
Fast, affordable Internet access for all.

When a $25 million broadband funding award for the Colorado River Indian Tribe (CRIT) was announced in July 2023, CRIT Chairwoman Amelia Flores celebrated it as a “game changer.”
“Broadband access is essential,” Flores’s statement read, making “remote learning, telecommuting, conducting business, and simplifying staying connected” possible.
Coming amid a rolling series of announcements from the Tribal Broadband Connectivity Program – each lauding millions of dollars in broadband funding for Tribes – it would have been easy to file away CRIT’s award as another from that pathbreaking broadband funding program for Tribes.
But this was not the TBCP. Rather, CRIT was among a handful of Tribes that received substantial funding awards from another federal source that has recently stepped up their grantmaking to Tribes – the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s (USDA) ReConnect Grant Program, administered by the department’s Rural Utilities Service (RUS).

CRIT’s award is a helpful reminder that TBCP is not the be-all-end-all of funding for Tribal broadband. With an award cycle now open, ReConnect offers powerful tools and incentives – including dedicated Tribal funding, 100 percent grants, and consent for any new infrastructure on sovereign lands – for Tribes looking to expand or launch broadband service.
TBCP, ReConnect, and Federal Funding for Tribal Broadband Infrastructure
A new $4 million project funded by the Appalachian Regional Commission (ARC) and the U.S. Economic Development Administration will help bring affordable fiber broadband to long underserved parts of West Virginia.
The project primarily targets the rural counties of Randolph and Tucker, long stuck on the wrong side of the digital divide.
The RFP for the open access middle- and last-mile file project was issued last summer, seeking partners to help maintain the network and manage access leases in partnership with the Woodlands Development Group (WDG), which will own the finished network.
“The Route 33 Broadband Deployment Project will deploy backbone fiber from Elkins along Route 33 through Bowden, north to Harman, up to Canaan Valley, and ending in Davis, establishing last-mile broadband access to 40 businesses, and enabling future last-mile projects to serve at minimum 480 households and 25 additional businesses located within 1,000 ft of the backbone fiber,” the RFP states.
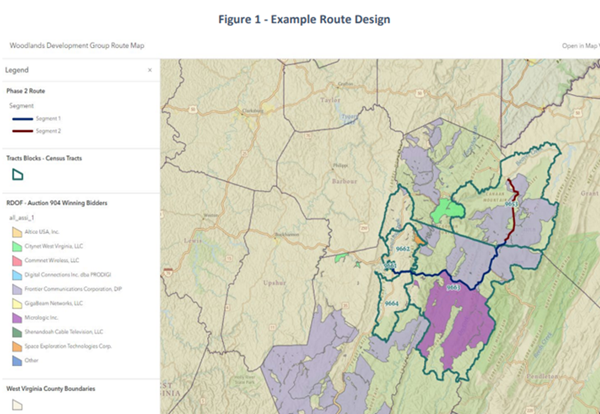
WDG, a 501(c)(3), had already been awarded a $1.7 million grant laying the foundation of the effort courtesy of 2021 COVID relief legislation (courtesy of the American Rescue Plan Act). The remainder of the $4 million project will be funded by the Appalachian Regional Commission and the U.S. Economic Development Administration.
The Rural Digital Opportunity Fund (RDOF) was supposed to drive affordable fiber into vast swaths of long-underserved parts of rural America. And while the FCC administered program accomplished some of that goal, a multitude of problems have plagued the program since its inception, putting both current and future broadband funding opportunities at risk.
The $20.4 billion RDOF program was created in 2019 by the Trump FCC as a way to shore up affordable broadband access in traditionally unserved rural U.S. markets.
The money was to be doled out via reverse auction in several phases, with winners chosen based on having the maximum impact for minimum projected cost.
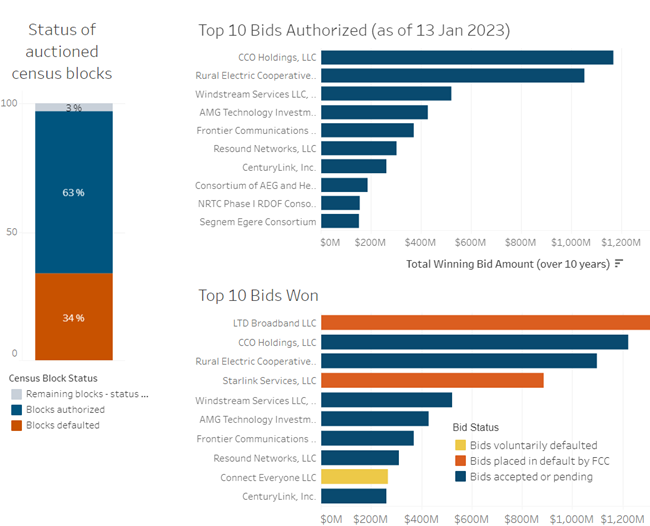
During phase one of the program, the FCC stated that 180 bidders won $9.2 billion over 10 years to provide broadband to 5.2 million locations across 49 states and the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands.
But, according to ILSR data, roughly 34 percent of census blocks that won RDOF funding–more than $3 billion in awards – are now in default. All told, 287,322 census blocks were defaulted on by more than 121 providers as of December 2023.
The defaults are only one part of a larger problem: namely that many communities bogged down in RDOF program dysfunction may risk losing out on the historic amount of federal funding to build modern broadband networks (BEAD) made possible by the 2021 bipartisan infrastructure law.
One Big Giant Mess
The rocky rural hills of West Virginia are a formidable foe when it comes to building high-speed Internet infrastructure that offers affordable high-quality service.
Nobody knows that better than Hardy Telecommunications (OneNet), a small community-owned cooperative that delivers affordable fiber to frustrated locals deemed too costly and cumbersome to be served by the incumbent telecom giants.
The cooperative serves parts of four counties (Hardy, Pendelton, Grant, and Hampshire). It connected its first fiber customer in 2013, after receiving $31.6 million in federal BTOP funding. Since then, the cooperative tells ILSR they’ve spent $20 million of their own funds to bring fiber to rural corners of the aptly-named Mountain State.
Derek Barr, Assistant General Manager at Hardy Telecommunications, says the cooperative currently delivers broadband service to 5,050 rural subscribers – 4,736 of which are on fiber lines that simply wouldn’t exist without federal funding programs. Hardy Telecommunications also provides 68 customers with fixed wireless access (FWA) broadband service.
“Our focus is fiber, and we're trying to build out fiber as much as we can,” Barr tells ILSR. “But it's very tough in our serving region. It's all mountains and a lot of trees, and a big chunk of our area is either state park or national forest land. It's also very hard to do fixed wireless because even if it might work in the winter, it's not going to work in the summer” when tree leaves block line of sight, he noted.
So the cooperative slowly and consistently expands fiber as it can, often in partnership with Pendleton County. As a result, locals have the option of a variety of double and triple play phone, cable, and fiber options, starting with a symmetrical 100 Mbps (megabit per second) downstream, 50 Mbps upstream fiber and phone bundle for $79 a month.
Officials in Washoe County, Nevada have struck a new public private partnership (PPP) with Digital Technology Solutions (DTS) to deploy affordable fiber service into the long-neglected rural towns of Gerlach and Empire, Nevada. The deal is part of a broader effort to bring affordable access to underserved residents just out of reach of broadband access.
Behzad Zamanian, Washoe County Chief Information Officer, tells ILSR that the county’s two-phased project first involved contracting with DTS to construct and maintain a $2.3 million middle-mile fiber network that connected Gerlach to Reno, culminating in a ribbon-cutting ceremony at the Gerlach Community Library last July.
“The reason [Gerlach] was identified as a high priority was that it was considered unserved or underserved; there was no presence of any of the major Internet service providers in that region,” he noted. “There was no high speed Internet available.”
Until last summer, area students and residents were completely cut off from online learning, employment services, remote health care, and other essential services and opportunities.
Expanding the middle mile network required close collaboration with the Pyramid Lake Paiute Tribe, which allowed the county to piggyback on the tribe’s existing fiber runs from Reno to Nixon, Nevada. The county then worked closely with the Nevada Office of Science, Innovation, and Technology (OSIT) and DTS to deploy fiber the remaining 60 miles from Nixon to Gerlach.
Alabama has announced the release of $148.3 million in new broadband grants via the state’s Capital Projects Fund (CPF), made possible by the 2021 American Rescue Plan Act (ARPA). While regional monopolies like Charter nabbed the lion’s share of state funding (once again), cooperatives also secured significant funding to tackle the rural digital divide.
“High-speed internet service continues to strengthen and expand across the state, and we are taking the necessary strides on this journey to achieve full broadband access for Alabama,” Alabama Governor Kay Ivey said in a prepared statement. “This has been a monumental task, but it is one that will pay multiple dividends for our state and its residents. Today is an exciting day as we announce these latest projects.”
Cable giant Charter Communications (Spectrum) was the biggest winner of state funds, awarded 23 grants totaling $44.8 million to shore up access to 22,000 underserved homes across 25 Alabama counties. The next biggest award recipient was Mediacom, which received $22.8 million in grants to fund deployment to 8,000 homes across six Alabama counties.

All told, 16 providers were awarded grants to expand access to 48 different Alabama counties. While regional monopolies were heavily represented in the awards, four different Alabama cooperatives received $34.8 million in grant funding to expand fiber access to more than 11,092 rural Alabama homes and businesses.
NEK Broadband continues to bring affordable fiber access to the long-neglected corners of the Green Mountain State. According to the latest update by NEK Broadband, a recently completed rollout has delivered affordable fiber access to 700 new addresses across multiple rural Vermont communities.
NEK Broadband is one of nine Communications Union Districts (CUDs) scattered across the state of Vermont. NEK Broadband alone represents 45 Vermont communities across Caledonia, Essex, Orleans and Lamoille Counties in the northeast part of the state (see the full list of communities here).
The CUD’s latest expansion plan primarily focused on bringing fiber access to parts of Danville, Kirby, Lyndon, St. Johnsbury, Walden and Wheelock, Vermont. With this latest expansion, NEK Broadband now provides fiber access to 2,100 predominantly rural Vermont residents in total, many of which only received broadband for the first time last year.
“We’re so pleased to end 2023 by giving more residents of the NEK access to high-speed internet,” Christa Shute, NEK Broadband’s Executive Director, said in a prepared statement. “We plan to bring even more residents online in early 2024.”

The CUD currently provides upgraded users with access to speeds that exceed those provided by cable and DSL providers, even in many more urban markets.
NEK Broadband currently offers four tiers of broadband service: symmetrical 50 megabit per second (Mbps) service for $80 a month; symmetrical 250 Mbps service for $103 a month; symmetrical 500 Mbps service for $135 a month; and a symmetrical gigabit per second (Gbps) offering for $250 a month.

Join us Tuesday, January 16th at 2pm ET for the latest episode of the Connect This! Show. Co-hosts Christopher Mitchell (ILSR) and Travis Carter (USI Fiber) will be joined by regular guests Doug Dawson (CCG Consulting), Kim McKinley (UTOPIA Fiber), and special guest Roger Timmerman (Executive Director UTOPIA Fiber) to prognosticate all of the broadband things for 2024: will ACP get renewed? Which states will get BEAD right, and which are showing signs of cracking under the pressure? What did we see at CES that will impact the broadband market? Is the fiber market going to pause? Tune in for titillating discussion on these topics and many more.
Email us at broadband@communitynets.org with feedback and ideas for the show.
Subscribe to the show using this feed or find it on the Connect This! page, and watch on LinkedIn, on YouTube Live, on Facebook live, or below.
Cullman, Alabama-based Cullman Electric Cooperative says it is launching a new phase of fiber deployment after receiving a $7 million grant to bring affordable fiber access to long-neglected Cullman and Winston counties.
The financing was made possible by the Alabama Broadband Accessibility Fund (ABAF), funded by the 2021 American Rescue Plan Act (ARPA). The state has already dedicated more than $82 million in funding for Alabama broadband deployments, bringing broadband access to 72,000 currently unserved residents.

Cullman’s $7 million portion will bring affordable fiber access to 1,300 families. Known as Sprout Fiber Internet, Cullman currently offers residential customers symmetrical 300 Mbps (megabit per second) service for $60 a month; symmetrical 1 Gbps (gigabit per second) service for $80 a month, and symmetrical 2 Gbps service for $120 a month.
That’s significantly faster and cheaper service than is currently offered by any of the dominant private telecom monopolies in Cullman (predominantly AT&T or Charter/Spectrum), without usage caps, hidden fees, or long-term contracts.
After decades of failed broadband policy-making and incumbent provider neglect, many Tribal communities continue to lack affordable and reliable Internet connectivity. Limited access to capital for last-mile deployment on Tribal lands has been exacerbated by a vast “missing middle mile” problem, and credible estimates put the costs of universal access on reservations at well over $10 billion.
Despite a historic investment in better Internet access from the federal government directly to Tribes, the problem is not even half solved. The first round of the Tribal Broadband Connectivity Program offered $2 billion in grants but received nearly $6 billion in requests from half of the 574 federally-recognized Tribes. With only $1 billion available in the final round of this program, an enormous funding gap remains.
Funding from the Broadband Equity, Access, and Deployment Program (BEAD) will have to be used strategically and collaboratively with Tribes to bridge this gap. The “high-cost area” match exemption could be an important tool to facilitate sustainable infrastructure deployment on Tribal lands, but it is not yet clear that states will make this exemption feasible.