
Fast, affordable Internet access for all.

A new project borne out out of the Michigan Moonshot Initiative promises to help thousands of families and students without home Internet access get online. Led by the Merit Network, a coalition of partners (including Toyota, Cisco, the Detroit Public Library, the Washtenaw County Broadband Task Force, and county school districts) is installing Wi-Fi hardware at 50 sites around the southeastern part of the state to bring broadband access to thousands. Nine locations are up and running, with more soon to follow.
The effort is taking place in the cities of Detroit, Inkster, Flint, as well as Washtenaw County. Toyota and Cisco are providing funds and hardware, and the project takes advantage of the Merit Network’s extensive fiber backbone running throughout the state (4,000 miles in total). Wayne State University is also participating, and inviting students and faculty and staff to participate in a broadband survey. Funds are being dispersed in the form of grants which will go to community organizations to boost existing Wi-Fi networks at schools and other anchor institutions across participating areas.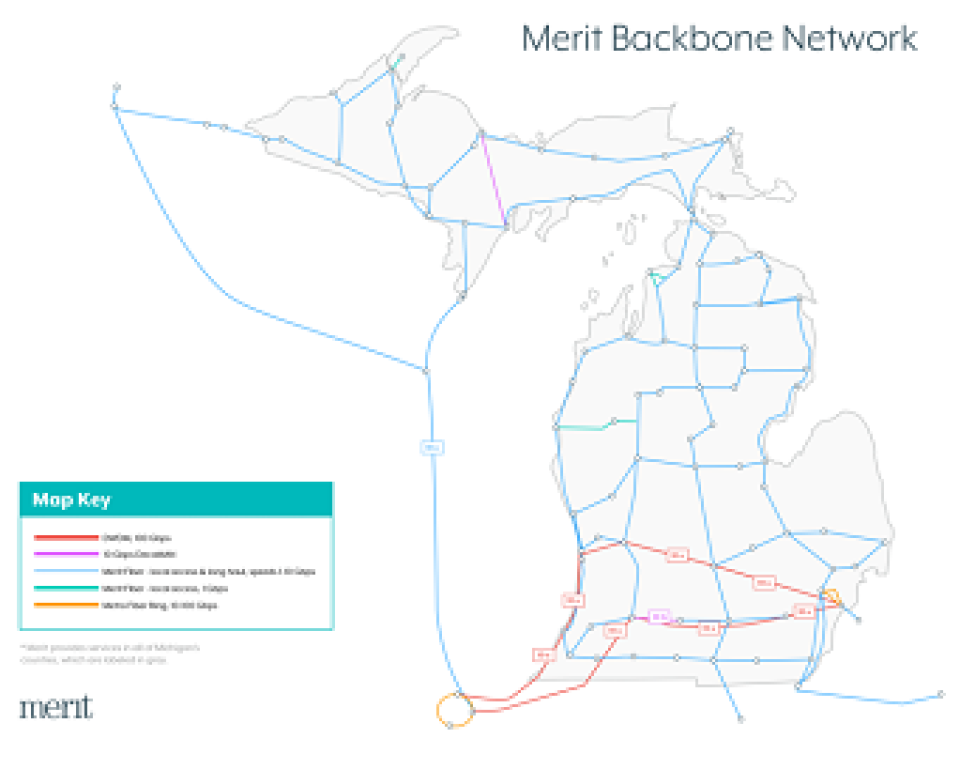

For timely updates, follow Christopher Mitchell or MuniNetworks on Twitter and sign up to get the Community Broadband weekly update.
Built in 2008 with an eye toward the future and operated with local priorities in mind, Greenlight has a long track record of putting people first. In a new case study, the Institute for Local Self-Reliance explores the wide-ranging community benefits of Greenlight, the city-owned Fiber-to-the-Home network in Wilson, North Carolina.
Download Wilson Hits a Fiber-to-the-Home Run with Greenlight Municipal Broadband Network.
The case study details how it has been able to quickly adapt and expand service during the pandemic, as well as the host of advantages and overall value brought to the city over the last decade in education, equity, and economic development. For example:
Access for All
Economic Development
Education
In a new case study, the Institute for Local Self-Reliance explores the wide-ranging community benefits of Greenlight, the city-owned Fiber-to-the-Home network in Wilson, North Carolina. The case study details how it has been able to quickly adapt and expand service during the pandemic.
Built in 2008 with an eye toward the future and operated with local priorities in mind, Greenlight has a long track record of putting people first. A few examples are:
Access for All
Economic Development
Education
States have gotten creative over the last half year in making use of CARES Act funding to improve connectivity for families and students, but one project in Mississippi shows that oftentimes a good old Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) build is best. The West Jasper School District (enrollment 1,700), sixty miles southeast of Jackson, partnered with telephone and network operator TEC to do just that with a project aimed at bringing Internet access to 125 families that do not have it in the area.
Reaching the Unconnected
The effort is funded by $390,000 in CARES funding via the Mississippi Pandemic Response Broadband Availability Act managed by the Mississippi Department of Education. The initiative was established by HB 1788, which aimed at “providing payments to eligible Mississippi public school districts, independent schools and Native American tribal school districts . . . as equitably and efficiently as possible after determining the unserved areas of the state . . . to increase or gain broadband access.” It passed both chambers unanimously in July, allocating $50 million for the effort.
Ten miles of new fiber were installed along County Road 12 to bring 135 previous unconnected homes online to TEC’s (a regional telephone and broadband company which offers services in Tennessee, Alabama, Louisiana, and Mississippi) network at the end of November. Current users connected to its fiber infrastructure can choose between symmetrical 250 Mbps, 500 Mbps, and gigabit tiers for $55/month, $65/month, and $80/month respectively.
School District Superintendent Warren Woodrow said of the project:
We felt like the best use of it would be to put fiber in the ground and to serve our students and our community.
Seattle, Washington sits at the technology epicenter of the Pacific Northwest, and its residents have historically enjoyed better wireline Internet access options than many Americans across the country. A new report, Seattle Internet for All [pdf], provides a wealth of analysis which identifies those remaining in the city who struggle to get online. And while it outlines a detailed set of steps the city can do to reach the 5% or so of residents who report not having any subscription, most of them remain small, with no bold strategies offered to solve the connectivity gap once and for all.
The report comes as a result of the Internet for All Resolution passed by the city council in July in order to address digital divide amplified by the ongoing pandemic. While the city has been successful in increasing Internet access over the last five years, there are important income- and race-based gaps that still need to be fixed. Currently, the report says, 17,575 households with 37,365 residents sit on the other side of the adoption gap, and it concludes that the majority of the disparity is driven by affordability and a lack of digital skills.
Summary of Findings
The report argues that Seattle remains one of the most connected cities in the country, with 93% of the city having access to gigabit broadband from one or more Internet Service Providers (ISPs); according to the FCC Form 477 data (which itself overstates competition) that number sits at 75%, but in either case it's worth noting that for Comcast and Wave subscribers this will be asymmetric gigabit with far slower upload speeds.
Over the last few months, a number of cities across the country have recognized the pressing need to find a way to get those in their community without Internet access connected. In San Rafael, California, San Antonio, Texas, and Champaign, Illinois, local governments along with a variety of philanthropic, technical, and private partners have developed a host of innovative ways to bring fixed wireless solutions to neighborhoods in need.
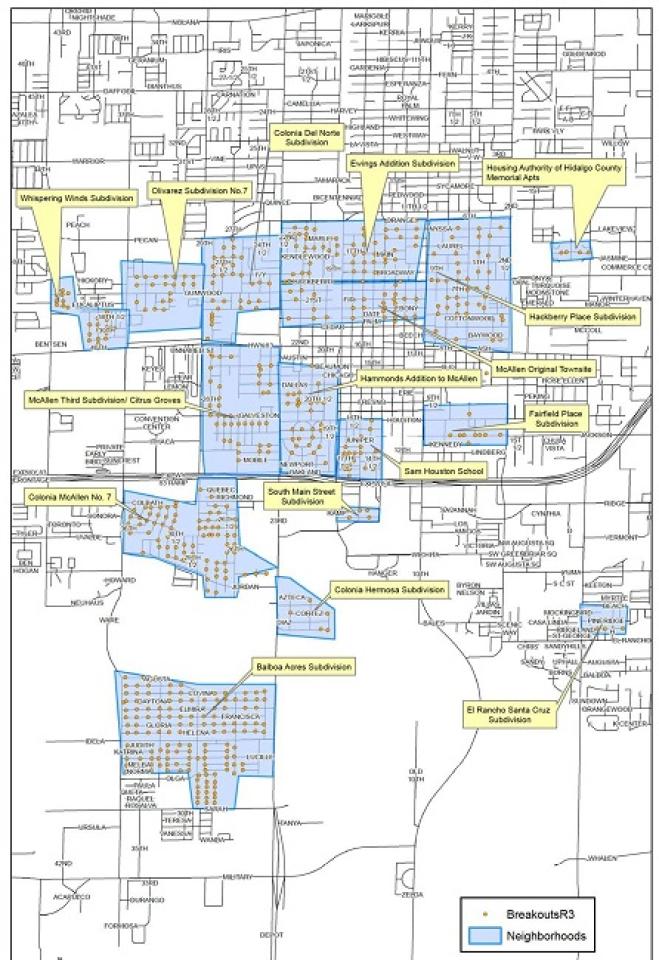
The city of McAllen (pop. 140,000) — near the mouth of the Rio Grande, at the southern tip of Texas — offers some additional lessons to be learned and a blueprint for success for other local governments thinking of doing the same. Quietly over the summer, it collected broadband data, designed, and deployed a fixed wireless network which to date covers more than three dozen neighborhoods and provides free connectivity for the city’s students and residents.
Fiber From the Water Tower
Citywide Wi-Fi has been a long time coming in McAllen. Mayor Jim Dalson and the IT Department have wanted to do it for years, IT Director Robert Acosta said in an interview, but finding a way to pay for it has been the major barrier. In the meantime, his department has been adding wireless coverage to public spaces for the past half decade, at city parks, outside of government facilities, at the Museum of Art and Science, and at the Boys and Girls club. He also extended the network to traffic cameras, water towers, and other government facilities, and when the pandemic hit his department had more than 60 miles of fiber to call upon.
When school shut down past spring, Unit 4 schools in Champaign, Illinois scrambled to get students connected like everyone else. The district handed out Chromebooks and teachers went to work transitioning to online instruction so the school year could continue. But the district noticed that a large percentage of its students weren't logging on and the bulk of them came from Shadowwood mobile home park, where although fiber ran up and down every street in the neighborhood only one family subscribed to wireline Internet access. So Mark Toalson, the city’s IT Director, began making calls, and by the end of the summer a coalition came together to build Shadowwood’s students a free fixed wireless network which went online in August.
Fiber Just a Few Feet Away

The mobile home park sits on the north side of the town of 90,000, and is largely populated by Hispanic residents. Roughly 250 students who attend the Unit 4 school district live there, and according to Toalson not a single one had Internet access beyond personal mobile phones before they began last spring. In late May Mayor Deborah Feinen asked the city manager what could be done, and Toalson was asked to take on the project.

This week on the podcast Christopher talks with Jill Levine, Chief of Innovation and Choice at Hamilton County Schools in Chattanooga, Tennessee, Evan Freeman, Director of Government Relations at the city’s municipal electric and fiber utility, EPB, and Deb Socia, President of the Enterprise Center.
Together, the group discusses the recent landmark announcement by Hamilton County Schools of HCS EdConnect, in which the schools, local government, EPB, and local stakeholders and philanthropic organizations have come together and made it possible to connect all school children on free or reduced lunch programs in the district to free 100 Mbps symmetrical Internet access for the next ten years. The initiative will include not only 32,000 students but their families as well, and is the first of its kind in the United States — a success story at using a city-wide network to bridge the digital divide for economically disadvantaged students, and a decisive move to respond to unequal Internet access during a worldwide public health crisis.
Jill, Evan, and Deb discuss the challenges of setting up the partnerships that made it happen, overcoming obstacles — including dealing with tens of thousands of new customers with unique skills and needs — and how they managed to pull it off.
This show is 31 minutes long and can be played on this page or via Apple Podcasts or the tool of your choice using this feed.
Transcript below.
We want your feedback and suggestions for the show-please e-mail us or leave a comment below.
Listen to other episodes here or view all episodes in our index. See other podcasts from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance here.
Thanks to Arne Huseby for the music. The song is Warm Duck Shuffle and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution (3.0) license.
While new municipal networks often (and rightly!) catch headlines for dramatically improving the lives of residents by giving them access to high-speed, reliable, low-cost Internet access, institutional networks also remain a tried-and-true model for cities and regions looking to begin investing in their information future. And, by connecting government buildings, schools, public libraries, and other community anchor institutions, they save communities money and can serve as an alternative when monopoly ISPs like Comcast try to negotiate huge fee increases to basic city services without any explanation (like in the case of Martin County, FL).
The Miami Valley, Ohio, region accomplished the same goal a year ago, when GATEway Fiber lit up its intergovernmental, multi-jurisdictional fiber network connecting eight member cities and dozens of municipal buildings, schools, and other public anchor institutions. The result of six years of effort, the project provides the capacity and technical expertise for present and future undertakings to enhance educational initiatives, public safety programs, and utility work, and provides a model for other communities looking to work together to secure their information infrastructure moving forward.


A Joint Venture
Millions of students do not have access to adequate connectivity, but Black, Latinx, and Native children are disproportionately impacted by the “homework gap” — a term that describes the divide between students with access to home broadband and Internet-enabled devices and those without, as well as the challenges that unconnected students face. One study found that children in one out of every three Black, Latinx, and Native American households did not have broadband access at home.
These disparities are even more pressing during the ongoing Covid-19 pandemic, which has turned the homework gap into a chasm. Schools across the country cancelled in-person instruction at the end of the last school year, and many continue to make plans for remote learning in the fall. As the nonprofit Common Sense pointed out in a recent report, “The ‘homework gap’ is no longer just about homework; it’s about access to education.”
School districts, cities, and states across the country are distributing hotspots, deploying wireless LTE networks, and paying for students’ Internet plans, among other efforts to quickly address the homework gap. However, many of these solutions are stopgap answers to a systemic problem.
UnidosUS President and CEO Janet Marguía said in a press release:
The COVID-19 pandemic has exposed the impact of the digital divide on the academic progress of our students, particularly from low-income, Black, Latino, and American Indian households. Roadblocks, including internet connectivity and access to a computer or tablet, have denied students of color the opportunity to meaningfully engage in online learning, resulting in learning loss and widening achievement gaps . . . We cannot continue to overlook the disproportionate impact of this divide.
Mind the Gap