
Fast, affordable Internet access for all.

With the Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP) poised to run out of funding in early Q2 next year, and no funding source lined up to keep the program alive, a recent U.S. News & World Report survey underscores the significance of the program in the face of rising prices from the nation’s major Internet Service Providers (ISPs).
The ACP offers a monthly benefit of $30 dollars for qualifying households and $75 for qualifying households on Tribal lands (as well as in some remote areas). Over 20 million Americans to date have enrolled in the program to help pay their Internet service bills, but with the $14.2 billion ACP program on track to run dry as soon as May of next year – even amid a historic national effort to establish “Internet For All” – the affordability crisis has become more worrisome for a growing number of Americans.
U.S. News & World Report’s survey found that Internet prices are going up and that families are compromising other expenses to pay for connectivity, affirming the urgency among digital equity advocates to identify a source of continued funding for ACP, as well as push for more structural solutions that address the root causes of why Americans pay among the highest prices for broadband service in the developed world.
While a racially-charged controversy swirls loudly around the Los Angeles City Council, a new study lays bare how low-income communities of color are impacted by the quiet business decisions of the region’s monopoly Internet service provider.
Slower and More Expensive/Sounding the Alarm: Disparities in Advertised Pricing for Fast, Reliable Broadband details how Charter Spectrum “shows a clear and consistent pattern of the provider reserving its best offers - high speed at low cost - for the wealthiest neighborhoods in LA County.”
Authored by Digital Equity LA, a coalition of more than 40 community-based organizations, not only highlights how economically vulnerable households in LA County pay more for slower service than those in wealthy neighborhoods, it also provides evidence for how financially-strapped households are also saddled with onerous contracts and are rarely targeted by advertisements for Charter Spectrum’s low cost plans.
A leading voice behind the Digital Equity LA initiative – Shayna Englin, Director of the Digital Equity Initiative at the California Community Foundation (CCF) – notes that higher poverty neighborhoods (which tend to be mostly made up of people of color) pay anywhere from $10 to $40 more per month than mostly white, higher-income neighborhoods for the exact same service.
Two decades into the twenty-first century, it still feels a little strange to justify all of the obvious ways that Internet access serves as a key pillar among the social determinants of health (SDOH) that govern our individual and collective wellbeing. The concept itself is at least two hundred years old: a German pathologist named Rudolph Virchow is often quoted as saying in the late 1840s, in response to the privation he saw in the run-up to the 1848 revolutions, that “medicine is a social science and politics is nothing else but medicine on a large scale.”
Our modern framing of the problem comes in large part from the World Health Organization, which in the preamble to its 1946 constitution wrote that “health is a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity.” In 2020, the FCC has called broadband access a “super social determinant of health” in 2020, precisely because it serves as a gateway to all of the other elements of life that foster healthiness and wellbeing, from access to education, information, better food, economic opportunity, and socialization.
But a recent study published to the JAMA Open Network makes the connection even more explicit. In it, a team of researchers at The Center for Spatial Data Science at the University of Chicago show that a lack of Internet access has been strongly correlated with higher Covid-19 mortality rates across every type of household and in rural, suburban, and urban areas alike.
Internet Access Most Strongly Correlated with Covid-19 Mortality Rates
A month ago we announced the launch of Let's Broadband Together, a coalition of organizations and advocacy groups led by Consumer Reports to collect as many broadband bills as possible and crowdsource the data necessary to fight the trend towards deliberately confusing, obfuscatory broadband pricing in the United States.
If you've had the intention to help out but were looking for that reminder, here it is. Head over to Let's Broadband Together and take a speed tests, submit a PDF of your bill, and answer a few questions. More submissions mean a better the dataset and more comprehensive evidence to support reform.
Click here to begin, and join Consumer Reports, ILSR, and dozens of other organizations.
Internet access in the United States is among the most expensive in the world, both in terms of absolute prices and in cost-per-megabit. Millions of families around the country can't afford to get online, making them even more disconnected from social services, family, and friends, more economically vulnerable, increasingly bearing the burden of the homework gap, and less healthy.
All of this is a direct result of the broken broadband marketplace, dominated by just a few monopoly providers regularly raising prices to extract wealth from communities. It's also the result of an FCC which has consistently refused to mandate the submission of pricing data from Internet Service Providers (ISPs), or collect it from users themselves. Instead of investing in infrastructure upgrades or innovating, huge providers like Charter Spectrum, AT&T, Comcast, and Suddenlink have sunk time and energy into making our broadband bills harder to interpret, all while raising prices, changing plan terms, and playing around with data caps to pad their profits.
Let's change that, together.
The Institute for Local Self-Reliance is joining with Consumer Reports to collect bills from 30,000 households across diverse geographic and demographic backgrounds in an initiative called Let's Broadband Together.
Schools offer not only education, but nourishment, a place to form friendships and bonds, and a way to make sure youth are safe. When the pandemic hit, schools had to transition to distance learning and, as a result, many students disappeared because their family didn’t have access to or couldn’t afford a home Internet connection. It became immediately clear, all over the country, that a lack of broadband access and broadband affordability were no longer issues that could be ignored.
Many cities throughout the U.S. have been working over the last year to address this issue, but one city in particular - Columbus, Ohio - has been taking a holistic approach to broadband access.
The Franklin County Digital Equity Coalition was borne out of the emergency needs presented by the pandemic, but has shaped up to be a good model for how to address the broadband issues facing urban communities across the country.
After 11 months of meeting and planning, the coalition released a framework in March outlining its five pillars of focus: broadband affordability, device access, digital life skills and technical support, community response and collaboration, and advocacy for broadband funding and policy.
The coalition also developed two pilot programs to increase broadband access.
The first, which was a quickly deployed and desperately needed response to the lack of broadband access, was the Central Ohio Broadband Access Pilot Program. Launched in September 2020 in anticipation of the upcoming school year, it offered hotspot devices with unlimited data plans to central Ohio households with k-12 students. The program, while still growing, has been deployed with about 2,300 hotspots distributed so far with the help of PCs for People.
The second (the City of Columbus and Smart Columbus Pilot Projects) uses the city’s existing fiber backbone to bring affordable Internet service to the Near East and South Side neighborhoods in Columbus.
Both pilot programs are the result of nearly 30 organizations coming together to get affordable access to some of the city and county’s most vulnerable populations.
There’s Power in Numbers
For communities across the country considering whether to invest in building a municipal broadband network, a new study published last week on the economic value of the EPB fiber network in America’s first “gig city” is a must-read.
The independent study, conducted by Bento Lobo, Ph.D., head of the Department of Finance and Economics at the Rollins College of Business at the University of Tennessee at Chattanooga, found that the celebrated city-owned fiber network has delivered Chattanoogans a $2.69 billion return on investment in its first decade.
In 2010, EPB Fiber, a division of Chattanooga’s city-owned electric and telecommunications utility formerly known as the Electric Power Board of Chattanooga, became the first city in the United States to build a Fiber-To-The-Home (FTTH) network offering up to 1 Gig upload and download speeds. In 2015, EPB began offering up to 10 Gig speeds.
It cost approximately $220 million to build the network, however, “the true economic value of the fiber optic infrastructure for EPB’s customers is much greater than the cost of installing and maintaining the infrastructure,” Lobo said. “Our latest research findings show that Chattanooga’s fiber optic network provides additional value because it provides high speeds, with symmetrical uploads and downloads, and a high degree of network responsiveness which are necessary for the smart grid and other cutting-edge business, educational and research applications.”
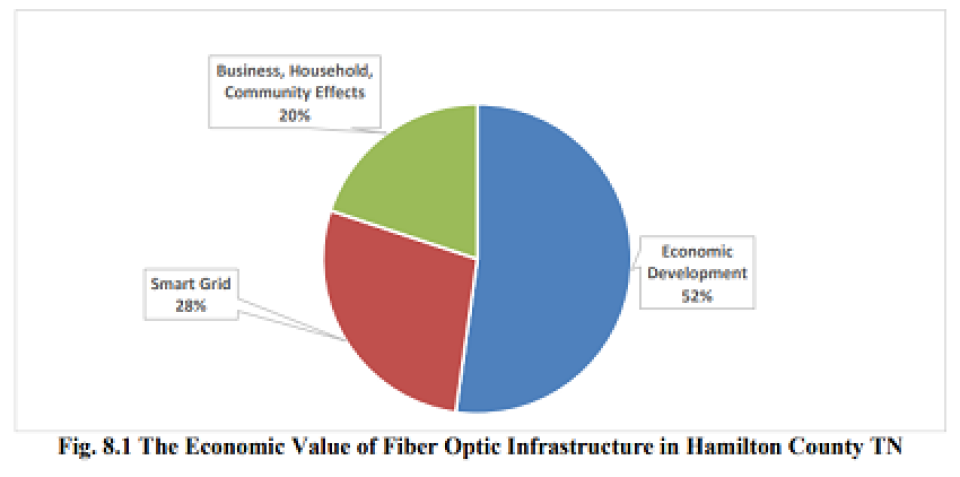
Among the study’s key findings:
A host of cities and counties in Arkansas are about to get a major broadband boost thanks to local officials taking steps to act on a grant program deployed by the state last year. Borne out of the state’s 2020 1st Extraordinary Session at the end of March 2020 in response to the Covid 19 pandemic, the new Rural Broadband I.D. Expenses Trust Fund Grant Program will disburse $2 million in funds divided into 30 one-time grants of $75,000 each to towns, cities, and counties to tackle the digital divide in the Toothpick State. The program is financed via Arkansas’ Restricted Reserve Fund with money given to the state by the CARES Act, and is administered by the University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences (UAMS) Institute for Digital Health & Innovation. And while an array of projects have been awarded funds, money remains available and applications are being accepted on a rolling basis for those who have yet to take advantage.
A Win for Local Self-Reliance and Increasing Competition
The program is expressly designed to bridge the gap for communities that want to begin to improve local Internet access but are stymied by a necessary first step: paying for those economic, design, and feasibility analyses which require pulling together the wide range of options available in the context of local conditions. That’s where this program comes in, according to Rachel Ott, the UAMS Institute’s for Digital Health and Innovation Grant Director. Communities can use the work produced to apply for federal grants down the road, including the recently concluded Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF), the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s ReConnect Program, funds from the Agriculture Improvement Act of 2018, and any other forthcoming federal funding programs.
Over the summer, Chicago Mayor Lori Lightfoot announced a new program to bring high-speed Internet service to the alarming number of households who do not have reliable access within the nation’s third-largest school district.
The initiative, referred to as Chicago Connected, aims to provide free high-speed Internet service to approximately 100,000 Chicago Public Schools (CPS) students. One of the ground-breaking features of the effort is that it includes funds to enlist the support of a number of Community Based Organizations to assist with enrollment in the program, digital literacy and skills development training.
At the end of September, during a virtual town hall meeting, Mayor Lightfoot said that while CPS was making progress connecting eligible families, they had not yet reached the goal.
“We’re not where we want it to be. And I think part of the difficulty is, even though it’s free, it’s about making sure that families feel safe in signing up,” Lightfoot said. “Currently, we have over 25,000 households that are signed up, and that is the equivalent of almost 38,000 students towards our goal of 60,000 households at 100,000 students.”
How It Works
Using a sponsored service model, Chicago Connected seeks to provide the high-speed connection for up to four years by directly paying for the service for eligible families. The program primarily relies on donations from philanthropic partners, CPS and city funds, with an additional $5 million from the CARES Act to fund the $50 million program. Donations, which includes a $750,000 commitment from former President Barack Obama and First Lady Michelle Obama, will cover the first two years, with CPS paying for the third and fourth years.
Along the banks of the Columbia River, Multnomah County (pop. 813,000), Oregon is considering a publicly owned Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) network after being handed a study more than a year in the making. The report estimates that a countywide network reaching every home, business, and farm in a five-city area would cost just shy of $970 million, and bring with it a wealth of savings and other benefits to the community it serves.
Origins
The study has its origins in a 2017 push initiated by an advocacy group called Municipal Broadband PDX which has sought more affordable and equitable Internet access in the region. In 2018, the County Board of Commissioners agreed that it should be explored and approved the funding of a study, with the city of Portland and Multnomah County each contributing $100,000 and the remaining towns of Fairview, Gresham, Troutdale, and Wood Village joining the effort to collectively contribute an additional $50,000 for funding. Over the next year, CTC Technology and Energy conducted a comprehensive survey, analysis, and evaluation, and the results were delivered at the end of September.
