
Fast, affordable Internet access for all.

Join us live this Thursday, October 14th at 5pm ET for Episode 22 of the Connect This! Show, where co-hosts Christopher and Travis Carter (USI Fiber) will be joined by Dennis Pappas (Longmont, Colorado) and Christy Batts (Clarksville, Tennessee) to talk about large municipalities successfully deploying broadband infrastructure for an array of community benefits.
Longmont, Colorado's Nextlight has been wildly successful during its first five years of life in uncommon ways. Clarksville, Tennessee's CDE Lightband has overcome early challenges to bring significant savings to the public, especially to members of the municipal electric utility. Christopher, Travis, Dennis, and Christy come together to unpack how they got there and what it means for the future.
Subscribe to the show using this feed, or visit ConnectThisShow.com
Email us broadband@muninetworks.org with feedback, ideas for the show, or your pictures of weird wireless infrastructure to stump Travis.
Watch here or below on YouTube Live, or via Facebook Live here.
Even before the central Florida city of Ocala in Marion County became officially known as “The Horse Capital of the World,” the city – home to 61,810 Floridians and over 1,200 county-wide horse farms – was already galloping toward high-speed Internet connectivity. In recent years, the Ocala Fiber Network (OFN) has expanded into offering residential service, trotting carefully towards a citywide fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) finish.
It began in 1995 with the Ocala municipal electric department upgrading its substation monitoring (SCADA) system, which has been estimated to have saved the city $25 million in networking costs since. Over the past two years, OFN has extended the network to bring affordable, reliable, high-speed Internet service to city residents, neighborhood by neighborhood.
While the municipal network has been providing high-speed Internet service for the past decade to area businesses, healthcare facilities, community anchor institutions, and schools throughout the county, OFN launched residential service in 2019 and is now serving 2,500 residential subscribers in four city neighborhoods.
“We did four pilot neighborhoods. Our target goal was to have a 30 percent take rate in each neighborhood. In the largest neighborhood (the Highlands neighborhood) with a thousand homes, we have a 42 percent take rate. We still have a challenge in one neighborhood (Happiness Homes) with about a 10 percent take rate that we think is mostly an educational challenge,” Ocala Fiber Network Director Mel Poole told us in a recent interview.
Hampton Roads, a metropolitan region bordering the Chesapeake Bay in southeastern Virginia, is known for its 17th century historical sites, shipyards crowded with naval aircraft carriers, and mile-long bridge tunnels. Home to 1.7 million Virginians, Hampton Roads is now looking to broaden avenues for economic development by leveraging existing transatlantic subsea broadband cables to transform the region into a technology-forward digital port. That’s why regional officials recently issued a Request for Proposal (RFP) seeking one or more private partner(s) to construct a regionally-owned 100-mile, open access fiber ring.
Private partners interested in responding to the RFP [pdf] must do so by August 24, 2021. Potential partners can decide to offer some or all of the project functions, choosing to: design, build, finance, operate, and/or maintain the regional fiber ring. (See instructions on how to respond to the RFP, as well as details on the selection process, under Section IV on Page 7.)
Five of the nine cities that make up the region colloquially referred to as “the 757” - Chesapeake, Norfolk, Portsmouth, Suffolk, and Virginia Beach - banded together to improve local fiber connectivity in 2018, forming the Southside Network Authority (the Authority).
According to the Authority's RFP, the project was undertaken to resolve the broadband issues faced by the cities, including:
a need for more and more affordable internal connectivity for governmental operations
equity and affordability concerns in general as compared to similar metropolitan areas
a perceived lack of responsiveness by incumbent providers to the needs of the business community and economic development prospects
a relative lack of broadband infrastructure by comparison to comparable metropolitan areas
and concerns about the security and scalability of existing, privately-owned regional networks
Regional Impacts
Since it was first introduced in Congress in March, the Community Broadband Act of 2021 has gained widespread support from over 45 organizations representing local governments, public utilities, racial equity groups, private industry, and citizen advocates.
The legislation -- introduced by U.S. Representatives Anna Eshoo, Jared Golden, and U.S. Senator Cory Booker -- would authorize local communities to build and maintain their own Internet infrastructure by prohibiting laws in 17 states that ban or limit the ability of state, regional, and local governments to build broadband networks and provide Internet services.
The Act also overturns state laws that restrict electric cooperatives' ability to provide Internet services, as well as laws that restrain public agencies from entering into public-private partnerships.
States have started to remove some long-standing barriers to public broadband on their own. In the last year, state lawmakers in both Arkansas and Washington removed significant barriers to municipal broadband networks, as high-quality Internet with upload speeds sufficient for remote work, distance learning, telehealth, and other online civic and cultural engagement has become essential.
Community broadband networks offer a path to connect the unconnected to next-generation networks. State barriers have contributed to the lack of competition in the broadband market and most communities will not soon gain access without public investments or, at the very least, the plausible threat of community broadband.
The Many Benefits of Publicly-Owned Networks
St. Louis Park (pop. 49,000), a suburb west of Minneapolis, Minnesota, has demonstrated commitment and creativity in bringing broadband access to the region over the last two decades. They’ve done so by connecting community anchor institutions and school district buildings, in supporting ongoing infrastructure via a dig once policy, by working with developers to pre-wire buildings with gigabit-or-better-capable connections, and by using simple, easy-to-understand contracts to lease extra dark fiber to private Internet Service Providers (ISPs) to improve connectivity options for local residents.
Conversations about improving broadband in St. Louis Park began in the 1990s, when local government officials and the St. Louis Park School District began talking about replacing the aging copper infrastructure it was leasing from the cable and telephone companies with fiber to support educational use and municipal services. At the time the city was paying about $45,000/year to stay connected and online. A 2003 projection suggested it could invest $380,000 to build its own network instead, take ownership of its infrastructure, and see a full return on investment in less than a decade.
Fiber, both the city and the school district decided, offered the best path forward for the range of tools and bandwidth that would bring success. The school district led off in connecting its structures, but by 2004 both were done, with each contributing to joint maintenance and operational costs. The city thereafter decided to keep going and expand its infrastructure wherever it made the most sense. In 2006 it advanced this agenda by adopting a dig-once policy by adding conduit — and sometimes fiber — any time a street was slated for repairs.
Municipal Wi-Fi
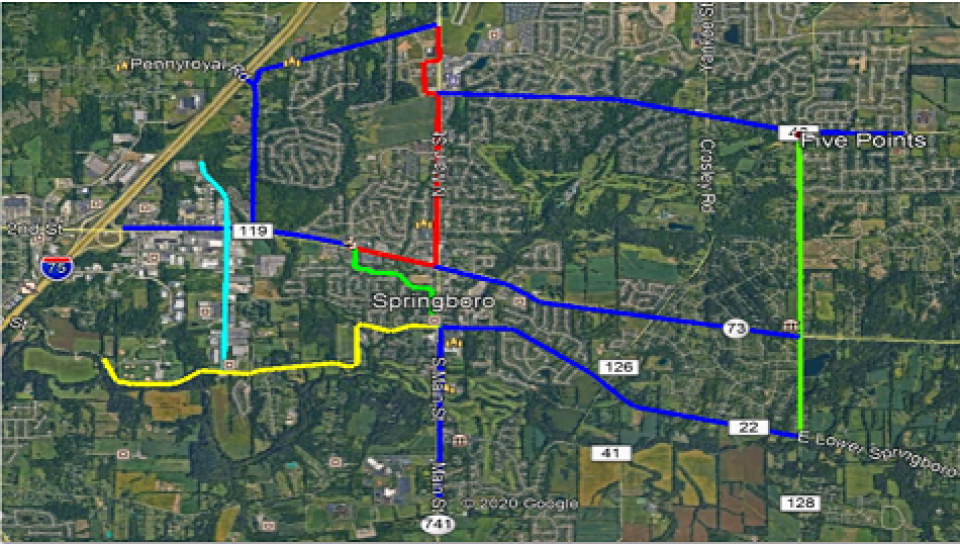
After years of fielding complaints from residents about the speed, reliability, and poor customer service of the city’s single wireline broadband provider, Springboro, Ohio (pop. 19,000) has decided enough is enough. Over the next year, the city (situated ten miles south of Dayton) will build a 23-mile fiber loop for municipal services and, at the same time, lay five additional conduits to entice additional Internet Service Providers (ISPs) to come in and offer service, stimulating competition and economic development in the region moving forward.
A Fiber Master Plan
City Manager Chris Pozzuto laid out the plan for the city council, which staff had been working on for the last half year, back in July. It was driven in part by the criticism his office had fielded for years about the incumbent wireline service provider (the two satellite providers also prompted plenty of complaints of their own). Out of a desire both to provide residents with symmetrical gigabit access and stimulate economic development on a 200-acre commercial plot, Pozzuto started talking with regional partners and putting together an alterative.
The city’s Fiber Master Plan [pdf] calls for a 72-strand, 23-mile loop to be built around Springboro, along every major street and thoroughfare and up to the entrance of every neighborhood. Via microtrenching, six conduits will be laid — one for the city, and the remaining for up to five new ISPs to compete for service.
Janesville, Wisconsin (pop. 64,000) Information Technology Director Gordon LaChance has been investing in fiber infrastructure for city needs for the last 12 years, but he’s been hoping it would lead to something more. That day may have come, with the recent award of a $114,000 grant from Wisconsin Public Utility Commission.
The grant allows the city to participate in a public-private partnership that will bring fiber to a handful of unserved or underserved commercial locations in town. The move is the first of its kind for the city, and involves an exchange of capacity that will allow WIN Technologies — a private Internet Service Provider (ISP) — to bring service to two SHINE Medical Technology locations (a small headquarters downtown as well as a large, new development being built south of town), the Janesville Centennial Business Park, the Beloit Avenue Corridor Business Park, and the Janesville Innovation Center.
The grant application was spearheaded by the city’s Economic Development Office, which gathered the players and helped iron out the details. LaChance described how the deal would work in a phone interview. The city will give WIN access to some of its dark fiber, which WIN will make use of along with the grant funds and additional private investment to build south and connect those areas of town. In return, WIN will lay extra fiber as it goes and hand it over the LaChance’s office, allowing the city plant to expand in that direction when it otherwise would not be able to justify the cost. It remains early, but the city estimates that around a dozen businesses will be connected with the expansion. Better connectivity will also spur the revitalization of the Janesville Assembly Plant, a General Motors factory decommissioned in 2008 that is being turned around by a commercial developer to bring manufcaturing production and jobs back to the area.
The Fruits of Forethought

Whenever Christopher attends a Broadband Communities event, he returns with great stories from cities and towns across the U.S. that have invested in publicly owned Internet infrastructure. This week, we share his interview with Mel Poole, Ocala Fiber Network Director.
You may automatically think of Kentucky when you consider horses, but Ocala, Florida, is considered the "Horse Capital of the World." Fast thoroughbreds may end up at The Derby, but they often start in Ocala. Whether it's gigabits or galloping horses, Ocala has found a way to capitalize on the concept of speed.
The city first began with publicly owned fiber optic infrastructure for SCADA operations and later expanded their use to reduce telecommunications costs. Since ending leased T1 lines, the city has saved millions and taken control of connectivity. That was before Mel worked for the city, but he's well-versed in the story of the Ocala Fiber Network, and describes how they expanded to offer services to more sectors of the community.
Mel and Christopher talk about the city's decision to begin working with the public and how, by educating local decision makers, Mel and his team were able to help them make an informed choice. As Ocala worked with more entities, they've also faced challenges related to deployment and marketing. There's a fine line they need to walk between spreading the word about great service and their ability to connect subscribers in a timely fashion. Christopher and Mel talk about demographics, economic development, and Mel's vision for Ocala that's tied into their fiber optic infrastructure.
Read more about Ocala and the development of their network here.
This show is 26 minutes long and can be played on this page or via Apple Podcasts or the tool of your choice using this feed.
Transcript below.
We want your feedback and suggestions for the show-please e-mail us or leave a comment below.
Listen to other episodes here or view all episodes in our index. See other podcasts from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance here.
Thanks to Arne Huseby for the music. The song is Warm Duck Shuffle and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (3.0) license.
Hilliard, Ohio (pop. 36,000), is moving forward with plans to deploy a carrier neutral dark fiber network after city council approved funds for the project last month. The 25-mile fiber network will connect government buildings and businesses in the Columbus suburb and will be capable of speeds up to 100 Gigabits per second, reports Columbus Business First. Officials hope that improving Hilliard’s broadband infrastructure will help the community attract and retain businesses, encourage local economic development, and reduce municipal connectivity costs.
Deployment Details
During the first phase of the project, Hilliard will run fiber to municipal buildings and local businesses. The carrier neutral network will connect to the Metro Data Center in nearby Dublin, Ohio (home to DubLINK), giving the city government and businesses access to a wide selection of providers, who will have the ability to lease fiber from the city. In the future, the network could expand to serve other entities, such as local schools. The city does not plan to connect residents.
The total cost of the network’s initial phase is $3.17 million; to fund the fiber rollout, Hilliard City Council set aside $2.9 million in January as part of the city’s capital improvements budget. This included a $1.25 million loan from the Franklin County Infrastructure Bank, which has also invested in two similar projects, including Grove City. Hilliard Economic Development Director David Meadows said that the remainder of the funding comes from a conduit and traffic signal project that was approved in the city’s 2018 budget.
Economic Benefits for the City
Ocala, Florida, is one of those communities that doesn’t think twice about offering high-quality Internet access to businesses and residents. They’ve been doing it for decades and, when media coverage around gigabit connectivity began to expand, they were a little surprised because they had been offering similar services since the early 2000s. The benefits were nothing new to Ocala.
A Familiar Story Taken to Its Logical Conclusion
We touched based with Arnie Hersch, Senior Broadband Engineer for the City of Ocala, who shared the story of the network. Arnie has spent more time working on the network than anyone else in Ocala.
As in many other communities, Ocala started deploying fiber between its municipal utility facilities, including electric substations and water and wastewater locations, to improve inter-facility communications. In 1995, copper connected the city’s substations for SCADA operations. The copper was aged and had been struck by lightning, which negatively impacted its ability to perform; decision makers at the utility decided to replace the copper with fiber optic lines. As they finished deploying that year, Arnie joined the city's telecommunications utility; one of his primary objective was making the most out of the new fiber network.
First, Ocala connected all of its 52 municipal facilities in order to improve connectivity and cut costs. At the time, city offices still used dial-up connections for Internet access. Within two years, Arnie had switched the city to an Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM), which allowed them to use the new infrastructure for computing and voice applications. The change opened new doors for the city.