
Fast, affordable Internet access for all.

As our team continues to work with state and local community organizations across the country to help build digital skills and offer broadband educational resources, we came across this handy Broadband Basics Fact Sheet we wanted to share from the Queens at Queens University of Charlotte Center for Digital Equity (CDE).
In simple, accessible language, the two-page fact sheet from CDE explains commonly used words related to Internet access that are often not well-defined or understood outside of the tech industry.
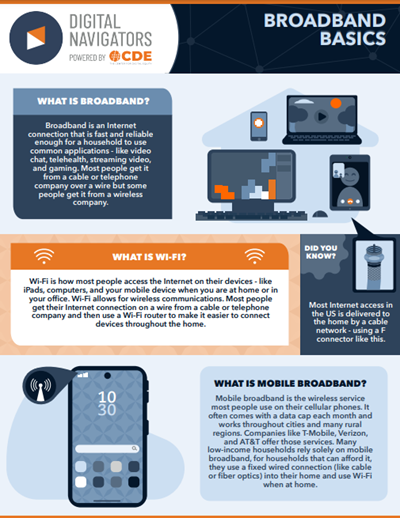
The fact sheet serves as a useful reminder that Internet access terminology itself can be a barrier to greater adoption, which is why we like CDE’s work here in answering the following questions:
The fact sheet can be found by clicking link below:
As the National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) continues to move forward in administering the single biggest federal investment to expand high-speed Internet access in U.S. history, each state and U.S. territory is wrestling with how to best spend the windfall as they lay out their Five Year Action Plans and Initial Proposals necessary to claim their portion of the $42.5 billion BEAD program.
One major barrier to providing universal access to fast, reliable and affordable Internet service–long recognized by ILSR, telecom experts, and a growing number of ordinary citizens–are the monopoly-friendly preemption laws that either outright ban or erect insurmountable barriers to building publicly-owned, locally-controlled broadband networks, aka municipal broadband.
Preemption in the BEAD Era
Currently, 17 states have such preemption laws, most of which have filed their Five Year Action Plans and/or their Initial Proposals. In each of those states, at the behest of Big Cable and Telecom incumbents, state lawmakers have erected legislative barriers to municipal broadband to protect the monopoly players from competition, which is at the very heart of why the digital divide exists in the first place and why tens of millions of Americans suffer from the slower speeds and higher costs that go hand in hand with monopoly service.

This week on the show, Christopher is joined once again by Sean Gonsalves, Associate Director for Communications for the Community Broadband Networks initiative at the Institute for Local Self-Reliance. After a short stop to talk about the establishment of a new municipal network in Timnath, Colorado, Christopher and Sean get down to talking about the BEAD 5-Year Plans that states are filing with NTIA to get their hands on the first tranche of what will be an historic pot of federal funds for new broadband investment.
Some states, like Maine and Vermont, Sean shares, are doing lots right: setting high bars for new infrastructure, listening to communities about their needs, folding in digital equity initiatives, and thinking about how to reach the last households that BEAD will fall short of. Others, like Pennsylvania, seem written with the intent to waste public money and leaves tens of thousands of households stranded with poor or no service - in other words, exactly what the monopoly cable and telephone companies want.
This show is 37 minutes long and can be played on this page or via Apple Podcasts or the tool of your choice using this feed.
Transcript below.
We want your feedback and suggestions for the show-please e-mail us or leave a comment below.
Listen to other episodes here or view all episodes in our index. See other podcasts from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance here.
Thanks to Arne Huseby for the music. The song is Warm Duck Shuffle and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (3.0) license.

May 2022 witnessed something remarkable: the birth of a new nonprofit advocacy organization whose sole purpose was to speak up for the hundreds of communities that have built municipal broadband networks, and the thousands more that want to but don't know where to start. Now, the American Association for Public Broadband has named as its Executive Director as Gigi Sohn, former Biden nominee to the Federal Communications Commission. And she's ready to get to work.
Gigi joins Christopher on the podcast this week to talk about standing up support systems to promote and defend community-driven models to double the number of municipal systems in the next five years - including providing resources and countering dark-money astroturf campaigns - while also making sure the Internet stays as open and equitable as possible, and not squandering the promise of BEAD.
This show is 46 minutes long and can be played on this page or via Apple Podcasts or the tool of your choice using this feed.
Transcript below.
We want your feedback and suggestions for the show-please e-mail us or leave a comment below.
Listen to other episodes here or view all episodes in our index. See other podcasts from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance here.
Thanks to Arne Huseby for the music. The song is Warm Duck Shuffle and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (3.0) license.
Historically, Enfield was known for its tobacco and peanuts. Today, there’s a new wave cresting in this small rural community in eastern North Carolina.
Thanks to a recent $350,000 investment from Connect Humanity, a start-up Internet service provider (ISP) – Wave 7 Communications – is now expanding its fledgling fixed wireless network to bring high-speed Internet service to nearly a quarter of the town’s 2,300 residents.
“This is in direct response to the need we identified,” Wave 7 CEO and Founder LaShawn Williamson told ILSR this week.
“We were finding customers who had Internet service before, but couldn’t pay the bill. We wanted to help people stay out of broadband debt," Williamson said. "There is an older population here and lots of industry has moved out of town so there is a challenge with poverty. But everyone deserves access to the Internet.”
Creating a Wave of Affordable Connectivity
Before Wave 7 came along, the choices were either SuddenLink, CenturyLink, or nothing. But, as Williamson explained, a number of residents were “paying a lot of money for a little bit of Internet and going into broadband debt.”
It was a recipe for financially-strapped households to be cut off from service and left on the wrong side of the digital divide.
Initially, Williamson wanted to launch Wave 7 in Greensboro where she lives with her husband. In 2018, a tornado hit the city. “The tornado tore through here and knocked out the Internet. It was taking a long time to get back up and running and even when they did the service was frustrating,” she recalled. “So I began to wonder what it would take to start our own Internet company.”
As voters went to the polls yesterday, broadband-focused initiatives and candidates could be found up and down the ballot all across the country.
Alabama
Alabama voters cast their ballots to decide on a state Constitutional amendment known as the Broadband Internet Infrastructure Funding Amendment. The measure sought to amend the state's constitution "to allow local governments to use funding provided for broadband internet infrastructure under the American Rescue Plan Act (ARPA) and award such funds to public or private entities."
That measure passed, garnering a “Yes” vote from nearly 80 percent of Alabama voters. With 73 percent of the vote counted late last night, 922,145 “Yes” votes had been tallied with 251,441 “No” votes.
Also in Alabama, Democratic U.S. Rep. Terri Sewell won her re-election bid to represent Alabama’s 7th congressional district. Sewell, whose district covers a large swath of the Alabama Black Belt, “spent much of her past two years in office bringing American Rescue Plan Act funds to rural Alabama, dedicated to healthcare, broadband access and infrastructure building,” as noted by The Montgomery Advertiser.
Colorado
The Centennial State is not listed as one of 17 states in the nation with preemption laws that erect barriers to municipal broadband because nearly every community that had a vote has passed it to nullify it. But more communities had to go through that unnecessary process yesterday due to the law known as SB-152 that bans local governments in the state from establishing municipal broadband service absent a referendum.
Welcome to In Our View. From time to time, we use this space to explore new ideas and share our thoughts on recent events playing out across the digital landscape, as well as take the opportunity to draw attention to important but neglected broadband-related issues.
As federal funds to expand high-speed Internet access began to flow to states and local communities through the American Rescue Plan Act, and with billions more coming under the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, Big Telecom is beginning to mount its expected opposition campaign designed to discourage federal (and state) decision-makers from prioritizing the building of publicly-owned networks.
Predictably, a centerpiece of this anti-municipal broadband campaign is the trotting out of well-worn - and thoroughly debunked - talking points, arguing that federal funding rules should not “encourage states to favor entities like non-profits and municipalities when choosing grant winners” because of their “well-documented propensity to fail at building and maintaining complex networks over time.” That’s what USTelecom, a trade organization representing big private Internet Service Providers (including the monopolies) wrote in a memo sent last week to President Biden, the FCC, cabinet secretaries, House and Senate members, Tribal leaders, as well as state broadband offices.
As you curl up by the fire this holiday season, we invite you to take the opportunity to watch (or rewatch!) a collection of excellent short films and documentaries that explore the challenges, obstacles, and success stories for communities all over the country looking to improve Internet access.
From Cullen Hoback's "Do Not Pass Go," chronicling the impact of monopoly power in Pinetops, North Carolina, to fun and informative tours of the community networks in Ammon, Idaho and Sandy, Oregon, to a short history of the birth of community broadband in the United States, there's something for everyone.
Check out the Fiber Film Festival collection here, and please share!

For episode 15 of our bonus series, “Why NC Broadband Matters,” Christopher Mitchell is joined by Catharine Rice (Co-founder of NC Broadband Matters and Project Manager at the Coalition for Local Internet Choice) and Doug Dawson (Owner and President of CCG Consulting) dig into what all these different pots of federal funding mean communities across the country. They talk about the communities that have already announced plans to use the funds for municipal networks. They offer advice and direct communities in the early stages of planning to resources on how to use the funds effectively.
This show is 38 minutes long and can be played on this page or via Apple Podcasts or the tool of your choice using this feed, or at the NC Broadband Matters page. We encourage you to check out other "Why NC Broadband Matters" content at the podcast feed so you don't miss future bonus content that may not appear in the Community Broadband Bits Podcast feed.
Transcript below.
We want your feedback and suggestions for the show-please e-mail us or leave a comment below.
Listen to other episodes here or view all episodes in our index. See other podcasts from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance here.
Thanks to Arne Huseby for the music. The song is Warm Duck Shuffle and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (3.0) license.
The Atlantic Telephone Membership Cooperative (ATMC) has worked to meet the communications needs of its members since its inception by the citizens of rural Brunswick County, North Carolina who were without telephone service in 1955. Nowadays, ATMC believes meeting members’ communications needs means ensuring all co-op members have access to gigabit fiber Internet service.
High-speed Internet access is currently available throughout 100 percent of the co-op’s service area in southeastern North Carolina. Most co-op members have access to fiber Internet service already, except for those living in ATMC’s Brunswick County service territory, where ATMC originally began offering Internet services.
Brunswick County is the last county ATMC needs to upgrade to fiber, in order to complete an overarching goal of delivering fiber-to-the-home Internet service to all existing members. The co-op recently announced it will soon start a project to replace all of its copper and coaxial wires in Brunswick County with fiber optic cables. It will cost $100 million dollars and take eight years to complete, but at the end of the project, all of the cooperative’s members in Brunswick County currently served by legacy infrastructure will be upgraded to fiber, offering even faster Internet access speeds and far greater reliability.
In the meantime, ATMC has increased the maximum broadband speed delivered to co-op members in Brunswick County from 200 megabits per second (Mbps) to 600 Mbps, a company press release states. Over 22,000 customers had their download speeds doubled without an increase in price.
“The project is slated to start in January 2022,” according to an ATMC press release announcing the project. “By constructing in the most densely populated communities first, the cooperative estimates that it can convert as many as 75 percent of homes and businesses to the new fiber optic network within the first 60 months.”