
Fast, affordable Internet access for all.


This week on the show, Christopher is joined by Stacy Evans, Chief Broadband and Technology Officer at BrightRidge, the municipal network for Johnson City, Tennessee. When last we spoke, the electric utility-powered network had just passed its first dozen homes. Three and a half years later, the municipal network has passed more than 10,000 premises. It returns more than $5 million per year to local goverment via payments in lieu of taxes (PILOT) (not to mention keeping electric prices low), and has driven both of the incumbent providers to increase speeds and lower prices. Christopher and Stacy talk about the value that's returned to the region, and how BrightRidge is only gaining steam - it's two years ahead of its build schedule, and using grants and Rescue Plan funds to reach thousands of households not accounted for in the original design, ensuring that as many people will get access to affordable, locally owned fiber as quickly as possible.
This show is 32 minutes long and can be played on this page or via Apple Podcasts or the tool of your choice using this feed.
Transcript below.
We want your feedback and suggestions for the show-please e-mail us or leave a comment below.
Listen to other episodes here or view all episodes in our index. See other podcasts from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance here.
Thanks to Arne Huseby for the music. The song is Warm Duck Shuffle and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (3.0) license.
In November, the Federal Communication Commission (FCC) unveiled its new Broadband Availability Map.
Along with a new map style, the FCC also introduced a challenge process that allows everyone – from governments to citizens – the ability to highlight false claims of availability and ensure that every home and business location is accounted for in the map.
With good reason, many are confused about the information shown in the map, the challenge process, and why we should care about helping the FCC make corrections.
While we too are frustrated about the cost and subsequent quality of this map, we believe it is important to contribute to improving this map to enable an equitable allocation of the $42 billion in Broadband Equity, Access, and Deployment (BEAD) Program funds to states next year.
Step-By-Step Guide
In an effort to provide a better understanding of the map itself, and the challenge process, we created a short series of instructional videos and a click-through guide. Through the videos we provide:
In a release today, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) announced it was voiding applications by two of the biggest Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) bidders from December 2020. This includes more than $885 million for Low-Earth Orbit (LEO) provider Starlink and more than $1.3 billion for LTD Broadband, Inc.
LTD’s original winning bids are spread across 15 states, but there has been speculation brewing since late last year from industry experts as to if funds would be released at all. We’ve seen 12 releases from the FCC since late winter authorizing funds for most of the winning bidders (from the monopoly providers to consortia of rural electric cooperatives), which we’ve collected in our Rural Digital Opportunity Fund Dashboard here. Conversely, there has been relatively little conversation about why Starlink had not yet received any of its winning bids.
Skepticism about Speed, Deployment and Cost
The National Digital Inclusion Alliance's (NDIA) expanded National Digital Navigator Corps is running its first round of awards, and will support new projects at 18 sites around the country (including six in Tribal communities) beginning in the second half of this year.
The deadline to apply via Letter of Intent is this Friday at 11:59pm, via this form. Applicants are asked to put together a 200-400 word summary of their project, including local needs, goals, potential impact, and any partners. More detailed instructions can be found here.
From, NDIA, a description of the program:
Digital navigators are trusted guides who assist community members in internet adoption and the use of computing devices. Digital navigators help demystify technology by providing one-on-one, ongoing assistance to connect residents to affordable internet, devices, technical skills, and application support.
NDIA will select 18 partner organizations in rural areas or that serve Tribal and Indigenous communities, with a minimum of six organizations that serve Tribal and Indigenous communities, to host a digital navigator program as part of the National Digital Navigator Corps. Selected grantees will be trusted community-based organizations or local agencies, which will include nonprofits, social service agencies, libraries, and Tribal governments.
Each applicant can apply for up to $389,000, representing a two-and-a-half-year commitment. The breakdown of those funds goes to everything from salary and benefits, to additional program management support, a device, data management, and indirect costs.
One bonus is that there is money for each new Digital Navigator set aside to attend the Net Inclusion conference during the second and third years of their tenure.
Applicants who submit Letters of Intent that pass the first round will be invited to submit full proposals by May 31, with winners notified at the end of July, and work beginning shortly thereafter.
Although we were initially concerned that certain language in New York’s proposed state budget would lock out municipal broadband projects from being able to capitalize on the federal funding bonanza contained in the American Rescue Plan Act and forthcoming money in the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, the bill that was ultimately signed into law by Gov. Kathy Hochul was amended and has some golden nuggets for municipal broadband.
The recently enacted $220 billion budget bill includes $1 billion for the state’s ConnectALL initiative, which Gov. Kathy Hochul’s office calls “the largest ever investment in New York's 21st century infrastructure (that) will leverage public and private investments to connect New Yorkers in rural and urban areas statewide to broadband and establish the first municipal broadband program of its kind in the nation.”
Cultivating a Municipal Broadband Ecosystem
In part MMM of the budget bill, it establishes a “municipal assistance program … to provide grant funding to municipalities, state and local authorities ... to plan and construct infrastructure necessary to provide broadband services.”
Municipal grant recipients, the bill says, will be required to build broadband infrastructure to “facilitate projects that, at a minimum, provide reliable Internet service with consistent speeds of at least 100 Megabits per second (Mbps) for download and at least 20 (Mbps) for upload.” That shouldn’t be a problem as most municipal broadband projects use fiber optics that can deliver far more than that.
How much of the ConnectALL money will be allocated for the municipal grant fund has not yet been determined. But, community broadband advocates should not lose sight of the significance of the broadband ecosystem that is being cultivated in conjunction with other parts of the budget bill.
With an unprecedented amount of federal funds to build broadband networks flowing into individual states, lawmakers in some states are doing the bidding of the big monopoly Internet Service Providers and potentially blowing a once-in-a-generation chance to invest in the locally-accountable infrastructure that offers the best chance to bridge the broadband gap for millions of families once and for all.
Two weeks ago we wrote about the anti-competition broadband legislation making its way through the State Legislatures in Illinois and New York as state lawmakers across the nation establish high-speed Internet grant programs.
That trend looks like it’s continuing in Michigan where Democratic Gov. Gretchen Whitmer and the state’s GOP-dominated Legislature recently reached a deal to pass a nearly $5 billion spending bill.
While the “Building Michigan Together Plan” is being “celebrated” by the governor’s office as a way to “grow the economy, create jobs, and benefit families in every region of the state,” the main supplemental spending bill, known as Senate Bill 565 (SB 565), may sink some hope community broadband advocates have for leveraging the windfall of federal funds the Great Lakes State is getting from the American Rescue Plan Act (ARPA) and the forthcoming funds in the Infrastructure Investment & Jobs Act (IIJA).
Protecting Incumbents from Competition
A recently announced $610,000 grant award from the Tennessee Valley Authority to a partnership in Chattanooga, Tennessee will fund a pilot project to fund a set of holistic interventions in the Orchard Knob neighborhood to create healthier, more cost-efficient, better-connected homes for 1,000 residents.
The initiative, driven by a coalition made up of the Enterprise Center, EPB Fiber, Parkridge Health System, Habitat for Humanity, Tech Goes Home, and the Orchard Knob Neighborhood Association, aims to tackling an array of social determinants of health all at once. From The Chattanoogan:
Together, the partners plan to simultaneously invest in infrastructure and test new strategies for improving social determinants of health and quality of life of residents within a historically underserved neighborhood. Ultimately, the program in Orchard Knob will serve as a model for other communities across the Tennessee Valley.

It's happening as a result of funds contributed by the TVA's Connected Communities initiative, which aims to help "communities within the Valley leverage tech- and data-driven solutions to improve residents’ lives, deliver environmental benefits and scale economic opportunities." So far, these include projects like outfitting the Cheatham County School District with a solar array and battery backup, technology upgrades at more than a dozen Knoxville Recreation Centers, and improved connectivity at public housing sites in Murfreesboro.
Jefferson County, Washington’s Public Utility District (PUD) is just the latest to take advantage of a flood of new grants — and recently-eliminated restrictions on community broadband — to expand access to affordable fiber across the state.
Over the last few months, the PUD - situated northwest of Seattle, just across the Puget Sound - has been awarded more than $11 million in grants, including $1 million from the Washington State Public Works board, and another $9.7 million in Broadband Infrastructure Acceleration grants doled out by the Washington State Department of Commerce. The funds will help the PUD connect 2,600 homes in Gardiner, Quilcene, Cape George, Discovery Bay, and Marrowstone Island over the next two years.
Locally Operated Infrastructure, Affordable Prices, Fast Speeds
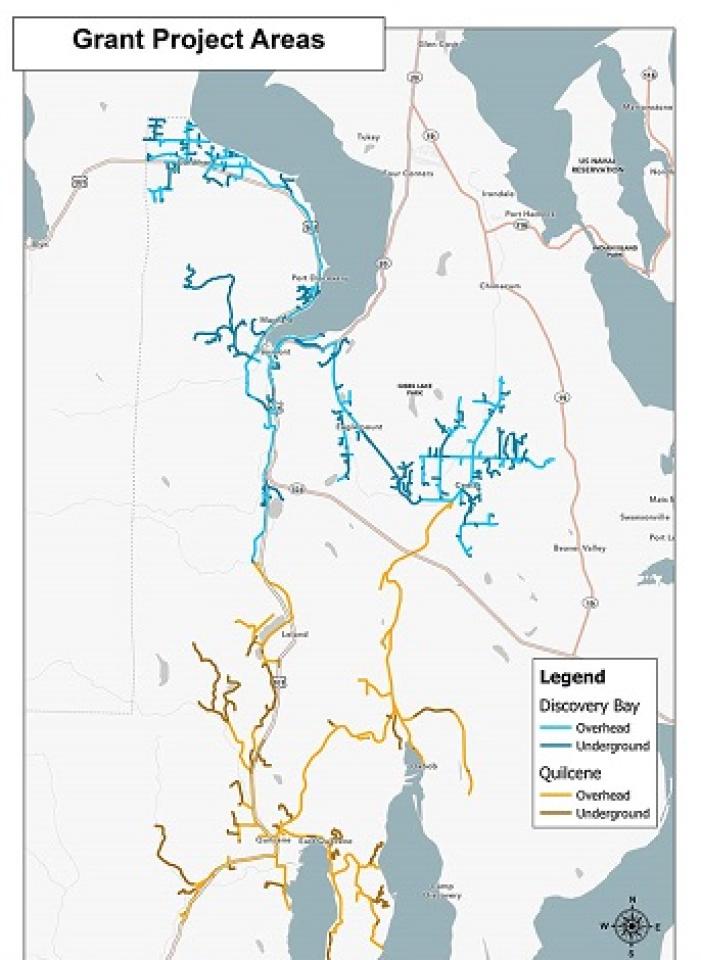
Construction is expected to start later in 2022, with the first subscribers to come online sometime in the first half of 2023. A project breakdown says they hope to provide basic speeds of 100 Megabits per second (Mbps) for $65 a month, and speeds of 1 Gigabit per second (Gbps) for $90 a month. The network will be open access, which means that additional ISPs (including, presumably, those currently offering service on the existing network) will be able to continue into the expanded areas.The PUD plans to offer a low-income tier for $45/month ($15 after the Affordable Connectivity Program subsidy), which is welcome to see.
Now that the fight over federal funding to expand broadband access has been largely settled with the passage of the American Rescue Plan Act (ARPA) and the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA), states and local communities are preparing to put those funds to work.
The Biden Administration had initially hoped to tip the scales in favor of building publicly-owned broadband networks as the best way to boost local (more affordable) Internet choice, and inject competition into a market dominated by monopoly incumbents. And while the Treasury rules on how Rescue Plan money can be spent does give states and local governments the ability to do just that, the rules for how the IIJA’s Broadband Equity, Access, and Deployment (BEAD) program can be spent have yet to be finalized by the National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA), the agency in charge of allocating those funds to the states.
Predictably, the big monopoly incumbents are focusing their lobbying efforts on state lawmakers as states funnel those federal funds into state broadband grant programs. In some states, Big Telco is getting the desired result: the shunning of publicly-owned network proposals to shield monopoly providers from competition. Of course, we expected some states – especially those with preemption laws that either erect barriers to municipal broadband or outright ban such networks – to shovel most of their federal broadband funds to the big incumbents, even though they have a long track record of over-promising and under-delivering.
But while we might expect Florida and Texas to favor the private sector and stealthily move to shut out projects that are publicly-owned, we’re surprised that the first place it’s happening is actually Illinois and New York.
Illinois Lawmakers Thumb Nose at Federal Law

This week on the podcast, Christopher is joined by Nancy Werner, General Counsel of the National Association of Telecommunications Officers and Advisors (NATOA). During the conversation, the two talk about NATOA and its role in supporting community broadband projects, how the Broadband Equity, Access and Deployment (BEAD) Act is structured, and how exactly BEAD grant money can be used. They also get into the nitty gritty of funding MDU deployment projects with BEAD money, and what priorities need to be considered to access those funds. The show ends with a discussion about the promise and shortcomings of taking a simplified approach to setting right of way and franchise fees.
This show is 30 minutes long and can be played on this page or via Apple Podcasts or the tool of your choice using this feed.
Transcript below.
We want your feedback and suggestions for the show-please e-mail us or leave a comment below.
Listen to other episodes here or view all episodes in our index. See other podcasts from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance here.
Thanks to Arne Huseby for the music. The song is Warm Duck Shuffle and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (3.0) license.