
Fast, affordable Internet access for all.

A pilot project in the City of Holland, Michigan is now delivering gigabit speed Internet service via a dark fiber network built by the city more than two decades ago; three commercial buildings are connected. The project, led by the Holland Board of Public Works (HBPW), is the first phase in an effort to develop a municipally owned and operated fiber network.
Holland is home to about 33,500 people and situated on the shores of Lake Michigan. The community is known for its roots in Dutch culture and is a popular summer tourist destination. Windmills and tulips dot the landscape.
Daniel Morrison, the president of a software company in Holland and a member of a local public interest group called Holland Fiber, recognizes that businesses need fast, affordable, reliable connectivity:
“Our whole business is online,” he told the Holland Sentinel newspaper. “We’re working with clients all over the world and we want to be able to work as quickly as possible.”
Morrison’s company is a pilot tester. After the testing program began in January, Morrison Tweeted out a screen grab showing his Internet speeds:
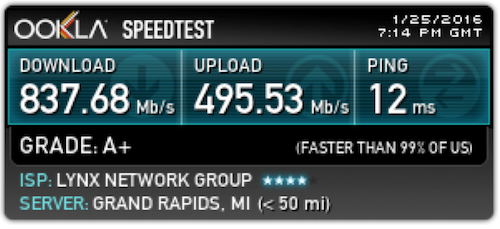
Pretty darn fast.
Toward a Municipal Network?
Pilot testing is set to last for three months to allow Holland’s Board of Public Works (BPW) to test out network technologies and solicit feedback from testers. All of the pilot testers are getting free fiber Internet service during the testing period.
Holland's BPW plans to apply their findings from the test toward a business plan for a municipal network for the entire service area. They will also use the business plan to support an application to the State of Michigan to become an authorized Internet Service Provider. BPW officials expect state regulators to respond to their application by the fall of 2016.
History of Holland’s Fiber Network
The publicly owned fiber optic network of Dakota County, Minnesota, and of cities within its borders may soon come under the oversight of a local joint powers board.
David Asp, County Collaboration Engineer, said the County started putting the network together in May of 1998. It has grown from 20 miles in 2005 to 112 miles in 2015, and then to 270 miles in 2016. The network provides speeds of up to 10 Gigabits per second (Gbps) download. This news marks a coming of age for the County’s 10-year-old Internet network which, together with the cities' related infrastructure, now spans 270 miles. The County network serves hundreds of public facilities and operations including county buildings, city halls, libraries, schools and more than 350 traffic control signals.
The County and 11 cities within its jurisdiction are now reviewing whether to approve a limited joint powers agreement that would have them inventory their fiber optic infrastructure to find out "what do we have and what are gaps in the system," said Matt Smith, Dakota County deputy manager. Their second objective is to develop a detailed financing system to operate an integrated Internet network, he said.
Asp said he expects the County and the cities will decide by April whether to take this first step in forming the joint powers alliance.
After these studies, the County and cities are then expected to decide if they want to participate in a broader joint powers agreement that would establish the Dakota Broadband Board. If the answer is "Yes," the joint powers board could begin operations in early 2017, Asp said.
Duties of the Board could include establishing policies, procedures, and pricing on leasing the network’s dark fiber, Asp said. Dark fiber is fiber-optic cable that is laid underground but currently not in use, and thus is dormant, or “dark.”
Dakota County, Dakota County Development Agency, Apple Valley, Burnsville, Eagan, Farmington, Hastings, Inver Grove Heights, Lakeville, Mendota Heights, Rosemount, South St. Paul and West St. Paul are reviewing the initial JPA.
Promoting Economic Development
Ting has chosen the Greater Sandpoint, Idaho, region as its next Internet access service area. The partnership will allow Ting to provide gigabit Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) Internet access to residents and businesses in Sandpoint, Dover, Ponderay, and Kootenai. The four communities are located in Bonner County, in the panhandle area of the state; approximately 9,700 people populate the proposed service area.
Rural Subscribers Want It, Need It, Will Use It
Potential subscribers can pre-order right away as part of Ting's "demand assessment" phase. Construction will begin later in 2016 when Ting determines there is sufficient demand in the region.
In a March 2nd announcement:
“Internet speed and infrastructure is an issue that is on the national agenda,” said Elliot Noss, CEO of Ting and its parent company Tucows. “While it’s obviously very important to get major metros connected with fast fiber Internet, Ting Internet is proving that the fastest Internet access available isn’t just for city centers. Smaller cities and towns need faster, more reliable Internet too. Maybe even more so.”
Ting has made it known that it is looking for more communities that are willing to lease their publicly owned fiber to the company. Ting hopes to build upon municipal fiber assets to bring FTTH to cities, towns, and villages of all sizes. We are pleased to pass on news of this plan to bring high quality Internet access to one of many less populated communities in the U.S. One should not have to live in a metropolitan area just to get fast, affordable, reliable Internet access.
The Ting Community Is Growing

Last week, we were excited at the announcement from Huntsville Utilities in Alabama. Huntsville is building a municipal dark fiber network to every premise in its territory that will be open to multiple service providers. Google has already committed to using it to bring real connectivity to the community. In this week's episode, 191, we are talking with Tom Reiman and Stacy Cantrell to understand the model. Tom is President of The Broadband Group, the consultant that is working with Huntsville on this project. Stacy Cantrell is the Vice President of Engineering for Huntsville Utilities.
We talk about how the model originated, some of the technical details behind the network, and what benefits they expect to see. This is an excellent discussion with many implications for the thousands of communities that want to improve Internet access locally but would prefer not to offer services directly.
This show is 33 minutes long and can be played on this page or via Apple Podcasts or the tool of your choice using this feed.
Transcript below.
We want your feedback and suggestions for the show-please e-mail us or leave a comment below.
Listen to other episodes here or view all episodes in our index. See other podcasts from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance here.
Thanks to Kathleen Martin for the music, licensed using Creative Commons. The song is "Player vs. Player."
Starting this spring, the City of Springfield, Massachusetts will offer free municipal Wi-Fi and new dark fiber capacity to a 7-block area of the city’s downtown known as the “Springfield Innovation District.”
As Masslive.com reports, the new dark fiber will create a connection between the city’s Springfield Innovation Center and an existing network of dark fiber capacity in this part of downtown. The publicly owned fiber currently provides gigabit connectivity to municipal buildings but the city will lease out excess capacity. The new Wi-Fi and dark fiber services are part of a broader plan aimed at boosting economic development and innovation in Springfield, the state’s third largest city at 150,000 and the fourth largest city in all of New England.
The project is phase one of a broader plan to soon expand the network even further in order to reach an additional downtown area and all of the city’s public parks. Springfield’s Chief Information Officer Kevin Kennedy estimates the project’s phase 1 total cost between $50,000 and $100,000. While users interested in connecting to the dark fiber will contract with a private provider for Internet service, the city will be the service provider for the free downtown Wi-Fi.
Preparing for New Tourism, Increased Economic Development, Better Livability
Over the next two years, the city will welcome a new Union Station transportation center and an MGM Casino in the city’s downtown area. With the increased tourism, Kennedy told WAMC Radio that it would be “embarrassing” for Springfield not to have free downtown Wi-Fi.
Delcie Bean, the founder of a Springfield IT company and the creator a downtown-based tech training organization called Tech Foundry, believes the new network capacity is essential to attracting people to work, live, and play in downtown Springfield:
Huntsville Utilities and Google Fiber announced today that the utility will construct a dark fiber network and that Google Fiber will offer services to the community via the city's new fiber infrastructure investment.
We applaud Huntsville and Google for helping develop an innovative model that will create more choices for local businesses and residents. We believe this is an important step that can lead to a true market for Internet access, allowing people a real choice in providers while ensuring the network is accountable to local needs.
Next Century Cities (NCC) describes the arrangement as a "promising new model for ensuring greater access to high-quality broadband Internet." We see this as a significant step forward in creating competition and bringing high quality Internet access to every one. For many years, we have seen communities desire to invest in infrastructure but not have to engage in service competition with powerful rivals like Comcast or AT&T.
Huntsville Is Different
Google Fiber is already known for bringing affordable gigabit service to subscribers in Kansas City and Provo, Utah and they have plans to expand in a number of other communities. Huntsville will be more than "just another" Google Fiber community because the infrastructure will belong to the community.
Other providers will be able to offer services via the network as well, ensuring more competition and providing choice for residents and businesses. Smaller providers will have an easier time establishing themselves in Huntsville with infrastructure in place on which to offer services. If subscribers are not happy with one provider, there is a good chance that there will be other options.

The St Vrain Valley School District, north of Denver and including the Longmont area, is transitioning from a shared gigabit network to dedicated 10 Gbps links for schools. Just what does it do with all that bandwidth? School District Chief Technology Officer Joe McBreen tells us this week in Community Broadband Bits podcast episode 186. We talk about why the need for so much bandwidth and the incredible savings the school district has received from the municipal fiber network.
Additionally, we discuss how self-provisioning would have been the second more cost-effective solution, far better than leasing lines from an existing provider. Toward the end of our conversation, we touch on how students get access in their homes and what any business or manager needs to do to be successful, regardless of what industry he or she is in. See our other stories about Longmont here.
This show is 24 minutes long and can be played on this page or via Apple Podcasts or the tool of your choice using this feed.
Transcript below.
We want your feedback and suggestions for the show-please e-mail us or leave a comment below.
Listen to other episodes here or view all episodes in our index. See other podcasts from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance here.
Thanks to Arne Huseby for the music, licensed using Creative Commons. The song is "Warm Duck Shuffle."
After a rocky start and a long period of transition, the Roanoke Valley Broadband Authority in Virginia is preparing for the years ahead. Hoping to snag schools, hospitals, government offices, and Internet carriers with their prices, the Broadband Authority just released its proposed rate structure.
They expect to complete construction of five major sections of the fiber network by early March. Starting in mid-April, customers will have service. The proposed rates are as follows:
The full preliminary proposed rate structure [PDF] is available from the Broadband Authority’s website.
The Authority will hold a public hearing on Friday, March 18 at 8:30 a.m. on the rate structure. After the public hearing, the board may request to adopt the preliminary proposed rates. Local news has the rest:
"We have fiber in the ground that is currently dark...It's a resource we have that other communities want," said Rochester, New York, Mayor Lovely Warren at a November press conference. The city is now working with Monroe County to take advantage of that dark fiber.
There are more than 360 miles of fiber under the ground serving public safety entities, suburban police and fire departments, libraries, schools, and public works facilities. In downtown Rochester, there is enough fiber to provide the redundancy that high tech companies need to establish operations. Over the past two decades, there have been several public works projects involving excavation. During those projects, crews installed fiber.
There are approximately 211,000 people living in Rochester, the county seat of Monroe County. The county is situated along the northwest border of the state, along Lake Ontario; about 750,000 people live there.
City and county officials estimate that more than 70 percent of the fiber network capacity is not being used. Local leaders are taking steps to change that. In November, the two entities released a joint request for proposals (RFP) seeking an expert to assess the current network and make recommendations on how to make the most of their investment.
At the press conference to announce the collaboration, Warren said:
The Rochester community is fortunate to have a substantial fiber optic network already in place. Very few cities have the advantage of this infrastructure in their city center. We need to be sure that its capacity is being used wisely and, ultimately, that this capacity is being used to help employers create more jobs. This fiber network gives Rochester a competitive advantage when it comes to attracting companies with high bandwidth needs and the jobs they bring with them.
According to Monroe County Executive Maggie Brooks and Warren, the city and county are hoping to work with private partners. At the press conference, they suggested leasing out capacity but they acknowledged that this is only the first step in a long process.
With construction of a major community broadband network behind them, local leaders in New York State’s Southern Tier region are now considering the potential for the recently completed dark fiber network.
Since becoming operational in 2014, the Southern Tier Network (STN) is already serving over 100 industrial and government service entities across the region. STN is a not-for-profit, local development corporation that built, owns, and manages the network for the region.
Jack Benjamin, president of economic development organization, Three Rivers Development Corporation, explained the value of the network to the region in a July Star Gazette article:
This backbone fiber that we've got here is a huge benefit for us going forward. As this technology piece continues to be even more important in the future, because it's going to be changing all the time, we will have the base here that allows us to change with the marketplace. Part of our thought process here is we want to keep what we've got in terms of businesses and provide the infrastructure that allows them to stay here and be competitive.
Building Out for the Future
When we wrote about the STN in 2011, the planned backbone of the network included a 235-mile fiber-optic ring stretching across Steuben, Schuyler, and Chemung counties. Glass producer Corning paid for $10 million of the initial $12.2 million cost to deploy with the remaining balance paid for by the three counties where the network is located. The STN is now 260 miles total, including strands that run to city centers and select business areas in the tri-county area.