
Fast, affordable Internet access for all.

West Springfield residents recently gathered to break ground on a plan to deliver affordable fiber access to all 28,000 city residents. The effort, first conceived in 2021 during the height of the pandemic, involves working with Westfield Gas and Electric's broadband subsidiary Whip City Fiber to deliver symmetrical gigabit fiber.
Whip City only currently offers residential customers one tier of service: symmetrical gigabit fiber for $75 a month. A recent OpenVault report found that the percentage of subscribers on gigabit speed tiers grew 29 percent last year, with one-third of subscribers now provisioned for gigabit speeds. Whip City users can also access phone service for an additional $20 a month.
The first subscribers should be lit up for service by the end of this year, officials say. It’s the culmination of a project that began in 2019 when city officials first considered the construction of a city-owned broadband network; emboldened in 2020 after city leaders and locals alike became frustrated by Comcast’s implementation of technically unnecessary and punitive usage caps.

In 2021 West Springfield voted to establish a public utility department tasked with creating a town-owned fiber-optic cable network. They urged locals to sign up for a $1.5 million pilot program in four local neighborhoods, and submitted applications to Verizon and Eversource to ensure access to utility poles to begin “make ready” fiber attachment preparations.
Martinsville, Virginia has technically owned a municipal fiber network for the better part of a generation. But the city never had the time, resources, or interest in maximizing the Municipal Internet Network’s (MINet) full potential until COVID demonstrated the importance of affordable access and federal broadband grants made expansion a viable reality.
At a Martinsville city council meeting on February 13, the council offered unanimous support for a phased expansion of the city’s fiber network.
What exactly the expansion will look like, and how it will be funded, very much remain a work in progress.
The core MINet fiber network originally consisted of 48 strands and 20 miles of fiber connecting city schools, municipal buildings, local businesses, and key anchor institutions. A 2009 estimate indicates the network has saved the city between $100,000 and $150,000 annually on telecom lease agreements every year since its inception.
Despite having been first constructed in the 1990s, Martinsville’s MINet only has about 376 customers (98 of them being residential) in a city of nearly 14,000 residents. There’s roughly 20 users currently on a multi-month waiting list, eager to get access to affordable fiber at speeds up to a gigabit per second (Gbps).
Mike Scaffidi has been the MINet director for 26 years. He tells ILSR that while the city has contemplated network expansion for a long time, the city never had the staff or resources to prioritize the expansion or marketing of the city-owned fiber network.
A plan in Jamestown, New York to deploy affordable fiber to every last city resident has received welcome support from state leaders, even though deployment details remain murky and network construction remains well over the horizon.
In 2021, Jamestown officials told ILSR they were working with Entrypoint Networks on a $25 million fiber network for the city of 28,000. The city hopes to deliver fiber in conjunction with the Jamestown Board of Public Utilities, leaning heavily on the federal Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP) to ensure low cost access to marginalized and low income communities.

The city’s plans got a needed attention boost last month when Empire State Development – tasked with boosting economic development across New York State – gave a nod to Jamestown’s efforts in the organization’s five-year development plan.
The plan, among other things, will shape how the state utilizes $664 million in federal subsidies made possible by the Broadband Equity Access and Deployment (BEAD) Program and the 2021 infrastructure bill. While Jamestown may qualify for BEAD funding, how much the city’s project could receive remains undetermined.
New England residents have been complaining about Verizon’s lack of meaningful fiber upgrades for the better part of the last two decades, prompting a steady parade of interest in community owned and operated fiber networks in states like Massachusetts.
But some of these community broadband efforts, such as West Springfield’s plan to deliver affordable fiber access to every city resident, are still being hampered by Verizon.
In 2021 the city (est. pop. 28,000) announced it would be partnering with Westfield Gas and Electric, the publicly owned utility in Westfield, Massachusetts, which has built and operates fiber networks in nearly two dozen communities in the Berkshires. The end result: Westfield Gas and Electric's broadband subsidiary Whip City Fiber plans to deliver West Springfield residents symmetrical gigabit fiber for $75 a month, without long term contracts or onerous hidden fees.
But efforts to launch a $1.8 million pilot project have been on hold thanks to ongoing delays by Verizon and Eversource to prepare local utility poles for fiber attachment, West Springfield Chief Technology Officer Stephanie Straitiff tells local news outlet The Reminder.
The city of Scranton, Pennsylvania has issued a request for qualifications (RFQ) for vendors that may be tasked with constructing an affordable citywide fiber network. City leaders say the RFQ is the opening chapter in a bid to bring affordable broadband access to city residents long neglected by dominant regional monopolies.
According to the full RFQ, officials are looking for partner companies capable of building a citywide network capable of providing 1 Gbps (gigabit per second) download and upload speeds to all premises in the City of Scranton, as well as expanded fiber access for city municipal services and key anchor institutions.
“The City does not require municipal ownership of the fiber or a City operational role,” the RFQ states. “However, the City does request connectivity to certain City sites, a 40-year indefeasible right of use (IRU) for 12 strands of fiber for municipal noncommercial purposes throughout the network, and an access and maintenance agreement governing these strands.”
As with so many U.S. markets, broadband competition in Scranton is hard to come by. The market is largely dominated by either Comcast Xfinity or Verizon, the latter of which has been heavily criticized by unions and consumer groups for failing to uniformly upgrade its aging DSL network to fiber, and failing to repair aging lines on a timely basis.
This lack of meaningful competition results in slow broadband speeds, spotty coverage, substandard customer service, and significantly higher prices. Even then, the city hasn’t been without signs of life in the marketplace.
Syracuse officials have launched a new wireless community broadband network they hope will help bring affordable broadband access to the city of 145,000.
Dubbed Surge Link, the effort is backed by more than $3.5 million in federal funding and aims to deliver free broadband access to the city’s lowest income neighborhoods.
Motivated by peak pandemic connectivity headaches, Syracuse put out a request for proposal (RFP) late last year. The city then hired US Ignite as an advisor, and selected Geneva-based Community Broadband Networks (no relation to our program here at ILSR) to build a fixed wireless network capable of delivering discounted access starting with 2,500 underserved Syracuse households.
City officials tell ILSR the network is using Fixed Wireless Access technology, specifically Citizens Broadband Radio Service (CBRS), which is an emerging technology a growing number of municipalities and other nonprofit community groups have been experimenting with as a way to bring broadband to unserved and underserved residents in dense settings. And while CBRS has promise, as US Ignite notes, “because the technology is relatively new, the hardware and software associated with CBRS networks is also new. Vendors may still be working out the kinks in their solutions, particularly if those solutions are being used in novel ways, or need to interface with other older systems.”
It should also be noted that another New York community (Westchester County) embraced CBRS, only to find that it could not deliver the capacity they wanted to many people who needed the service.
With the Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP) poised to run out of funding in early Q2 next year, and no funding source lined up to keep the program alive, a recent U.S. News & World Report survey underscores the significance of the program in the face of rising prices from the nation’s major Internet Service Providers (ISPs).
The ACP offers a monthly benefit of $30 dollars for qualifying households and $75 for qualifying households on Tribal lands (as well as in some remote areas). Over 20 million Americans to date have enrolled in the program to help pay their Internet service bills, but with the $14.2 billion ACP program on track to run dry as soon as May of next year – even amid a historic national effort to establish “Internet For All” – the affordability crisis has become more worrisome for a growing number of Americans.
U.S. News & World Report’s survey found that Internet prices are going up and that families are compromising other expenses to pay for connectivity, affirming the urgency among digital equity advocates to identify a source of continued funding for ACP, as well as push for more structural solutions that address the root causes of why Americans pay among the highest prices for broadband service in the developed world.
In this week’s round-up of broadband news, we culled three stories we think are worth reading.
How Much is Fast Enough?
The first is a story from Ars Technica – FCC chair: Speed standard of 25Mbps down, 3Mbps up isn’t good enough anymore – written by veteran IT reporter Jon Brodkin.
For years now, broadband-for-all advocates have lamented the FCC’s minimum broadband speed standard of 25 Megabits per second (Mbps) download and 3 Mbps upload as being laughably antiquated. Indeed, it’s been almost three years since we made the case for Why 25/3 Broadband Is Not Sufficient, though it was outdated long before then.
But as Brodkin reported this week, the FCC’s minimum speed standard “could finally change under Chairwoman Jessica Rosenworcel, who is proposing a fixed broadband standard of 100Mbps downloads and 20Mbps uploads along with a goal of bringing affordable service at those speeds to all Americans.”
Under Rosenworcel’s plan, the FCC would look at availability, speeds, and prices to determine whether the agency should take regulatory actions under Section 706 of the Telecommunications Act, which requires the FCC to determine if high-speed Internet access is being deployed "on a reasonable and timely basis" to all Americans.
In Cambridge, Massachusetts, digital equity advocates and city leaders have been debating the idea of building a citywide municipal fiber network for years now, mostly over whether the estimated $150 to $200 million it would cost to build the network would be worth it.
In a tech-savvy city, home to Harvard and MIT, the former city manager was resistant to a serious inquiry into municipal broadband. He retired last summer. But before he left, he relented on the broadband question – under pressure from city councilors and a local citizen group advocating for municipal broadband, Upgrade Cambridge.

With many residents weary of being held hostage to the whims and high cost of service from the monopoly provider in town (Comcast), which currently controls 80 percent of the city’s market, in 2021 the city hired the well-regarded Maryland-based consulting firm CTC Technology & Energy to conduct a thorough feasibility study. Now, with a new supportive city manager in office, city leaders have agreed to continue to investigate the options laid out in the recently published study.
‘Significant Public Support’ Even If It Requires Tax Money
After decades of frustration, Block Island residents are finally getting access to affordable, next-generation broadband. The Island’s freshly-launched BroadbandBI fiber network is not only utterly transformative for island residents, it’s the first municipal owned and operated broadband network in Rhode Island history.
The first wave of island residents were able to sign up for service in April; the beginning of a staggered deployment rollout island leaders say is very much on schedule. It’s a monumental occasion for the 1,410 island residents spread across nearly ten square miles, who’ll be holding a June 5 event at the island’s Southeast Lighthouse to celebrate the long-awaited launch.
For years, island residents have had to make due with an underwhelming combination of spotty and aging Verizon DSL, or costly and heavily capped satellite broadband—assuming they could get broadband service at all. Private providers generally didn’t see investing in the island community as something worth their time or money.
Running 'A Bit Ahead'
Enter the Town of New Shoreham’s municipal broadband effort: an organic response to market failure, built on the backs of decades of frustration. A network that’s both on budget and on schedule, New Shoreham Land and Finance Director Amy Lewis told ILSR.
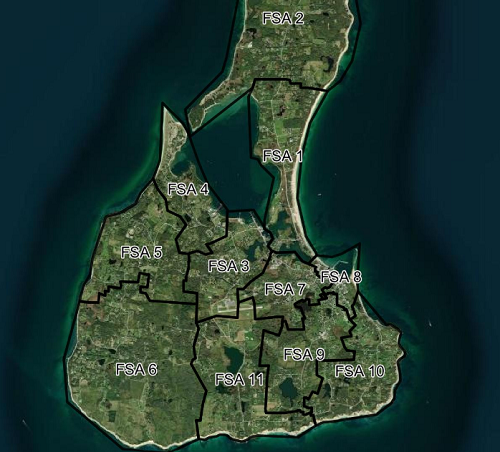
“We are running a bit ahead on FSA (fiber service area) openings at the moment and expect to have all subscribers installed and operational in the fall of 2023,” Lewis said.