
Fast, affordable Internet access for all.

Fiber to the Home
Even as the Internet is changing every aspect of our lives and communities, most Americans are intimidated by confusing jargon and misconceptions about Internet policy. We are developing a series of fact sheets that make these issues understandable to everyone.
We presently have fact sheets from the Institute for Local Self-Reliance and other organizations that cover broadband, financing networks, wireless Internet, economic development benefits from community owned networks, and the public savings from community owned networks.
Stay up to date with these fact sheets and other developments in community owned networks, subscribe to our one-email-per-week list. Once a week, we send out an update with new stories and resources.

The municipal broadband movement continues to gain momentum. Since January 1, 2021, at least 47 new municipal networks have come online with dozens of other projects still in the planning or pre-construction phase, which includes the possibility of building 40 new municipal networks in California alone. To help encapsulate this dramatic surge in the number of communities building publicly-owned, locally controlled high-speed Internet infrastructure, we created this fact sheet to provide pertinent numbers and highlight four recently launched networks now providing service to communities hungry for high-quality Internet connectivity, choice, competition.
With good reason, many are confused about the information shown in the FCC's new Broadband Availability map, the challenge process, and why we should care about helping the FCC make corrections. We believe it is important to contribute to improving this map to enable an equitable allocation of Broadband Equity, Access, and Deployment (BEAD) Program funds to states next year. In an effort to provide a better understanding of the map itself and the challenge process we created a short series of instructional videos and a click-through guide. FCC Broadband Map Challenge Guide [pdf]

Cities across Ohio have expanded Internet infrastructure in thoughtful, forward-looking ways. These municipal networks have created local government savings, increased speeds, promoted service competition, and powered economic development. Some cities have specifically addressed the affordability gap in cities, where many residents have been left behind in a broken market where large Internet Service Providers (ISPs) have underbuilt networks, leaving hundreds of thousands of broadband-hungry Ohioans in the digital dust. This fact sheet outlines the many long-term benefits that municipal broadband projects have brought to the state.
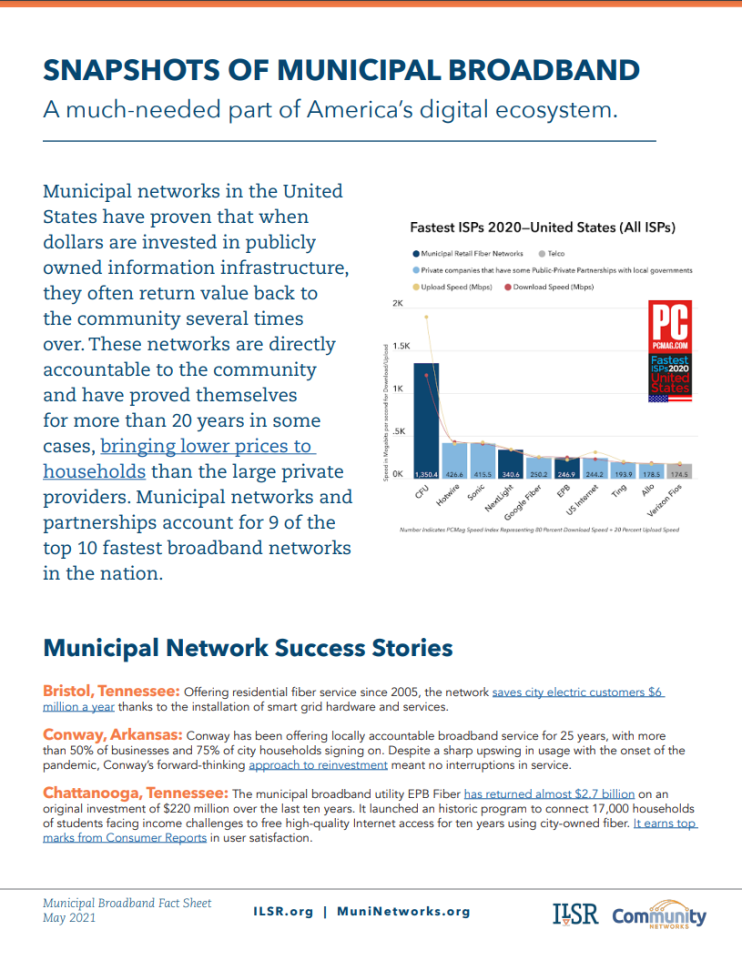
Municipal networks in the United States have proven that when dollars are invested in publicly owned information infrastructure, they often return value back to the community several times over. These networks are directly accountable to the community and have proved themselves for more than 20 years in some cases, bringing lower prices to households than the large private providers. Municipal networks and partnerships account for 9 of the top 10 fastest broadband networks in the nation. This new fact sheet highlights municipal broadband success stories from across the country and some of the many benefits the networks have brought to the communities they serve.

Despite raking in hundreds of millions in government broadband subsidies, Frontier Communications has failed time and time again to bring reliable, high-speed connectivity to the rural communities it serves. Instead of investing in network upgrades, Frontier has neglected its rural infrastructure to the detriment of its subscribers and the company’s own financials, with its worsening service quality paralleling its plummeting stock value. This fact sheet presents evidence of Frontier’s negligence and suggests that rather than continuing to trust Frontier, government officials should look to publicly owned and community-minded providers to connect rural residents, businesses, and institutions.

Next Century Cities (NCC) helps communities across the U.S. connect to each other, find resources, and discover ways to improve local Internet access options. NCC’s fact sheet uses examples from municipal network history. Communities have invested in publicly owned fiber optic infrastructure to obtain better connectivity and to reduce telecommunications costs for municipal facilities. In more than a few places, those investments became the foundation for what later became networks to serve local businesses and residences. The fact sheet also delves into other benefits, such as economic development, improved efficiency of other utilities, and accountability.
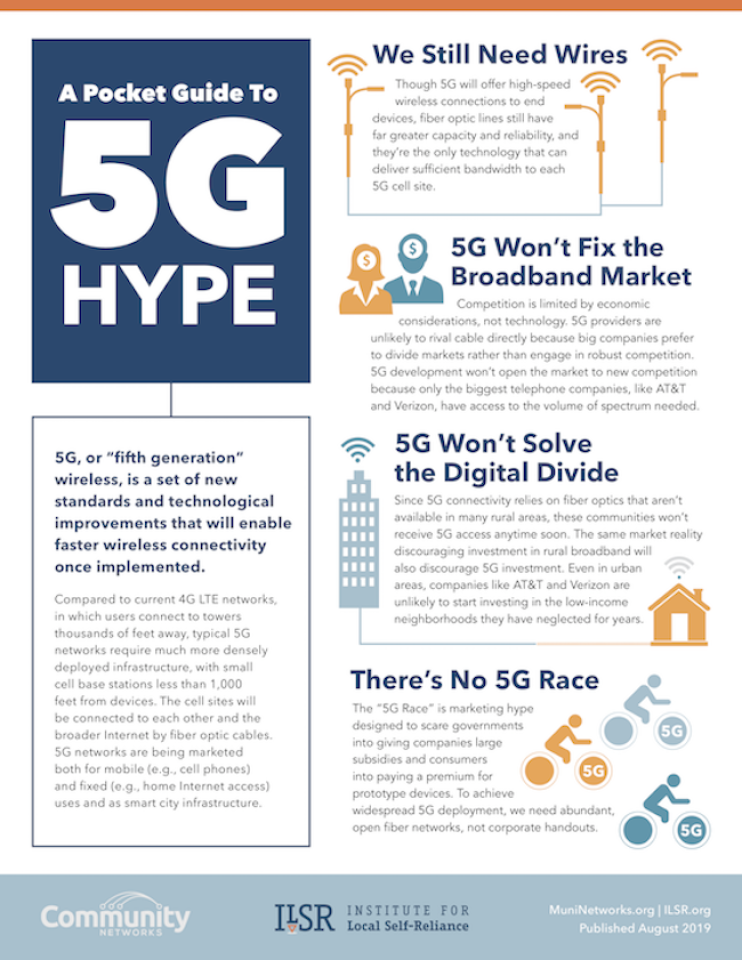
It’s difficult to separate 5G fantasy from reality as reported in traditional news sources. Misunderstandings surrounding the demands and capabilities of 5G has snowballed, creating an incorrect assumption that the technology will solve America’s many connectivity problems. It’s true that 5G is an improvement, but it has limitations. This fact sheet addresses the most repeated errors surrounding 5G and explains why the technology should be considered another tool, not an exclusive remedy.

Local governments spend billions on all sorts of infrastructure every year to advance the public good for their communities. Roads and bridges keep day-to-day activity moving. Investments such as water and sewer infrastructure keep cities clean and livable. Fiber infrastructure is used for a wide range of purposes, including economic development, education, and to keep a city’s administration connected. To get a look at how fiber network infrastructure compares to other public investments, we've developed the Broadband is Affordable Infrastructure fact sheet.

As interest in publicly owned broadband network infrastructure increases, local communities seek new ways to fund municipal networks. Revenue bonds, interdepartmental loans, and avoided costs have been the three most common methods for funding Internet network infrastructure, but local leaders are finding creative approaches to get the job done. In this fact sheet we analyze some new approaches to funding fiber optic infrastructure, pros and cons, and offer some examples.

As a nation our goal is ubiquitous broadband coverage so every person, regardless of where they live, can obtain the fast, affordable, reliable Internet access necessary for modern times. For people in rural areas, where large national wireline providers don’t typically invest in the infrastructure for high-quality connectivity, satellite Internet access is often their only choice. In this fact sheet we address some of the reasons why depending on satellite Internet access to serve rural America is a mistake.
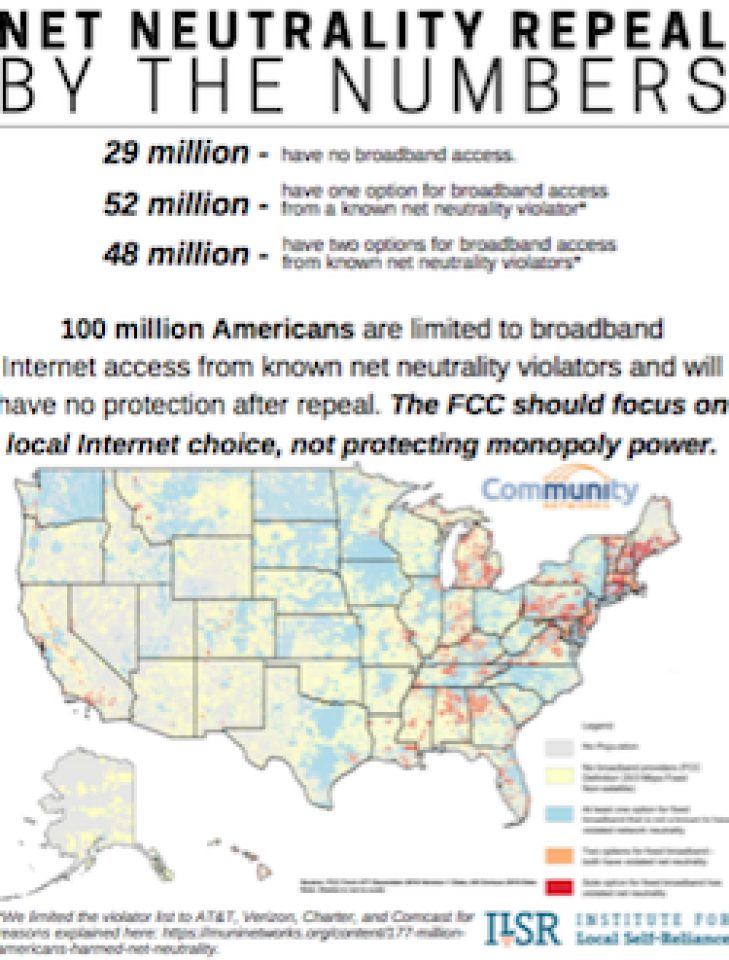
As the vote to repeal network neutrality protections approached in 2017, we started digging into the FCC’s data to determine how eliminating the policy would affect subscribers whose ISPs might take advantage of future changes. We learned that, due to existing monopoly and duopoly conditions, many millions of people would have no recourse but to pay known network neutrality violators for Internet access. We developed visuals and facts sheets with frank data that describes the problem in the U.S., California specifically, and on the East Coast from Maine to Virginia.
Net Neutrality Repeal By The Numbers, U.S.A. Edition fact sheet [pdf].
Net Neutrality Repeal By The Numbers, California Edition fact sheet [pdf].
Net Neutrality Repeal By The Numbers, East Coast Edition fact sheet [pdf].

The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) manages the CAF program, which provides billions of dollars in subsidies to Internet service providers for areas where the cost of building networks is prohibitive. Some large providers decided not to accept some of the subsidies during Phase I - about $198 million annually for 10 years. This fact sheet details the most important aspects of the Connect America Fund (CAF) Auction. What is it? What should it do? Who does it affect?

When you think “municipal fiber network,” you may think Chattanooga or Wilson, North Carolina - places where the city utility offers retail services directly to subscribers. That’s only one of several possible models that are emerging as an increasing number of communities use publicly owned assets to improve local connectivity. This fact sheet offers five of the most well known models that local governments are investigating and implementing as they become more self-reliant. Examples and characteristics of each model help illustrate.
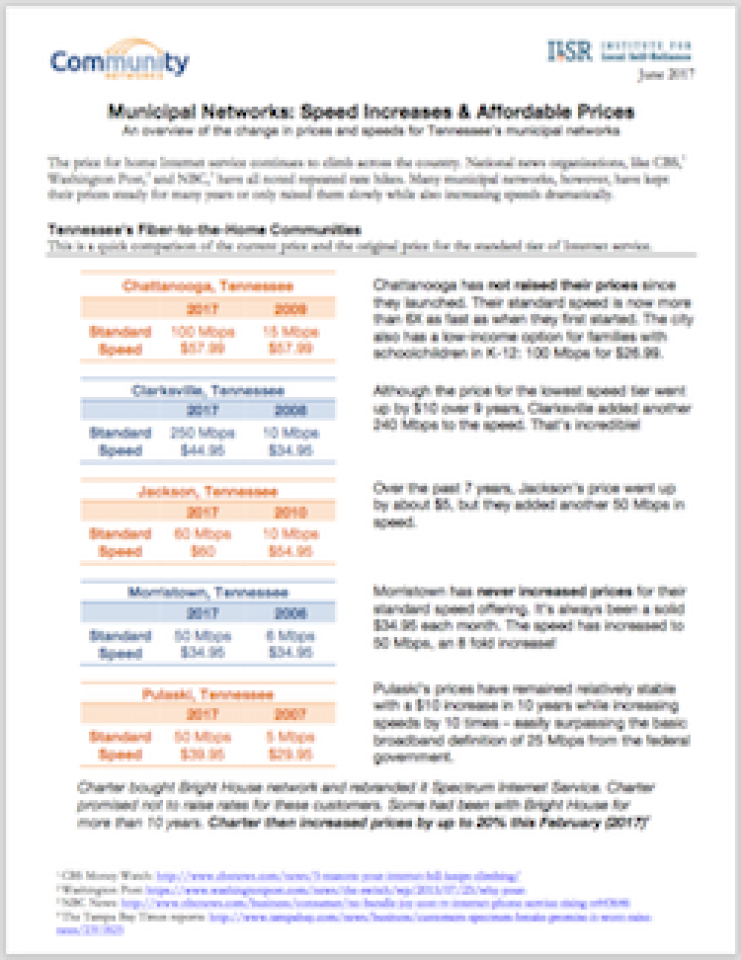
The large corporate national Internet Service Providers seem to raise their monthly rates every year but don’t give subscribers anything more for their money. On the flip side, we noticed that municipal networks tend to increase speeds for subscribers with very modest or no price increases over long periods of time. In order to illustrate this phenomenon, we looked back in time at rates and speeds in eight Tennessee communities that have invested in publicly owned Internet network infrastructure. You will see how speeds have increased significantly, but rates have only inched up.
Municipal Networks: Speed Increases & Affordable Prices [pdf]

The next time you’re attending a city council meeting, a local broadband initiative, or just chatting with neighbors about better local connectivity, take a few copies of our fact sheet. In addition to providing some basic talking points to get the conversation moving, the fact sheet offers resources to guide you to more detailed information on publicly owned Internet networks. You've already started to get people interested in all the advantages of high-quality connectivity, now show them how local self-reliance it the most direct route to better access.

This fact sheet provides an overview on how Internet access and fast, affordable, reliable connectivity reaches most aspects of our lives. It provides statistics on economic development, education, and methods of delivering Internet access and is a good introductory tool that points out how Internet access is much more than just social media.

This fact sheet on municipal networks in Virginia describes how economic development, public savings, and better connectivity have contributed to the health of local communities with publicly owned networks. Virginia local governments have improved public safety, healthcare, and connectivity in local schools. Rural areas are better able to compete for high-tech and manufacturing jobs because high-speed connectivity is now an essential service for day-to-day business.
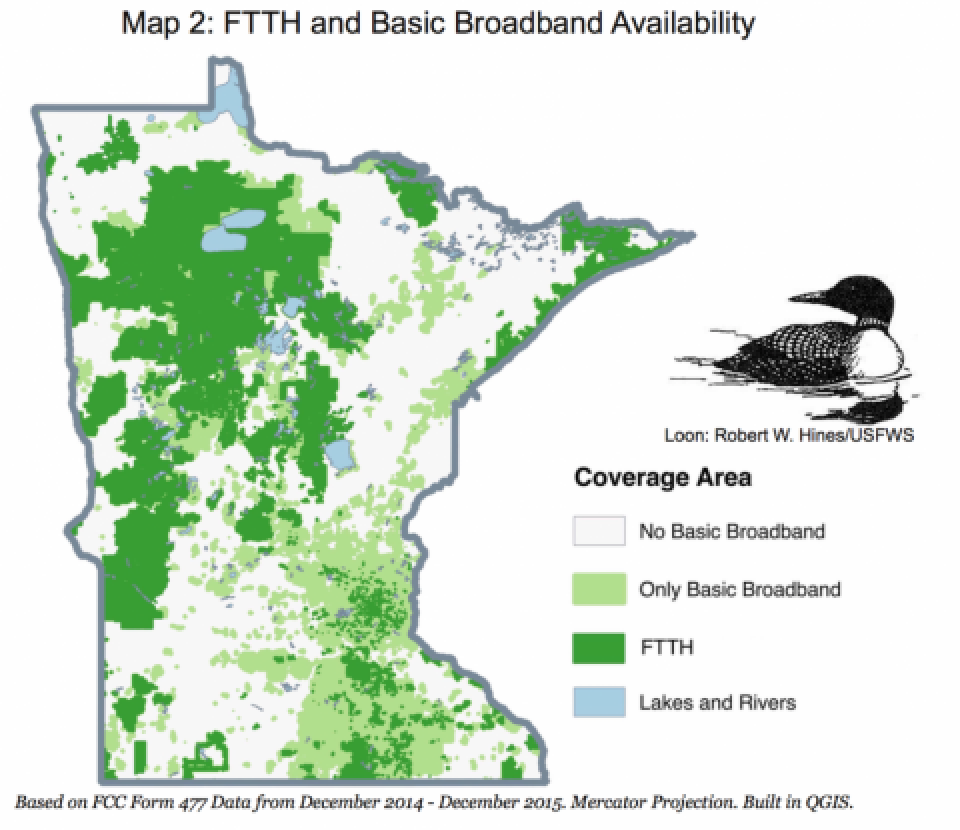
This fact sheet highlights the great work that Minnesota cooperatives and municipalities have done to bring fast, affordable, reliable Internet service to rural areas throughout the state. They've built many Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) networks, but there is still much work left to do. One in 4 Minnesotans lives in a rural area, and of those rural households, 43 percent lack access to broadband, defined by the FCC as 25 Megabits per second (Mbps) download and 3 Mbps upload. Resilient, robust, fiber is the long-term goal, but fixed wireless can help extend coverage in hard-to-reach rural areas.
Minnesota Cooperatives and Local Governments Can Solve Rural Digital Divide[pdf]

This fact sheet emphasizes the deepening divide between urban and rural connectivity. The fact sheet can help describe why people who live in the country need services better than DSL or dial-up. This tool helps to visualize the bleak situation in rural North Carolina, how it can be improved, and offers links to resources.
Fast, Affordable, Modern Broadband: Critical for Rural North Carolina [pdf]
Communities across the nation have invested in publicly owned cable and fiber infrastructure. ILSR's Community Networks Map documents over 500 communities where municipal networks serve residents and businesses. This fact sheet provides a quick introduction to the interactive online map.
When a community decides it needs to establish its own publicly owned network infrastructure, one of the biggest challenges is financing the investment. Each community is unique but three main methods of financing are most popular. This fact sheet offers a quick look at these common approaches and provides real-world examples.
This is a handy resource for elected officials and activists that are confused by some of the jargon or just want to make sure they understand some key ideas around broadband and telecommunications.

Community Broadband Networks have a very good track record in creating jobs. This fact sheet details where publicly owned network attracted new businesses or helped existing businesses to thrive.

Though schools, libraries, and other community anchors need access to faster, more reliable networks, the big cable and telephone companies have priced those services so high that they are breaking the budget. But when communities create their own connections, affordable high capacity connections aren't the only benefits.
Wireless networks may appear to be magical, but are actually driving investment in fiber optic wires. This resource defines many terms, key points, common speeds, and offers insight into wireless technology and policy.
This 2 page fact sheet explores the issue of preemption - how at least 19 states have made it impossible or more difficult for communities to build their own networks. It includes some history, legal issues, and quotes from FCC Commissioners.


In late 2006, Wilson, North Carolina, voted to build a Fiber-‐to-‐the-‐Home network. Wilson’s decision came after attempts to work with Time Warner Cable and EMBARQ (now CenturyLink) to improve local connectivity failed.
Wilson’s decision and resulting network was recently examined in a case study by Todd O’Boyle of Common Cause and ILSR's Christopher Mitchell titled Carolina’s Connected Community: Wilson Gives Greenlight to Fast Internet. This new report picks up with Wilson’s legacy: an intense multiyear lobbying campaign by Time Warner Cable, AT&T, CenturyLink, and others to bar communities from building their own networks. The report examines how millions of political dollars bought restrictions in the state that will propagate private monopolies rather than serve North Carolinians.
Download the new report here: The Empire Lobbies Back: How National Cable and DSL Companies Banned The Competition in North Carolina
These companies can and do try year after year to create barriers to community-‐owned networks. They only have to succeed once; because of their lobbying power, they have near limitless power to stop future bills that would restore local authority. Unfortunately, success means more obstacles and less economic development for residents and businesses in North Carolina and other places where broadband accessibility is tragically low.
It certainly makes sense for these big companies to want to limit local authority to build next-‐generation networks. What remains puzzling is why any state legislature would want to limit the ability of a community to build a network to improve educational outcomes, create new jobs, and give both residents and businesses more choices for an essential service. This decision should be made by those that have to feel the consequences—for better and for worse.
This story was originally posted on the ILSR website.
This past spring, we introduced you to the small town of Leverett, in rural western Massachusetts. Having been largely ignored by the cable companies and left behind by Verizon's DSL service, the community overwhelmingly approved a town-owned network initiative in a May vote. They decided to finance the FTTH network with a 20-year bond measure.
The debt will be serviced by both the revenues from selling services on the network and a modest increase in property taxes estimated at 6%. Local leaders calculate the increase in property taxes will amount to less than the savings created by lowering existing DSL and telephone services.
Peter d'Errico, of the Leverett Broadband Committee gave us an update via email:
We issued a Request for Information (RFI) in September. Thirteen respondents gave us a wealth of information about the state of the industry and their readiness to engage with our project. Based on this information, together with our already-completed network design, we are now crafting an Invitation for Bids (IFB) for the network build and one year's maintenance. We expect to issue the IFB early January, with a return date in February, which will allow us to select a contractor shortly thereafter.
As soon as we issue the IFB, we will draft a Request for Proposals (RFP) for network operator / service provider. This will also be based on the information gathered from the RFI and our design.
We have initiated the 'make-ready' process with the local utility and phone company.
A November Gazette.Net article [requires login] on the project described some temporary setbacks due to Hurricane Sandy and an October storm that came through the area. In order to keep the project momentum going, the committee is gathering the pieces needed now and in the future. Early prep work will make launching the network that much easier. From the article:
In August, we reported on the results of a report on UTOPIA by the Office of the State Auditor General of Utah. As you will recall, the results were less than favorable and presented more fodder for those opposed to municipal telecommunications infrastructure investment.
The same old arguments often rest on the financial investment in municipal networks - they are considered failures if they don't break even or make money. Pete Ashdown, founder of ISP XMission in Utah, addressed those arguments in the Salt Lake Tribune:
UTOPIA provides broadband service in 11 Utah cities. Today, communication infrastructure is no less critical than transportation, sanitation and clean water. Government is not a business, but the infrastructure it provides contributes to a robust business environment.
Consider how private businesses rely on government funded infrastructure. Why don’t entrepreneurs clamor to build the next generation of roads? Why don’t airline companies get off the public dole and build their own facilities? Why are sewer facilities so rarely handled by anyone else but the state?
Does effective infrastructure cost? Considerably. Does it make a profit? No.
For decades now, public service entities have contended with the argument that if they are "run it like a business" they will be more efficient, productive and even profitable. While lessons from the private sector may contribute to increased efficiency at times, government is NOT a business. Applying business tenets should be done sparingly and not in the case of critical infrastructure like electricity, roads, and yes, access to the Internet.
Gary D. Brown, who lives in Orem, shared a guest opinion through the Daily Herald and drew a similar parallel between UTOPIA's status and the business world:
Back in 2010, we reported on SuperNet in Alberta, Canada. We noted how, even though it resulted in significant middle-mile infrastructure expansion, there were still many, many Canadians along the route that were not connected. We drew a parallel between that experience and the focus on middle mile infrastructure via the broadband stimulus programs.
In October, Broadband Communities Magazine carried Craig Settles' article on Olds, a small community in Alberta that overcame the last-mile challenge by working for over 10 years to create that last-mile connection, culminating in O-Net. This town is an inspiration for other communities who decide to take matters into their own hands and find a way to get members connected and engaged.
Settles tells how the process began as a collaborative effort to get organized and revitalize the economy. A technology committee was charged with bringing fiber throughout the county, but the expense was prohibitive. From the article:
"The initial estimate to lay fiber optic cable throughout the county was approximately $80 million [Canadian dollars], well beyond OICRD's [Olds Institute for Community and Regional Development] funding ceiling,” states Joe Gustafson, who was OICRD chairman at that time. “The Tech Committee subsequently refocused on just the town of Olds and its population of just over 8,000, which brought the estimate down to $13.5 million, or about $3,140 per premises passed.”
The story goes on, taking us through several stops and starts the community experienced when working with private providers:
“To date, few incumbents see value in working with a community on a network such as this,” states Craig Dobson, currently the director of Olds Fibre Ltd. (OFL) and initially a consultant for the institute. “In essence, they believe strongly in facilities-based competition and appear to be threatened by market- based services competition that open- access networks enable.” Open-access networks rely on service providers for revenue – without them, the networks are not sustainable.
We, the members of the Lafayette Democratic Parish Executive Committee, believe the project will enhance businesses, enrich our lives, and prepare our children for the future. With proper planning, future generations will see profits generated by this project stay in this community and improve businesses and lives for generations to come. Improving local communities has been the traditional purpose of the Democratic Party. With that in mind, we commend City-Parish President Joey Durel for his bold initiative to make this plan a success.A few weeks later, the Lafayette Republican Party endorsed the network [pdf] as well:

...

We have covered developments in the town of Indianola, Iowa, where the community decided to build their own network in 1998. The original purpose for investment was to use the network to enhance public safety and increase efficiency with SCADA applications. In 2005, however, the network began offering telecommunications services to local businesses. As of October, Indianola Municipal Utilities (IMU) began offering fiber-to-the-home to residents as it gradually begins expanding the use of its fiber asset.
You can now hear firsthand about the network, its history, and how the municipal utility navigated the journey to its next-generation open access network. Craig Settles interviewed Todd Kielkopf, General Manager of IMU, in an August Gigabit Nation podcast. The two discuss IMU's evolution since 1998. They also talked about the unique advantages that exist when a community considering network infrastructure investment already has a municipal utility in place.
Kielkopf tells how the driving factor for the fiber installation was to allow easier management and communication between utilities. When a 1990 franchise agreement with MediaCom was about to expire, the city investigated options. Hopes were that that the city could build a fiber network and MediaCom would offer services over that network, but that vision was never embraced by MediaCom.
Iowa law allowed the city to hold a referendum asking residents for permission to provide telecommunications services through the municipal utility's network. The referendum passed and they created a five year financial plan. Financing was with taxable and tax exempt bonds. The electric utility would build and own the network and a new telecommunications utility would license to a private partner that would offer retail services. Now, IMU and Mahaska Communication Group (MCG) have an agreement whereby MCG provides retail services over the network. While the agreement is not exclusive, no other providers currently use the network.
We have covered happenings at Burlington Telecom, both positive and negative, extensively. We are glad to report some interesting new developments of this Vermont municipal network. BT is rolling out faster connections and using its competitive advantage in customer service to offer some computer repair services. Joel Banner Baird at the Burlington Free Press reported:
Without cash reserves and promotional enticements available to BT’s commercial competitors, the fiber-optic Internet/phone/cable provider will focus on its strength in customer service, said interim General Manager Stephen Barraclough.
As our readers know, BT is in the midst of a pending lawsuit with Citibank, wherein the financial giant says the city still owes it $33.5 million. The network's troubles, including misuse of public funds by the previous Mayor, have hurt its ability to generate income and Burlington's credit rating has suffered.
While fixing PCs certainly won't pay mounting legal fees, it will make life easier for customers. Details include a $25 diagnostic fee and a rate of $45 per hour plus materials. More about the service is available on the PDF of the official anouncement.
A more recent announcement puts Burlington among the few communities with citywide access to a gig. Burlington Telecom is in the midst of upgrades and will be offering 1 Gbps service and 40 Mbps service starting on December 1, 2012. Both options are symmetrical.
40 Mbps - $99.99 per month
1 Gbps - $149.99 per month when committing for one year; or $199.99 per month with a month-to-month arrangement