
Fast, affordable Internet access for all.

Fiber to the Home
It’s official. Falmouth, Massachusetts has established a legal framework, a telecommunications utility, that is a key milestone in a local effort to bring fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) Internet service to this seaside community of approximately 32,000 famous for being home to a world-class marine science community as well as a popular summer vacation destination.
In the fall, Town Meeting voters voted 175-13 for the creation of the utility called a Municipal Light Plant (MLP). The law, however, requires two separate ‘yes’ votes with a 2/3 majority within a 13-month period. That second vote came earlier this month, when Town Meeting voters said “yes” to establishing an MLP by a vote of 159 to 25, well in excess of the 2/3 majority that was needed.
It allows Falmouth to move to the next step – figuring out the financing – which would allow Falmouth to join the growing ranks of communities in the Bay State (and be the first of 15 Cape Cod towns) to have undertaken municipal broadband projects over the last several years.
Voters Reject Opposition Arguments
Though a small group of municipal broadband critics strenuously argued in opposition to the formation of an MLP by raising a number of thoroughly debunked claims about locally-owned networks, ultimately Town Meeting voters were more persuaded by the experiences of resident’s such as Marilois Snowman who owns a digital marketing agency in town.
Over the past eighteen months, southeastern-Mississippi based Dixie Electric Power Association (Dixie EPA) has gone from presenting its initial buildout plans for a fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) network, all the way to connecting its 5,000th subscriber. Because of electric cooperatives like Dixie that are getting organized and prioritizing connectivity for their members, Mississippi is likely to become one of the states with the best rural connectivity within the next five years.
Founded in 1938 in Laurel, Mississippi, Dixie EPA’s present-day coverage area stretches across southeastern Mississippi in parts of Covington, Jasper, Jones, Clarke, Wayne, Perry, and Forrest counties. The cooperative provides electric service to 30,000 premises.
In September 2020, about six months into the COVID-19 pandemic, Dixie began pre-registering subscribers for Internet service under the cooperative’s newly-created subsidiary, DE Fastlink. Dixie was part of a collective of electric cooperatives that had just received a recent state appropriation of $65 million in CARES Act funding for rural broadband deployment. The funding was administered under the Mississippi Electric Coop Broadband Covid Grant Program by Mississippi Public Utilities. Dixie planned to match in full its own $3.3 million award, which, according to the terms of the grant, had to be spent by the end of that year.
Last week, the Golden State Connectivity Authority (GSCA) announced it has entered into formal partnership with the municipally owned open access network UTOPIA Fiber, for the Utah-based owner and provider to design, build, and operate a new open access fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) network across the 38 rural counties in the state of California. It's a move that not only offers the chance to bring future-proof connections to millions of rural California households in the near future, but have wide policy and industry implications for open access fiber networks down the road.
Local Governments Band Together
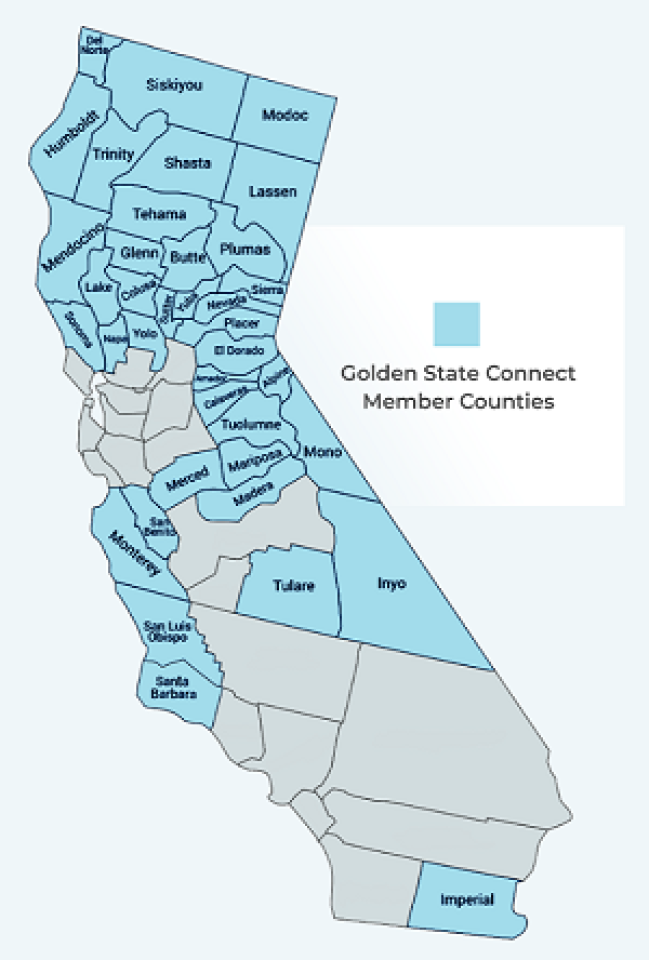
The Golden State Connectivity Authority is a joint powers authority (JPA) created by the Rural County Representatives of California (RCRC), which represents more than three dozen rural counties across the state. RCRC seeks to tackle the variety of shared problems that the state's rural communities face by advancing concrete policy solutions across transportation, energy, natural resources, governance, healthcare, and a collection of other arenas.
Although we were initially concerned that certain language in New York’s proposed state budget would lock out municipal broadband projects from being able to capitalize on the federal funding bonanza contained in the American Rescue Plan Act and forthcoming money in the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, the bill that was ultimately signed into law by Gov. Kathy Hochul was amended and has some golden nuggets for municipal broadband.
The recently enacted $220 billion budget bill includes $1 billion for the state’s ConnectALL initiative, which Gov. Kathy Hochul’s office calls “the largest ever investment in New York's 21st century infrastructure (that) will leverage public and private investments to connect New Yorkers in rural and urban areas statewide to broadband and establish the first municipal broadband program of its kind in the nation.”
Cultivating a Municipal Broadband Ecosystem
In part MMM of the budget bill, it establishes a “municipal assistance program … to provide grant funding to municipalities, state and local authorities ... to plan and construct infrastructure necessary to provide broadband services.”
Municipal grant recipients, the bill says, will be required to build broadband infrastructure to “facilitate projects that, at a minimum, provide reliable Internet service with consistent speeds of at least 100 Megabits per second (Mbps) for download and at least 20 (Mbps) for upload.” That shouldn’t be a problem as most municipal broadband projects use fiber optics that can deliver far more than that.
How much of the ConnectALL money will be allocated for the municipal grant fund has not yet been determined. But, community broadband advocates should not lose sight of the significance of the broadband ecosystem that is being cultivated in conjunction with other parts of the budget bill.
Last month, PCMag released its ranking of the best work-from-home (WFH) cities in the United States. On this year’s list, two of the cities in the Top 20 are Chattanooga, Tennessee and Longmont, Colorado – both of whom have municipal broadband networks that make those communities among the friendliest remote work locales in the nation.
As a remote-first media outlet itself, PCMag explains what should be obvious to anyone who hasn’t swallowed whole the propaganda of the Big Telecom lobby, which among other falsehoods claims that municipal broadband is simply too complicated for municipalities to build and operate, and is ultimately a financial boondoggle for taxpayers.
“The number-one requirement for a good work-from-home location is fast, reliable Internet access,” PCMag explains.
NextLight Catapults Longmont as Top WFH City
Launched in 2010, Chattanooga’s EPB Fiber network is a well-known and documented municipal broadband success story with independent analysis having shown that in its first 10 years of operation it has brought the city a $2.7 billion return-on-investment.
However, Longmont’s rising star on the municipal broadband stage (coming in at No. 17 on PCMag’s Best WFH list) is because, as aptly described by PCMag, the city is a “more affordable alternative to expensive Boulder, with 300 days of sunshine each year, a municipal fiber provider, and an easy drive to both Boulder and Denver.”
Jefferson County, Washington’s Public Utility District (PUD) is just the latest to take advantage of a flood of new grants — and recently-eliminated restrictions on community broadband — to expand access to affordable fiber across the state.
Over the last few months, the PUD - situated northwest of Seattle, just across the Puget Sound - has been awarded more than $11 million in grants, including $1 million from the Washington State Public Works board, and another $9.7 million in Broadband Infrastructure Acceleration grants doled out by the Washington State Department of Commerce. The funds will help the PUD connect 2,600 homes in Gardiner, Quilcene, Cape George, Discovery Bay, and Marrowstone Island over the next two years.
Locally Operated Infrastructure, Affordable Prices, Fast Speeds
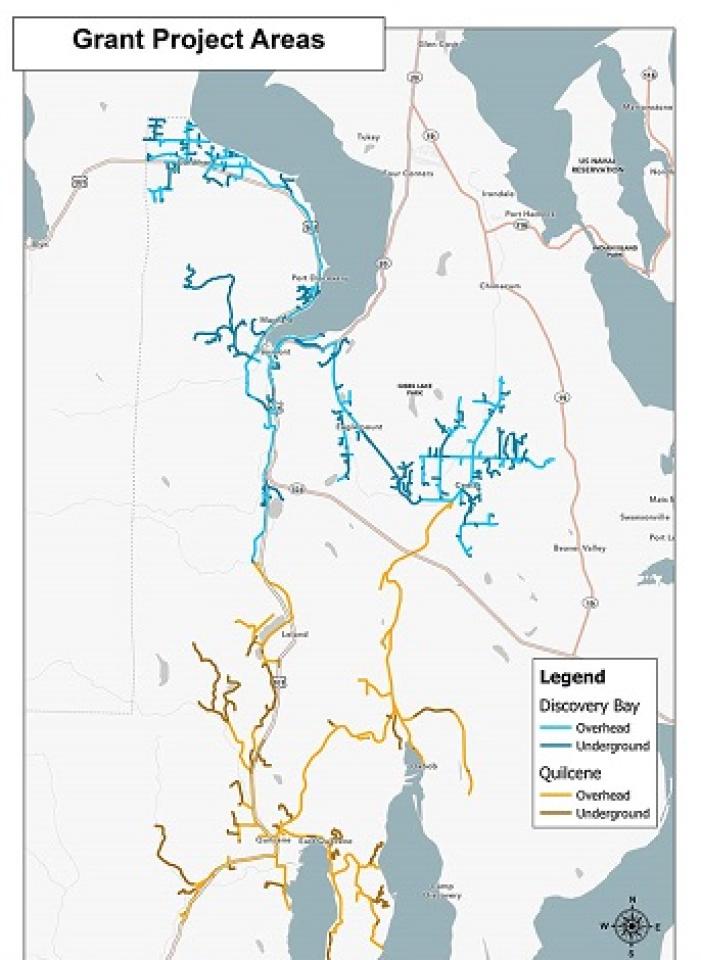
Construction is expected to start later in 2022, with the first subscribers to come online sometime in the first half of 2023. A project breakdown says they hope to provide basic speeds of 100 Megabits per second (Mbps) for $65 a month, and speeds of 1 Gigabit per second (Gbps) for $90 a month. The network will be open access, which means that additional ISPs (including, presumably, those currently offering service on the existing network) will be able to continue into the expanded areas.The PUD plans to offer a low-income tier for $45/month ($15 after the Affordable Connectivity Program subsidy), which is welcome to see.
Consultants working with the City of Mansfield – the seat of DeSoto Parish – are nearing completion of a comprehensive community assessment as the small northwest Louisiana community of about 4,500 is setting the table to build a municipal fiber network.
In October 2021, Mansfield’s five-member city council voted unanimously to hire Louisiana Connected to lead the study in partnership with Lit Communities. After the council vote, Mansfield Mayor John H. Mayweather, Sr. described the decision as the first step in establishing a public-private partnership to bring reliable and affordable high-speed Internet access to every household and business in the city.
In a press statement released after the October vote, Mayor Mayweather said:
Representatives of Louisiana Connected were allowed to make a presentation to the City Council at one of our meetings earlier this year regarding a consideration to build our own broadband system. After hearing the advantages of bringing such a network to Mansfield, we were on board then. And now after listening further, we are even more excited about this opportunity. This will be good for all the citizens of Mansfield.
Pandemic Push to Action
As with many communities around the county now considering building their own municipal broadband network, a major motivator for Mansfield was the number of students in this majority African-American city who struggled to participate in distance learning triggered by the pandemic.
In a press release after the vote to move forward with the community assessment, Mansfield parent LaKimberly Edwards spoke to the need for universal access to high-speed Internet connectivity.
Named for its iron-rich natural springs, Yellow Springs is a hip and diverse village of approximately 3,600 Central Ohioans that most recently made headlines because of the controversy over comedian and actor Dave Chappelle’s opposition to a housing development proposal in the hometown of its most famous resident.
While the Village Council ultimately sided with Chappelle and other resident opponents in scaling back the planned development, in January the council gave their unanimous support for a different project that promises to connect village residents.
The vote gave the green light to move forward with a plan to bring municipal fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) service that will offer more affordable and reliable high-speed Internet connectivity (and competition) in a market already served by AT&T and Spectrum about 30 minutes east of Dayton.
Last fall, as Yellow Springs pursued state grant funding, Village Manager Josué Salmerón told WHIO-TV they were moving forward because “we felt we needed to do this from a business perspective and a human rights perspective. There’s a problem when our folks couldn’t do the essential things. They couldn’t go to work online. They couldn’t go to school online, and they couldn’t visit their doctors online. That’s a problem we were trying to solve. That’s why we went down this path.”
Thinking Big, Starting Small
The plan is to start with a small pilot project by connecting to the fiber backbone of the Miami Valley Educational Computer Association (MVECA), which has been expanding a 44-mile fiber ring in the region, having built one of the country’s first multi-jurisdictional networks, the GATEWay Public Fiber Network.
This week, we bring you a special field report from Maryland-based radio and podcast producer Matt Purdy. Through interviews with citizens, digital equity advocates, and the city's new Director of Broadband and Digital Equity, Purdy documents the connectivity struggles that have persisted in Baltimore's historically marginalized neighborhoods for decades.
Those challenges have only become more pronounced with the pandemic, prompting local officials to begin making moves in the direction of something we've not yet seen in a community the size of Baltimore: building a city-owned, open access fiber network.
This is a great story, so we won't give anything else a way. Listen below, or here.
Pierce Pepin Electric Cooperative (PPEC), headquartered in Ellsworth, Wisconsin (pop. 3,300), announced in July of 2021 the start of a new phase of life, and the beginning of a fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) project that will connect its 6,800 members by 2025.
The $32 million-dollar project was begun at the end of last year. The move, powered by financial commitment from the cooperative but also state grants so far, will roughly double the cooperative’s physical plant assets, and ensure that member-owners will get fast, locally accountable broadband access for the lifetime of the infrastructure.
Bringing Service to Areas Ignored by Others
Incorporated in 1937, today PPEC serves the majority of Pierce County and parts of Buffalo, Pepin, and St. Croix counties just across the Minnesota-Wisconsin border, along the Mississippi River.
It operates almost 1,350 miles of electric lines, about half of which are overhead and half underground, with 12 substations scattered throughout its territory. The cooperative serves an average of 5.7 households per mile. More than 90 percent of its member-owners live on residential properties or farms, though it has 600 commercial and industrial accounts and also powers more than three dozen public authority cites.
The move towards broadband for PPEC, as with so many other electric cooperatives around the country, has been driven by dual forces: an internal push by member owners, and the lack of any evidence that outside providers will expand new infrastructure to the area anytime soon.