairPoint), while a few have access to cable from Spectrum (formerly Time Warner Cable); expensive and unreliable satellite is also an option and there's some limited fixed wireless coverage in the area. A few larger businesses that require fiber optic connectivity can find a way to have it installed, but Julie tells us that it's incredibly expensive in the area and most can't afford the high rates for fiber.
Economic Development Driven
 Organized in 2015, the nonprofit DEDC came together with the focus on recruiting new businesses to the area and to support existing businesses. As DEDC quickly discovered, unless the region could offer high-speed, reliable Internet infrastructure, attracting new businesses and helping existing businesses expand would be extremely difficult. They also determined that new families would not be interested in Baileyville or Calais without high-quality connectivity. "It was a no-brainer," says Julie, "you have to go fiber."
Organized in 2015, the nonprofit DEDC came together with the focus on recruiting new businesses to the area and to support existing businesses. As DEDC quickly discovered, unless the region could offer high-speed, reliable Internet infrastructure, attracting new businesses and helping existing businesses expand would be extremely difficult. They also determined that new families would not be interested in Baileyville or Calais without high-quality connectivity. "It was a no-brainer," says Julie, "you have to go fiber."
Internet access isn't effective when it takes forever to load a single webpage or when subscribers spend hours babysitting their computers to ensure files make it through the upload process. At the Institute for Local Self-Reliance, we create maps analyzing publicly available data to show disparities in access and highlight possible solutions. We've recently taken an in-depth look at Georgia and want to share our findings with two revealing maps. According to the FCC's 2018 Broadband Deployment Report, 29.1 percent of the state's rural population lacks broadband access, but only 3 percent of the urban population shares the same problem. Cooperatives and small municipal networks are making a difference in several of these rural communities.
Technology Disparities Across the State
The map below shows what kinds of technology Internet Service Providers (ISPs) are using to offer Internet service to homes or businesses in Georgia. To differentiate areas of the state, the lines represent the subdivisions within counties. Our analysis focuses on wireline technologies, specifically fiber, cable, and DSL. Satellite and fixed wireless services are too dependent on the weather and the terrain for our analysis.
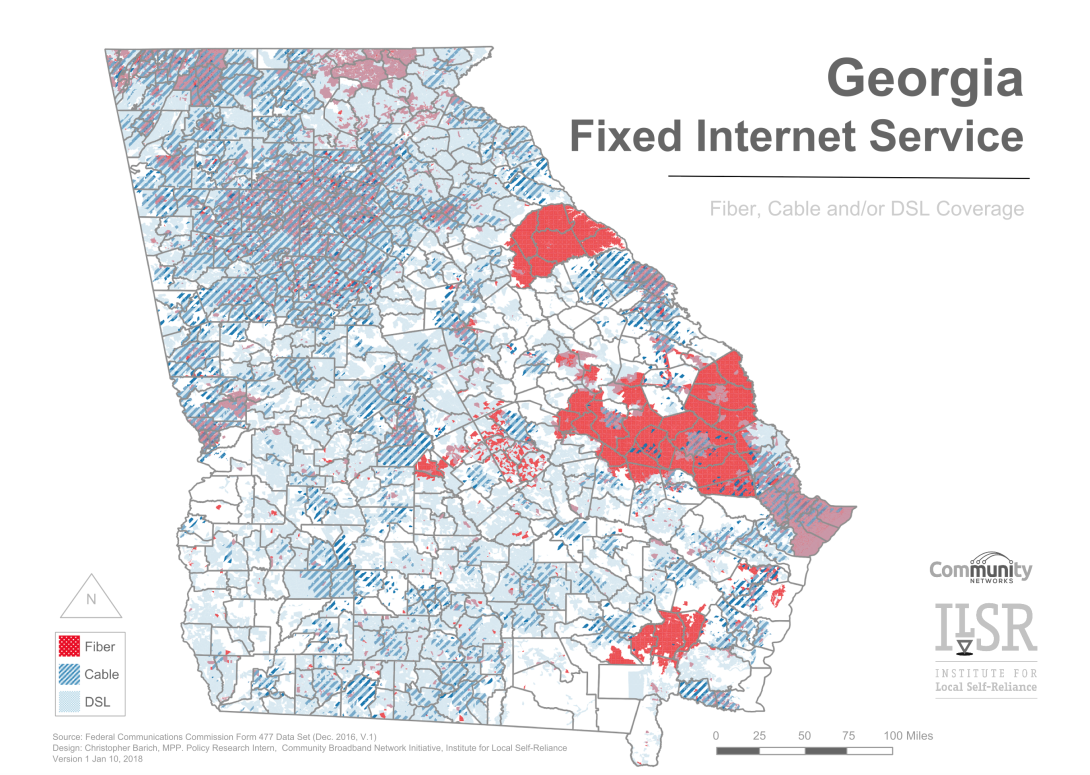
In rural Georgia, premises with wireline access most often rely on DSL; cable and fiber tend to be clustered around towns and cities where population density is higher. Google, for instance, operates a fiber network within Atlanta, Georgia. The large amount of fiber in the eastern half is the Planters Rural Telephone Cooperative, one of the many rural cooperatives that are taking steps to help rural communities obtain the access they need to keep pace with urban centers.